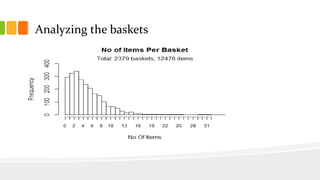
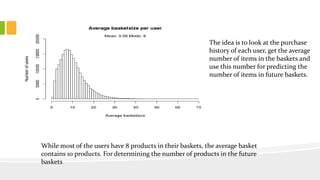
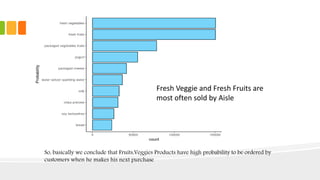
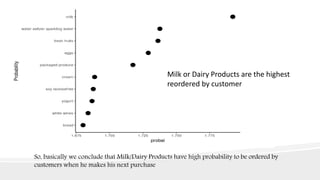
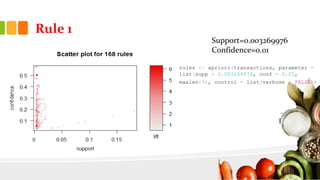
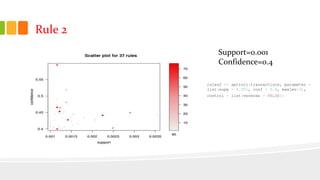
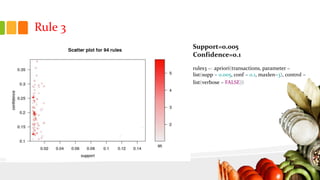
This document presents an analysis of Instacart's customer transaction data to identify item relationships through association rules. The analysis used tools like R Studio and Excel, focusing on data extraction, cleansing, and the modeling process to uncover purchasing patterns. Findings indicate that fresh produce and dairy products have high probabilities of being re-ordered by customers, enabling predictions for future purchases based on historical data.