Embed presentation
Download to read offline


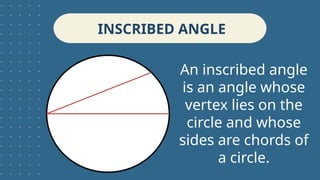
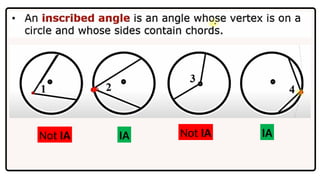
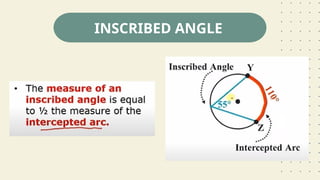
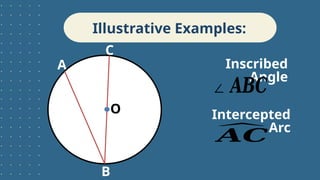
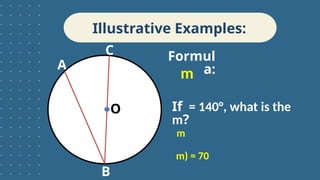
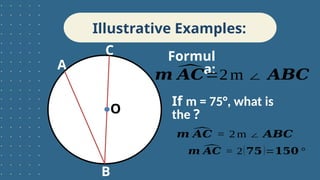

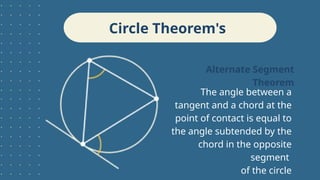
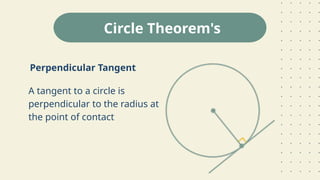
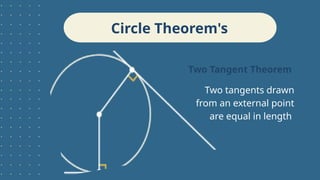
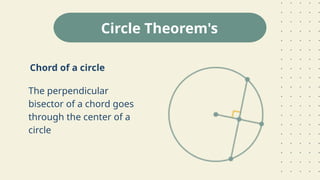

The document outlines learning objectives related to inscribed angles and intercepted arcs, including definitions, relationships, and methods for finding measures. It explains the concept of an inscribed angle and includes examples and formulas. Additionally, it covers several circle theorems, such as the perpendicular tangent theorem and properties of tangents and chords.













