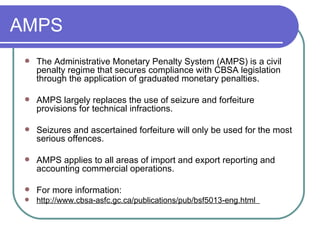
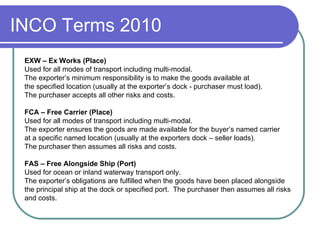
The document provides an overview of international trade training topics including:
1) Harmonized System (HS) codes, valuation of imported/exported goods, importing/exporting procedures for Canada, the US, and other countries.
2) NAFTA and requirements for trade between Canada, US, and Mexico.
3) Documentation and programs for export controls, customs clearance, trade security.









![Export Control Export Controls Online (EXCOL) The Export Controls Division (TIE) has developed an electronic business solution to replace the current permit tracking system developed in 1988. Export Controls On-Line (EXCOL) is a user friendly web-based application. Exporters are able to submit applications for export permits and certificates, as well as request amendments. EXCOL also offers the functionality to submit online, quarterly utilisation reports for military goods, as well as the ability to print selected permits in your office. EXCOL Help Desk (613) 944-1265 or toll free 1-877-808-8838 Email: [email_address] Mailing Address: EXCOL Registration Export Import Controls Bureau (TIE) Department of Foreign Affairs and International Trade 125 Sussex Drive, Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0G2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internationaltradetrainingmarch2012-13308688625972-phpapp02-120304075112-phpapp02/85/International-Trade-Training-March-2012-11-320.jpg)
![Carnet The ATA Carnet is an international, unified customs document which simplifies customs procedures for the temporary duty free admission of three main categories of goods traded internationally: commercial samples, goods for presentation or use at trade fairs, shows, exhibitions or similar events and professional equipment. Essentially the carnet is a merchandise passport that facilitates travel with goods, into foreign countries, making travelling abroad easy and hassle-free. The ATA Carnet can be used for unlimited entries and exits from foreign countries and Canada for up to one year. An ATA Carnet saves time, effort and money as it facilitates international business by eliminating extensive customs procedures, the payment of duties and/or value added taxes and the purchase of temporary import bonds. The carnet is recognized in over 58 countries and territories worldwide. Carnet and Document Certification Services c/o Canadian Chamber of Commerce 360 Albert Street, Suite 420 Ottawa, Ontario K1R 7X7 Tel: (613) 238-4000 Fax: (613) 238-7643 To obtain a Carnet: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internationaltradetrainingmarch2012-13308688625972-phpapp02-120304075112-phpapp02/85/International-Trade-Training-March-2012-12-320.jpg)