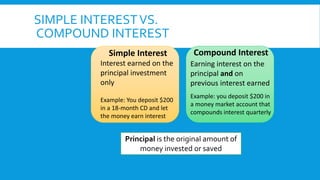
This document discusses the power of compound interest for savings and investments. It explains that compound interest is earned on both the principal amount and accumulated interest over time. This leads to much higher returns compared to simple interest, where interest is only earned on the principal. The document uses online calculators and examples to demonstrate how factors like investment amounts, interest rates, and length of time impact compound growth. It emphasizes that starting investments earlier and allowing interest to compound more frequently can significantly increase the total accumulated value of savings and retirement accounts.
![SAVING AND
INVESTING
TARGET
EXPLAIN HOW SAVINGS AND
INVESTING CONTRIBUTETO
FINANCIALWELL-BEING,
BUILDING WEALTH, AND HELPING
MEET PERSONAL FINANCIAL
GOALS
USEAN ONLINECOMPOUND INTEREST
CALCULATORTO CALCULATETHETOTAL
AMOUNTAN INDIVIDUALWOULD HAVE IN A
SAVINGSOR RETIREMENT ACCOUNT
IDENTIFYWHAT FACTORS IMPACT
COMPOUNDING AND HOW
EXPLAIN WHY COMPOUNDING CAN BE A
POWERFUL SAVINGAND INVESTING
STRATEGY
Meet short-term
goals
Keep funds secure
while growing
Simple interest
Plan for long-term goals
like retirement
More risk for more return
on an investment
Compound interest-
interest on initial principal
and all accumulated
interest
(I = P [(1 + i)n -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interest-211028161432/75/Interest-1-2048.jpg)