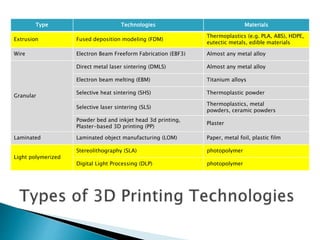
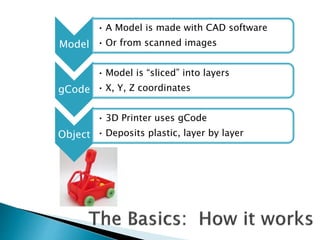
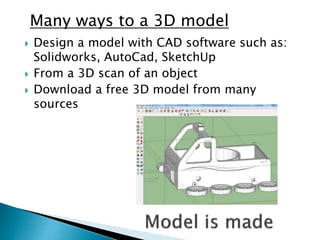
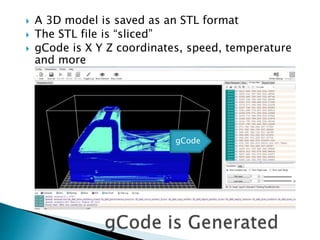
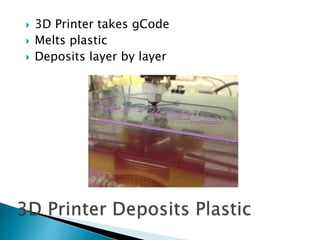
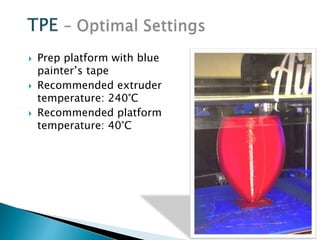
The document discusses various 3D printing technologies and materials. It provides information on common 3D printing materials like ABS, PLA, nylon and describes their properties and best printing practices. Examples of applications are given, such as using ABS to make printer components and polycarbonate for parts requiring heat resistance. Overall guidelines are provided on preparing models and converting them to G-code for 3D printing.