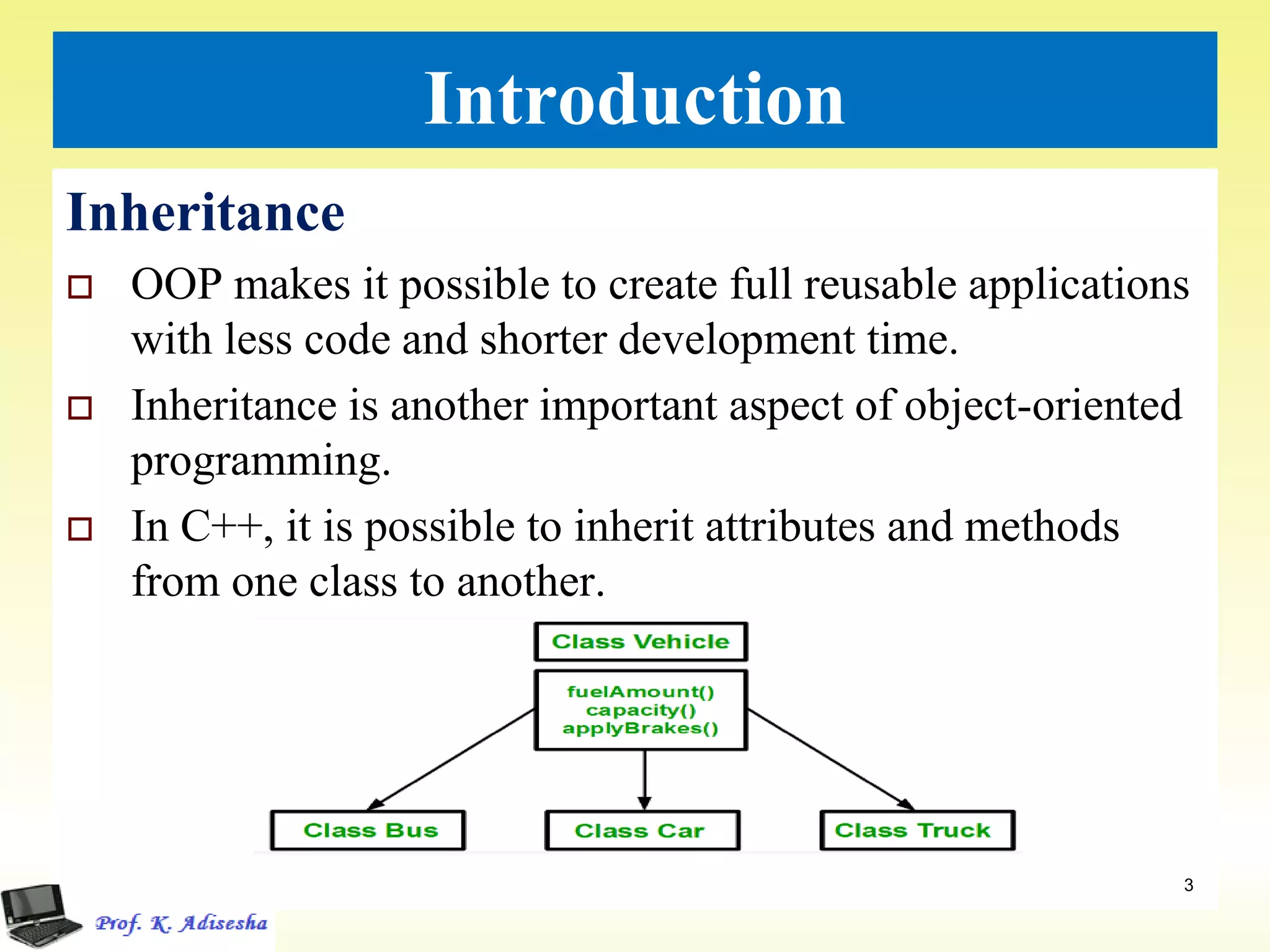
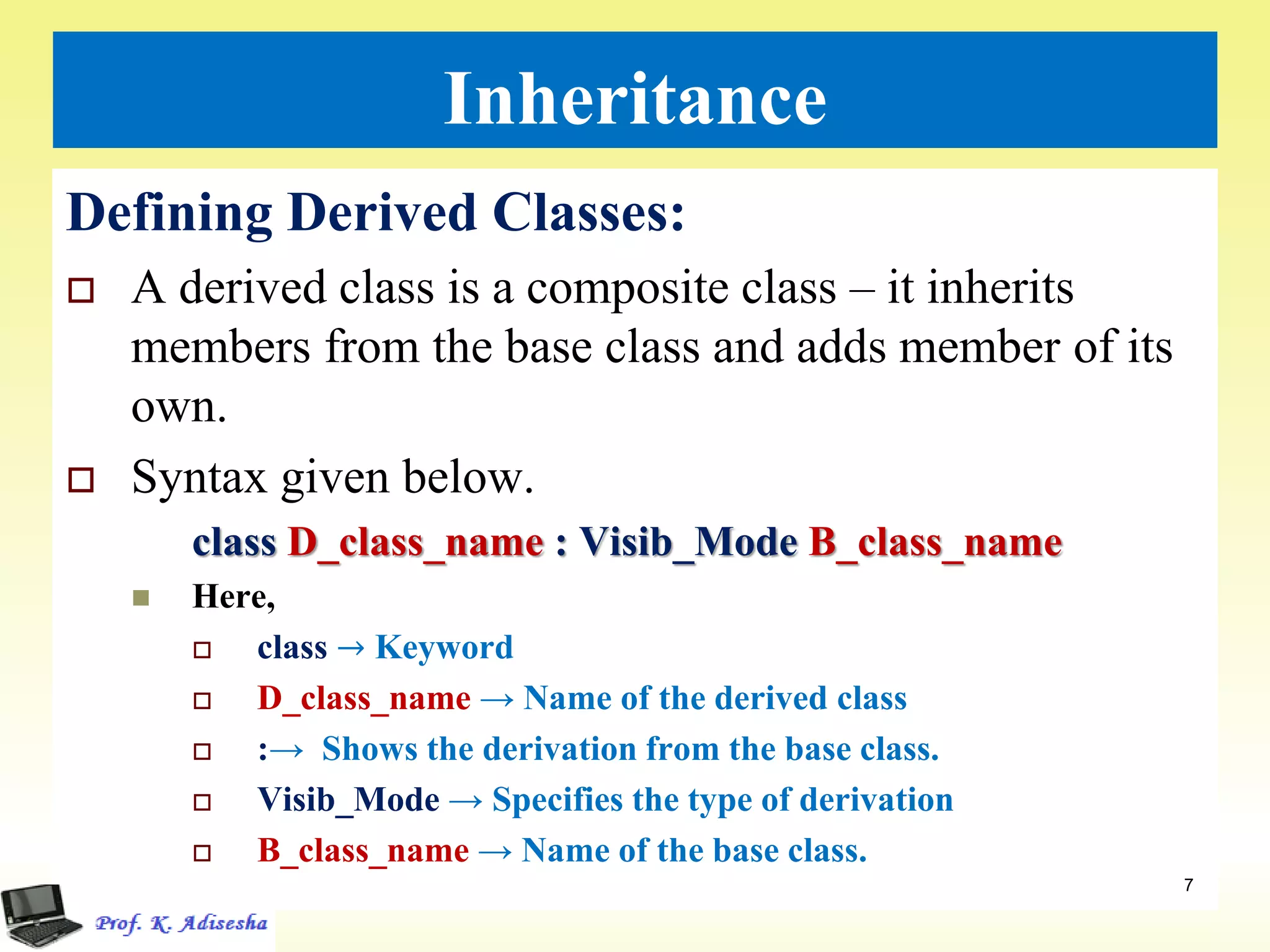
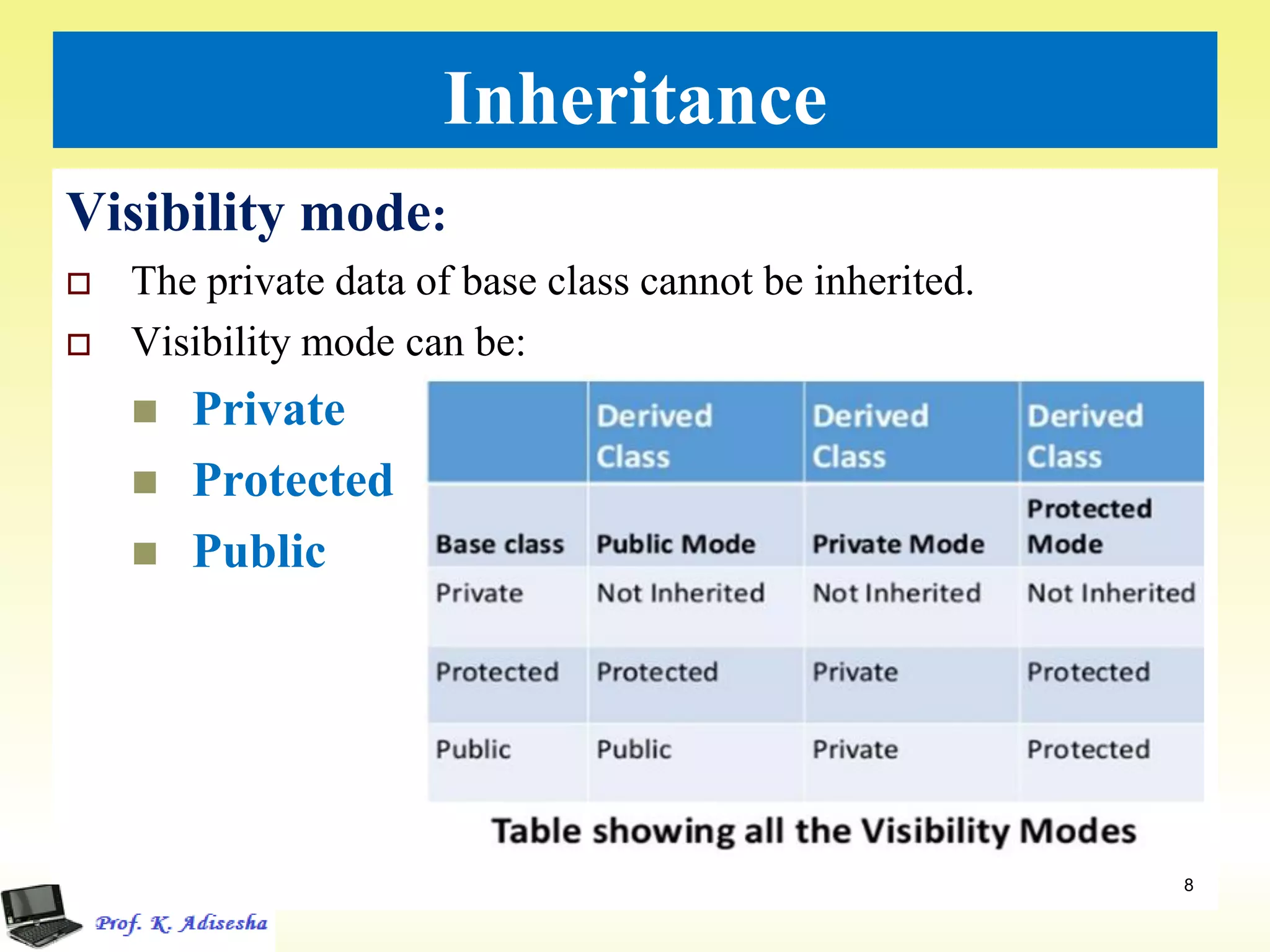
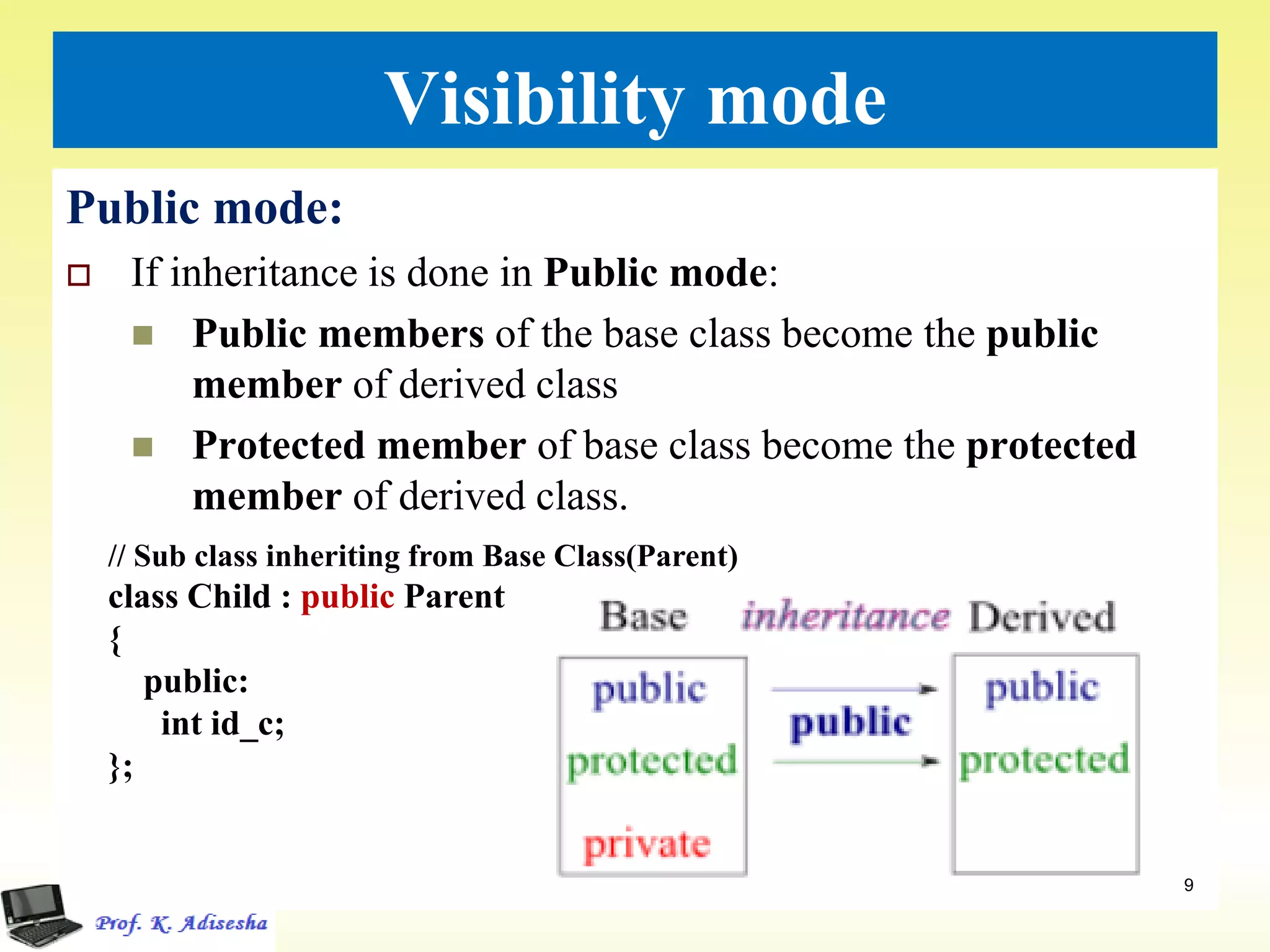
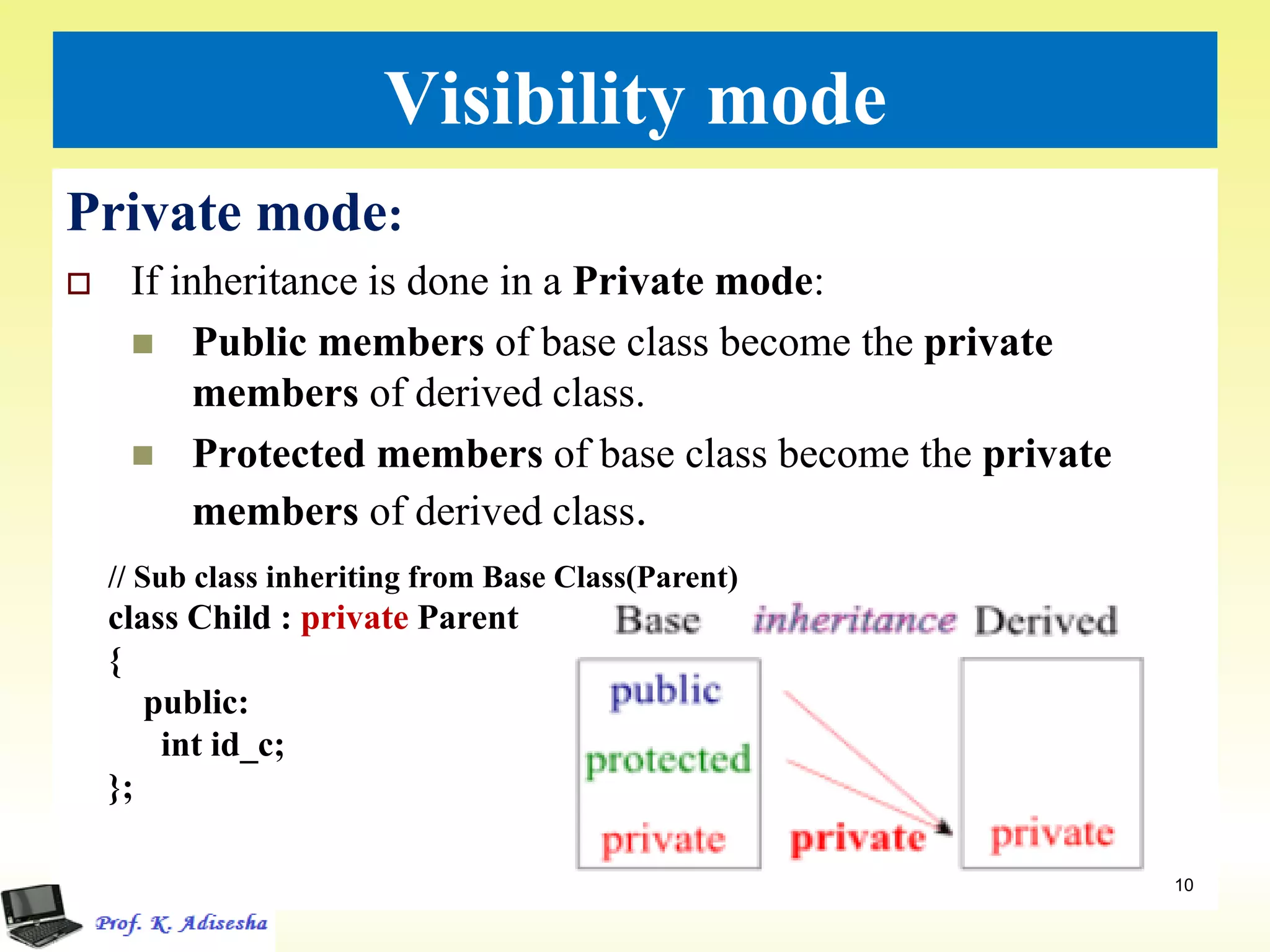
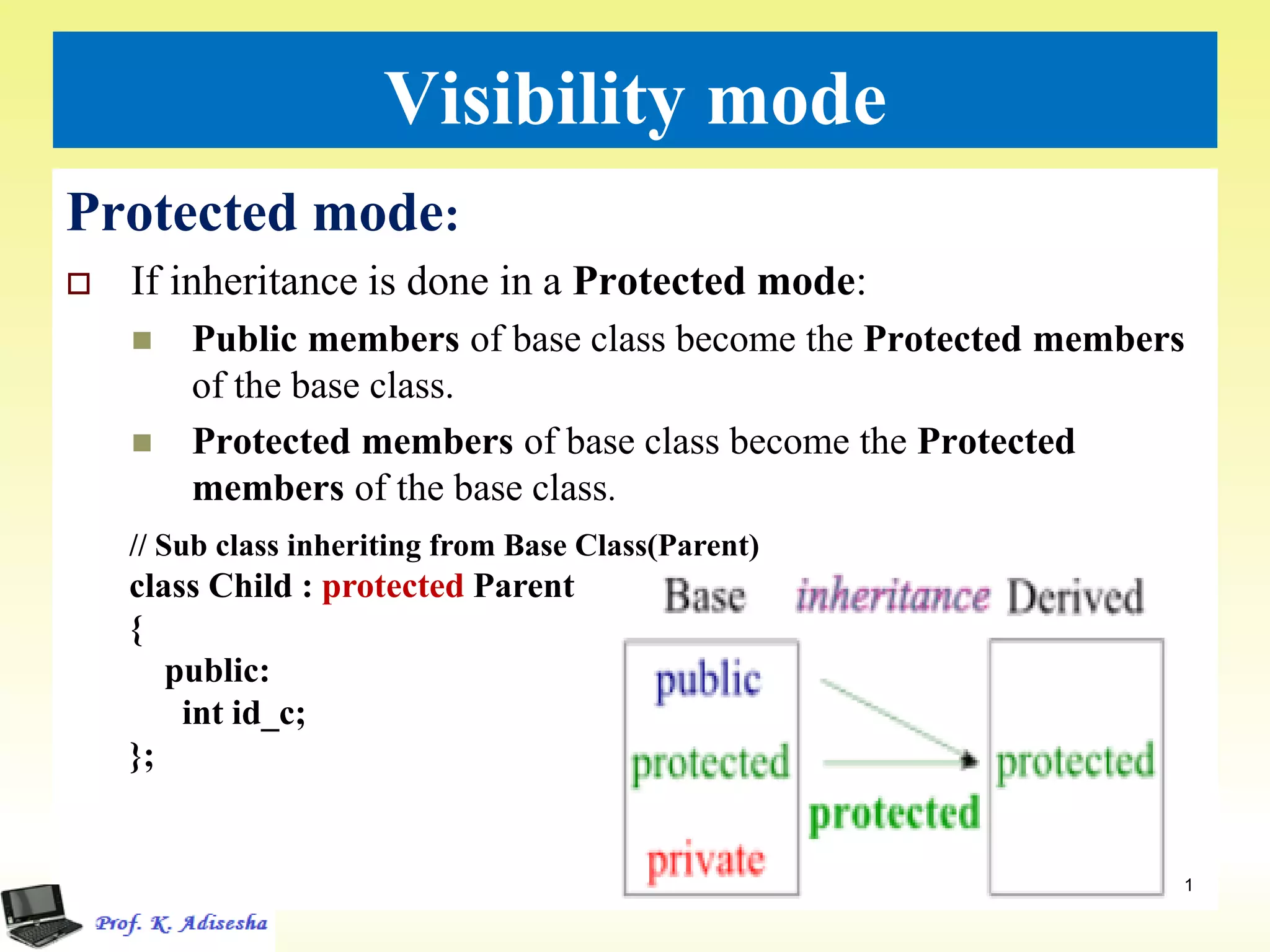
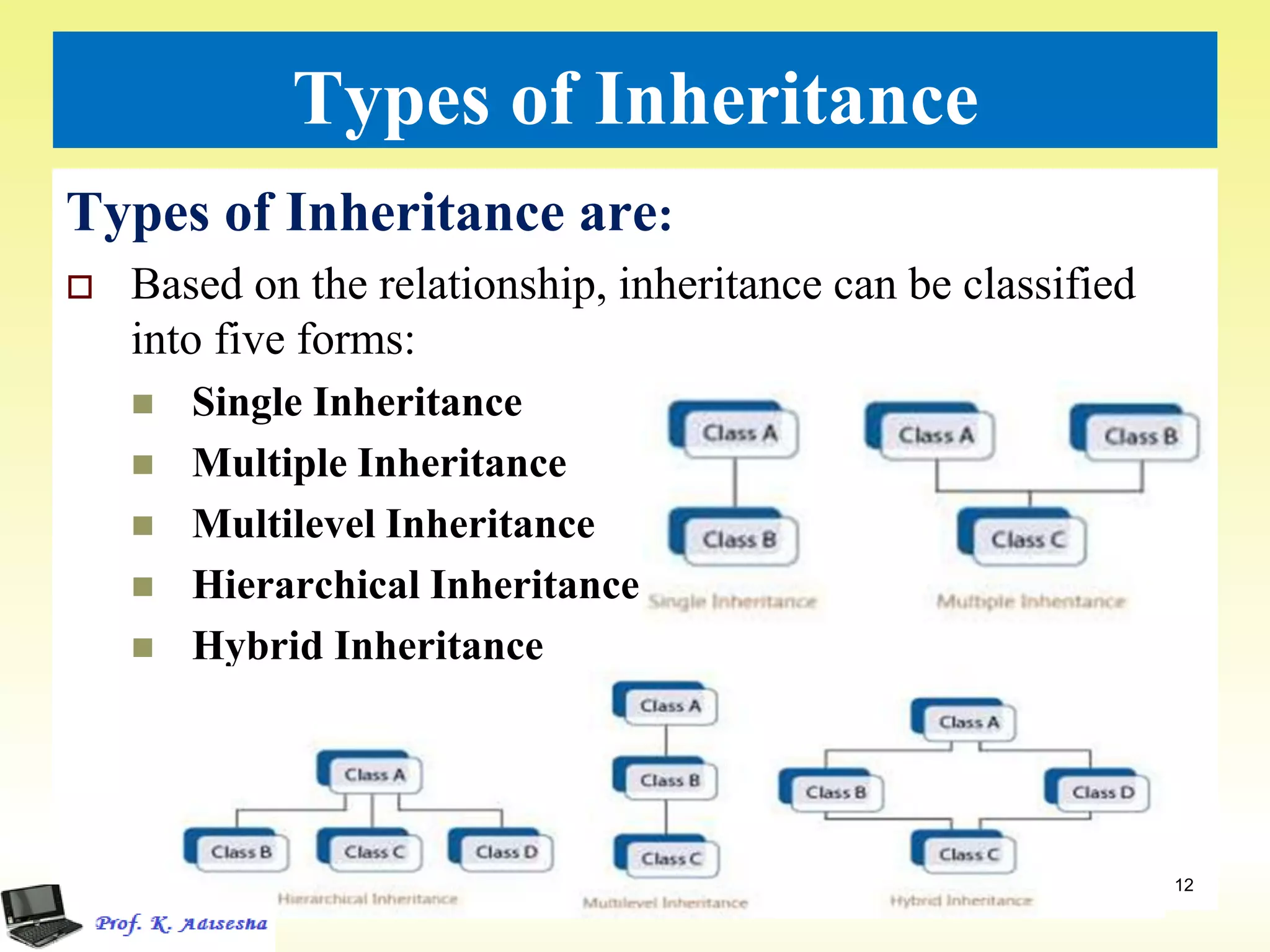
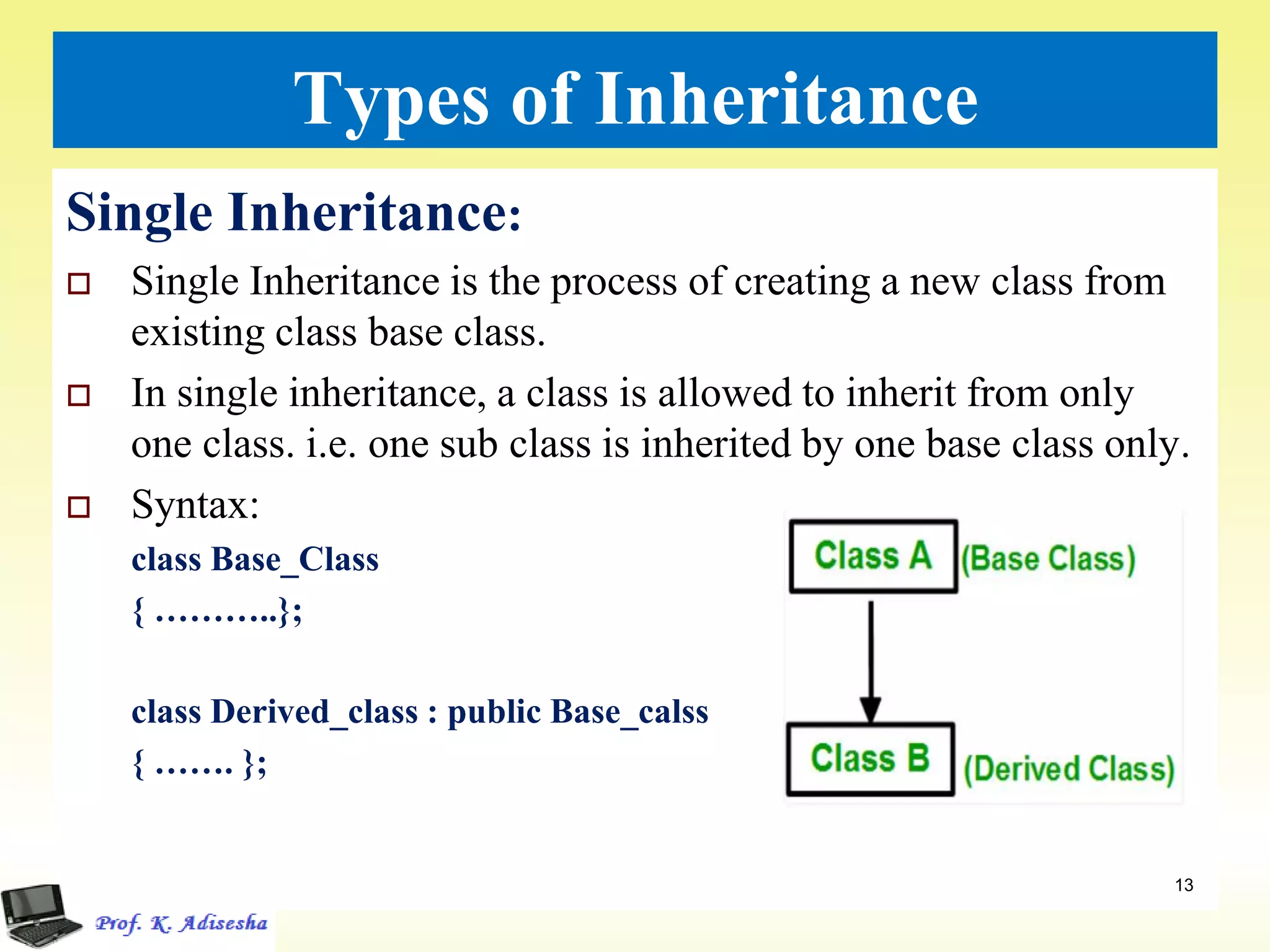
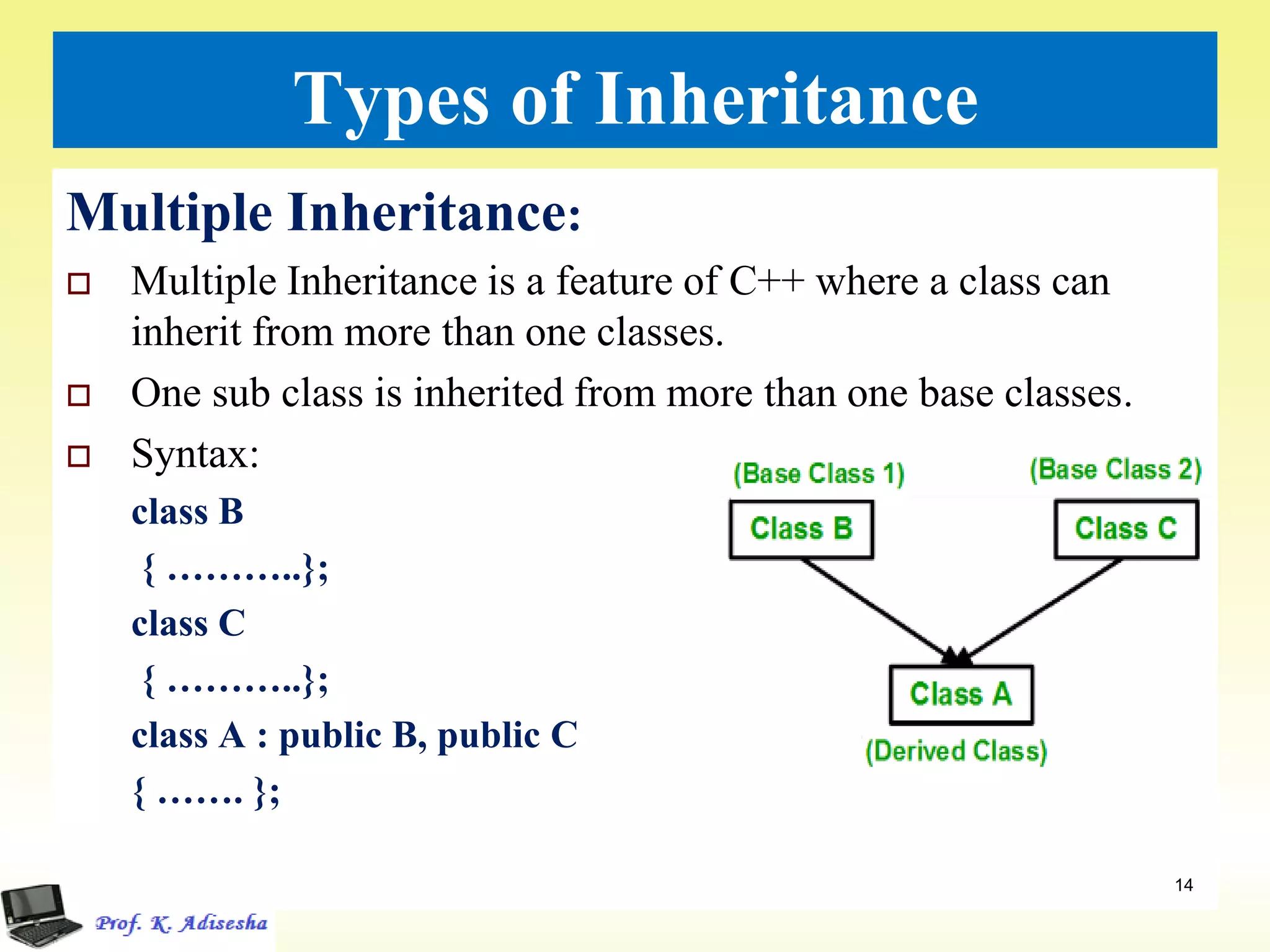
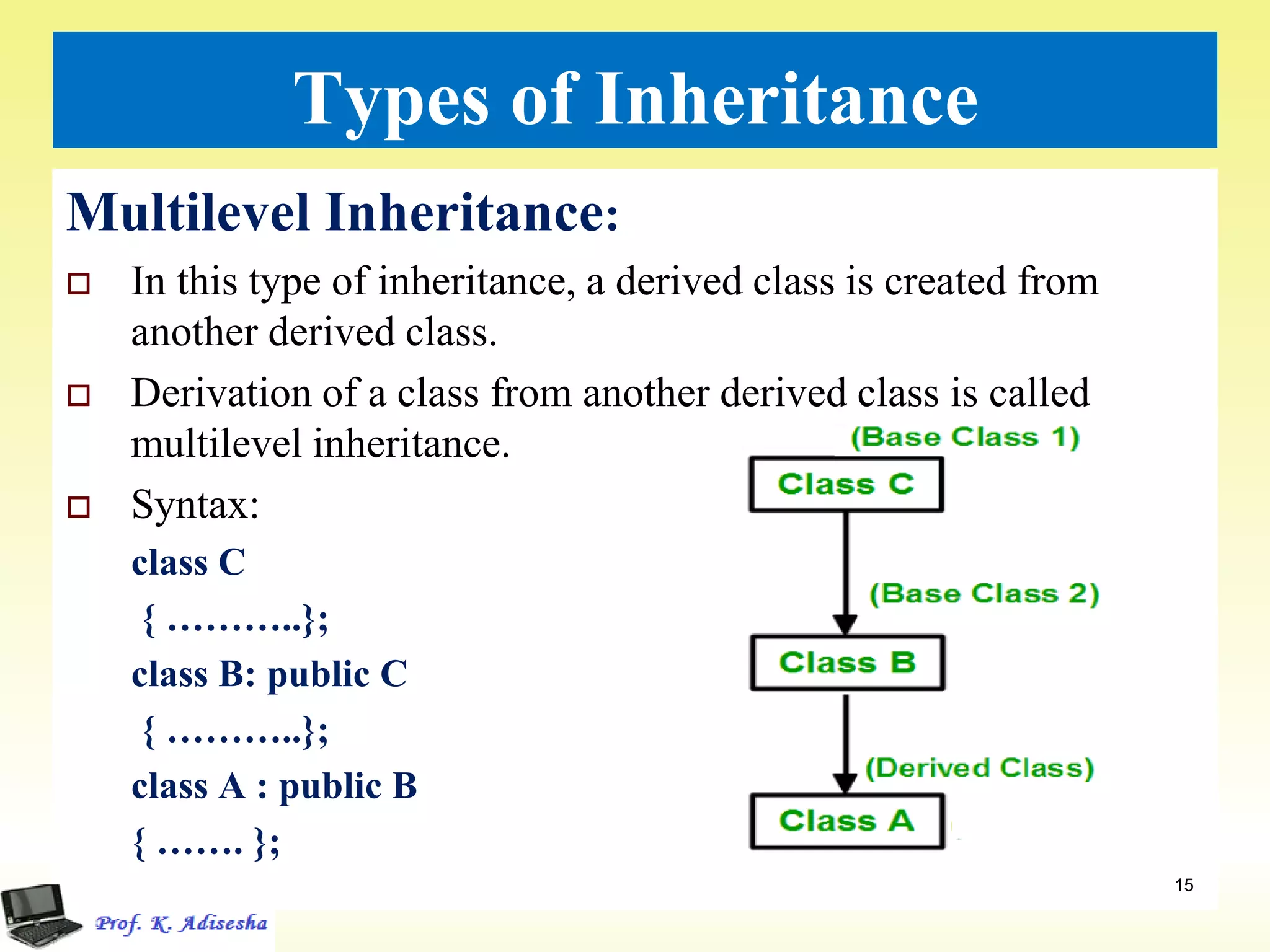
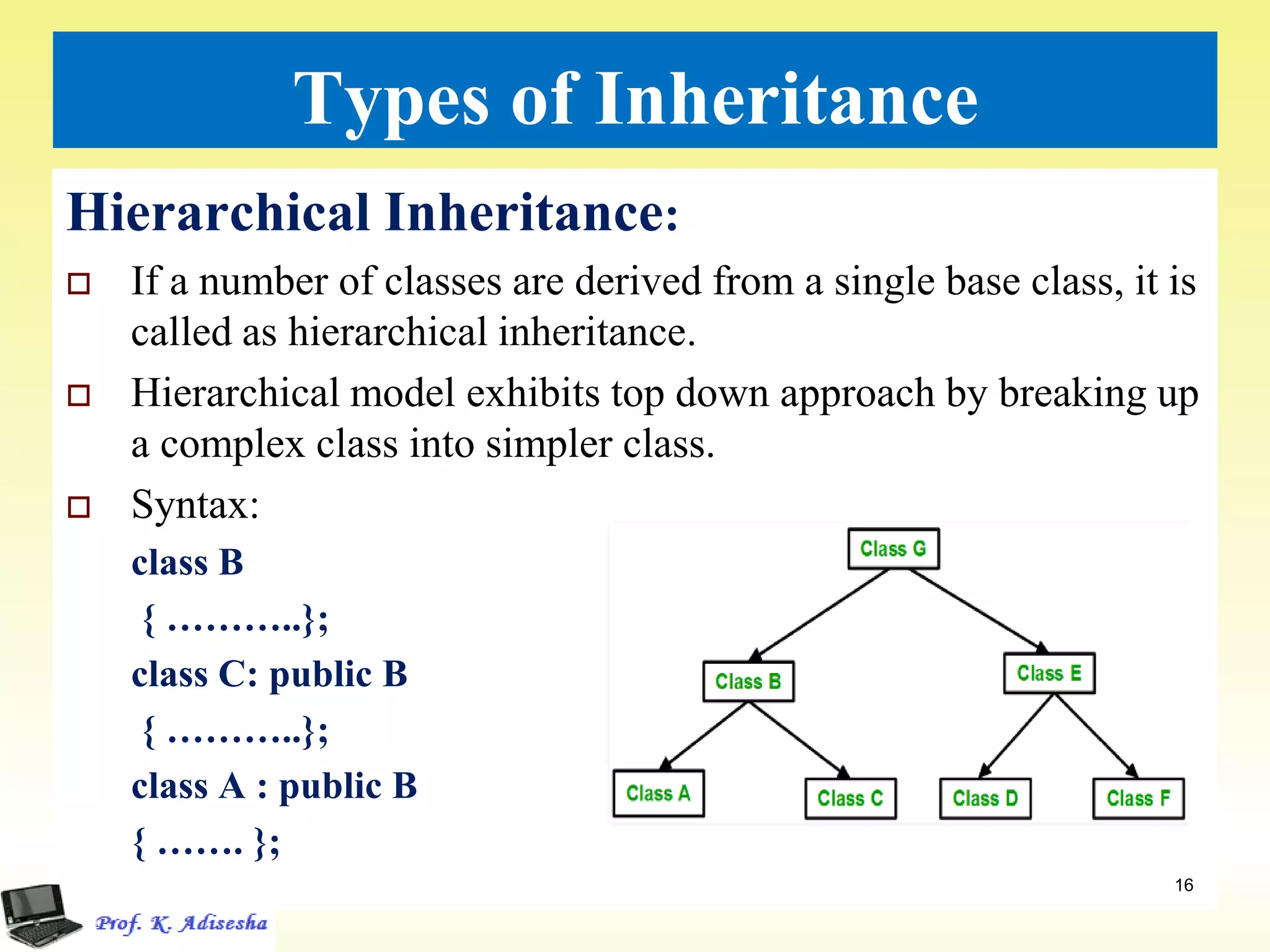
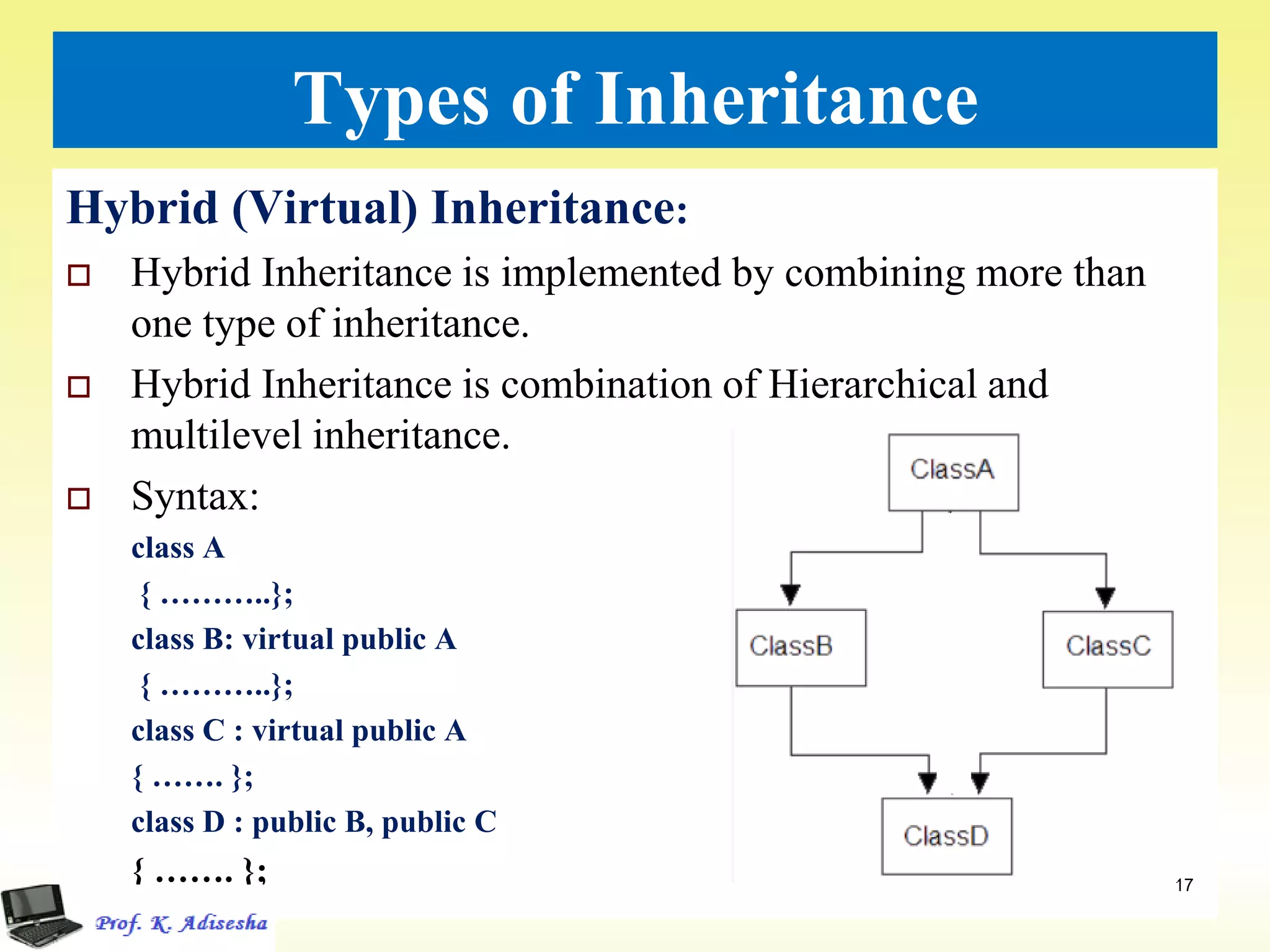
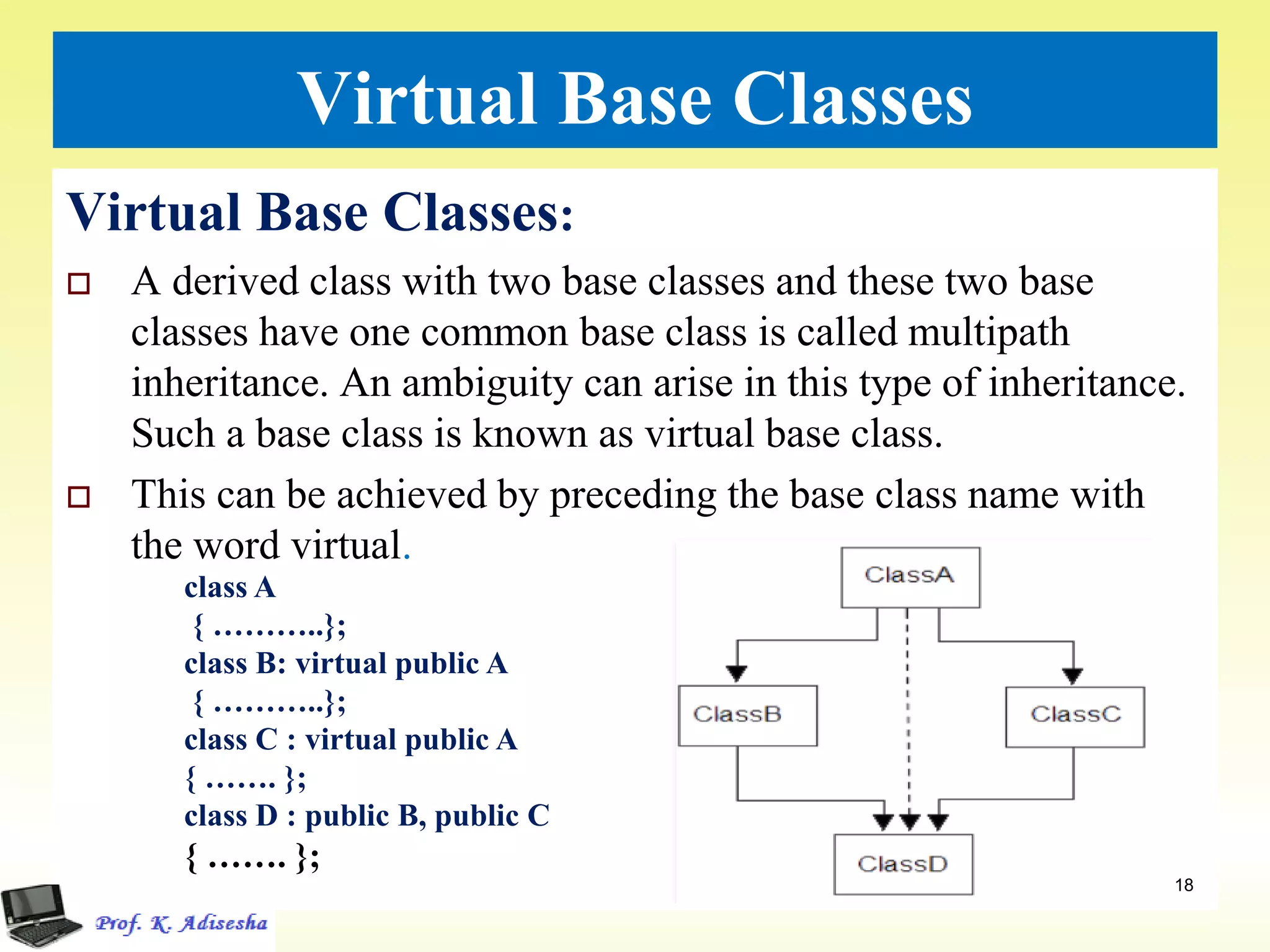
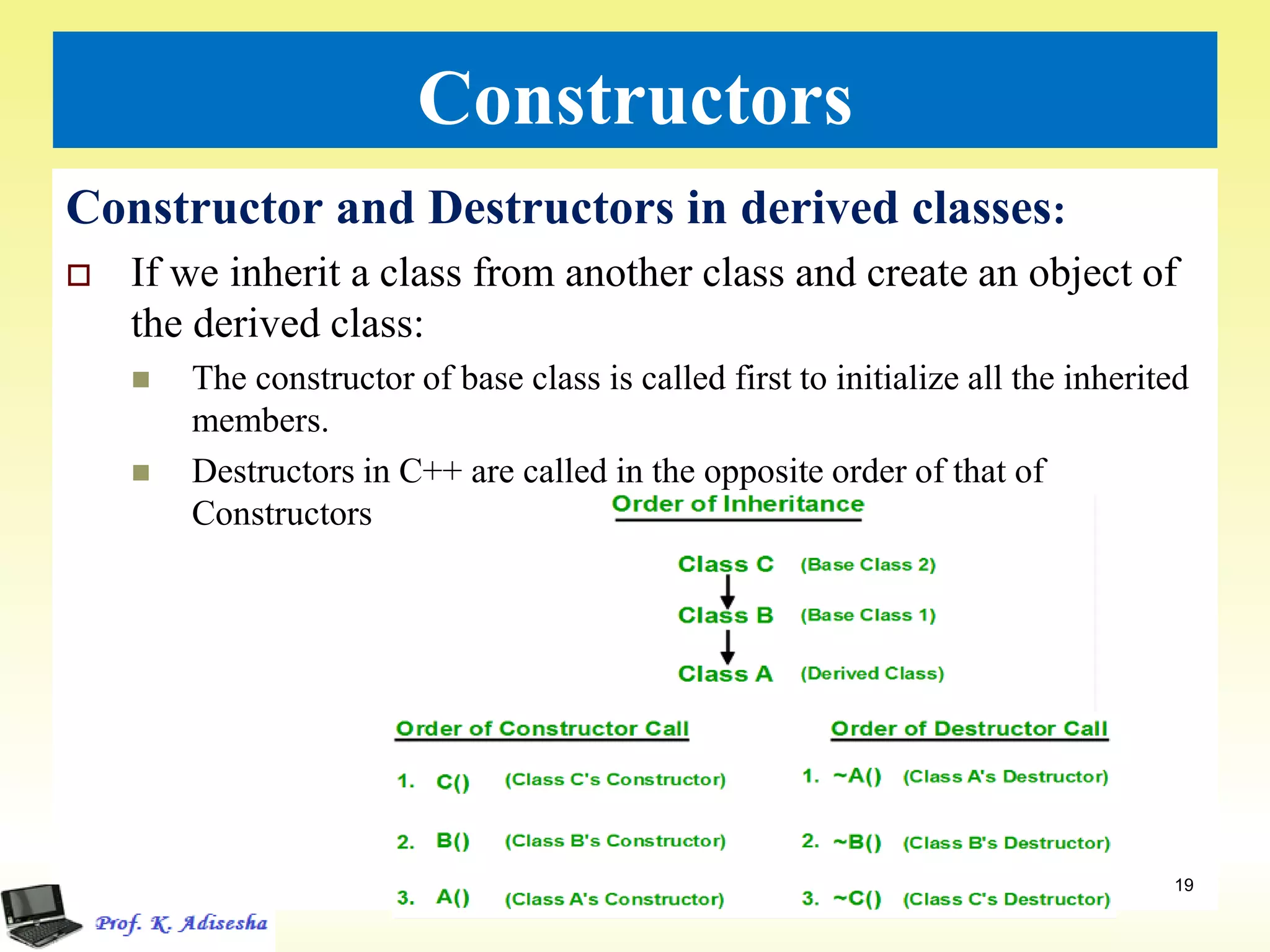
Inheritance allows classes to establish a hierarchical relationship between base and derived classes so that the derived class can inherit attributes and behaviors from the base class. There are several types of inheritance including single, multilevel, and multiple inheritance. Visibility modes like public, private, and protected determine which members are inherited from the base class. Virtual base classes are used to resolve ambiguities that can arise from multiple inheritance hierarchies sharing a common base class.