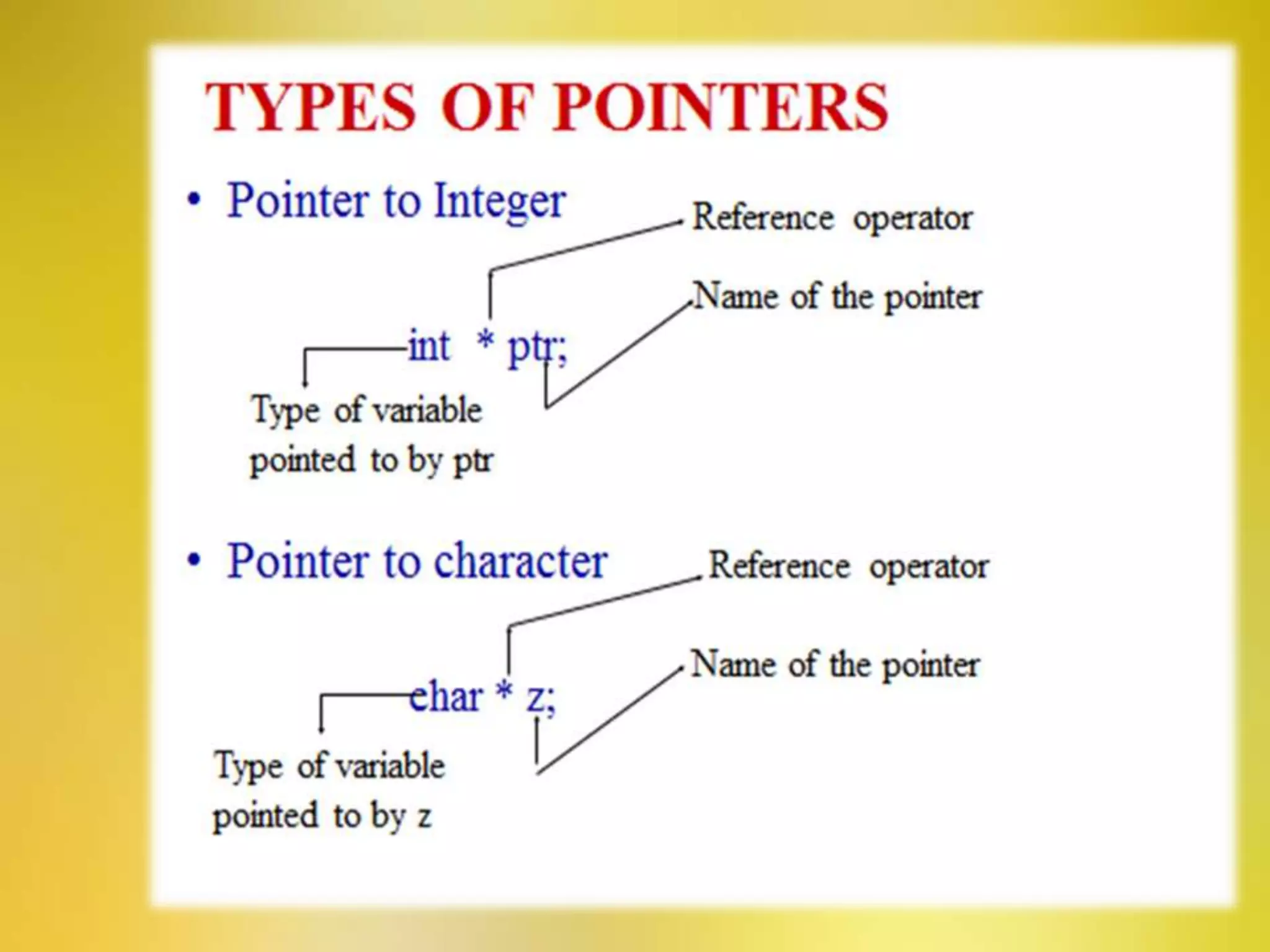
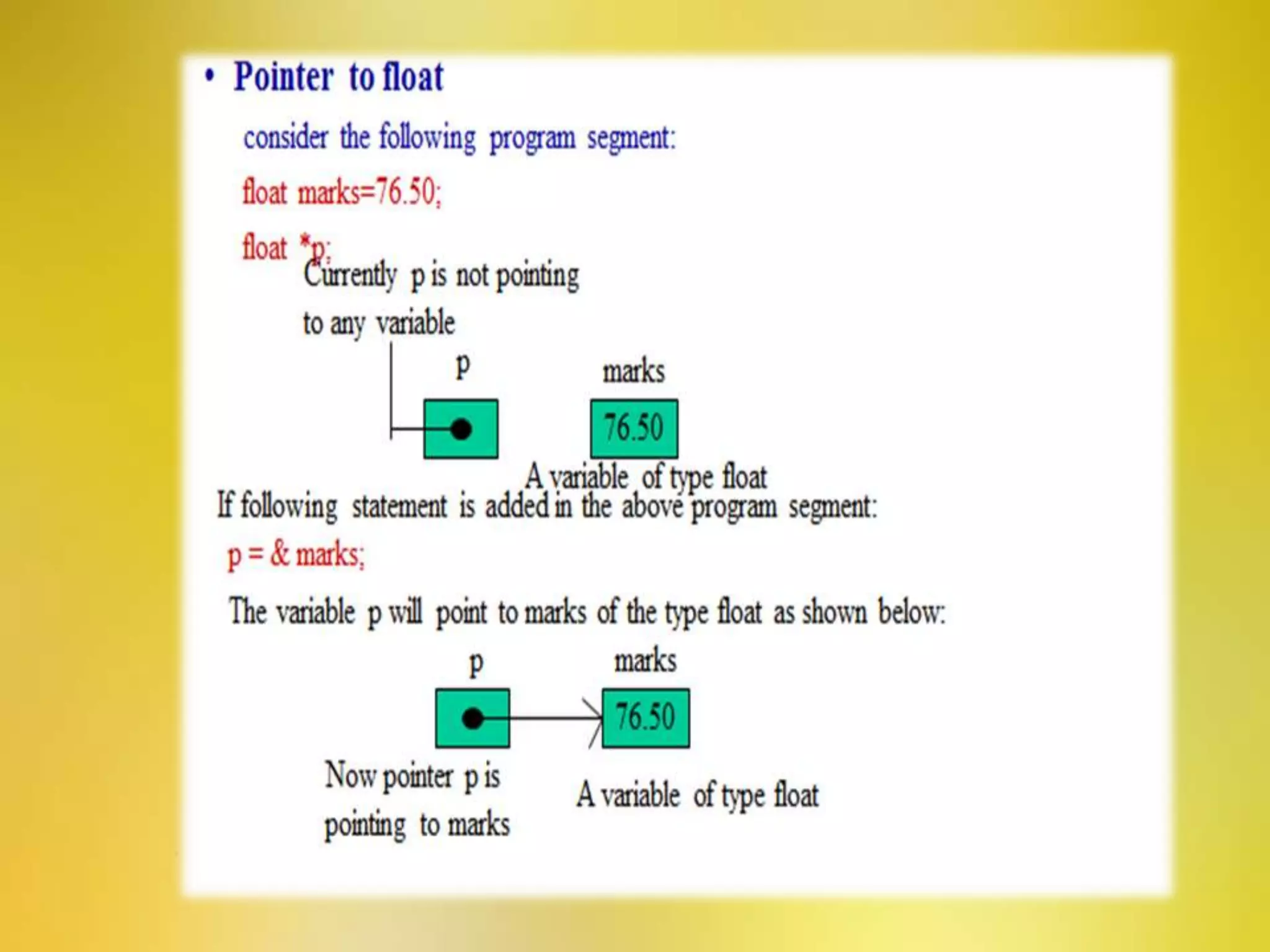
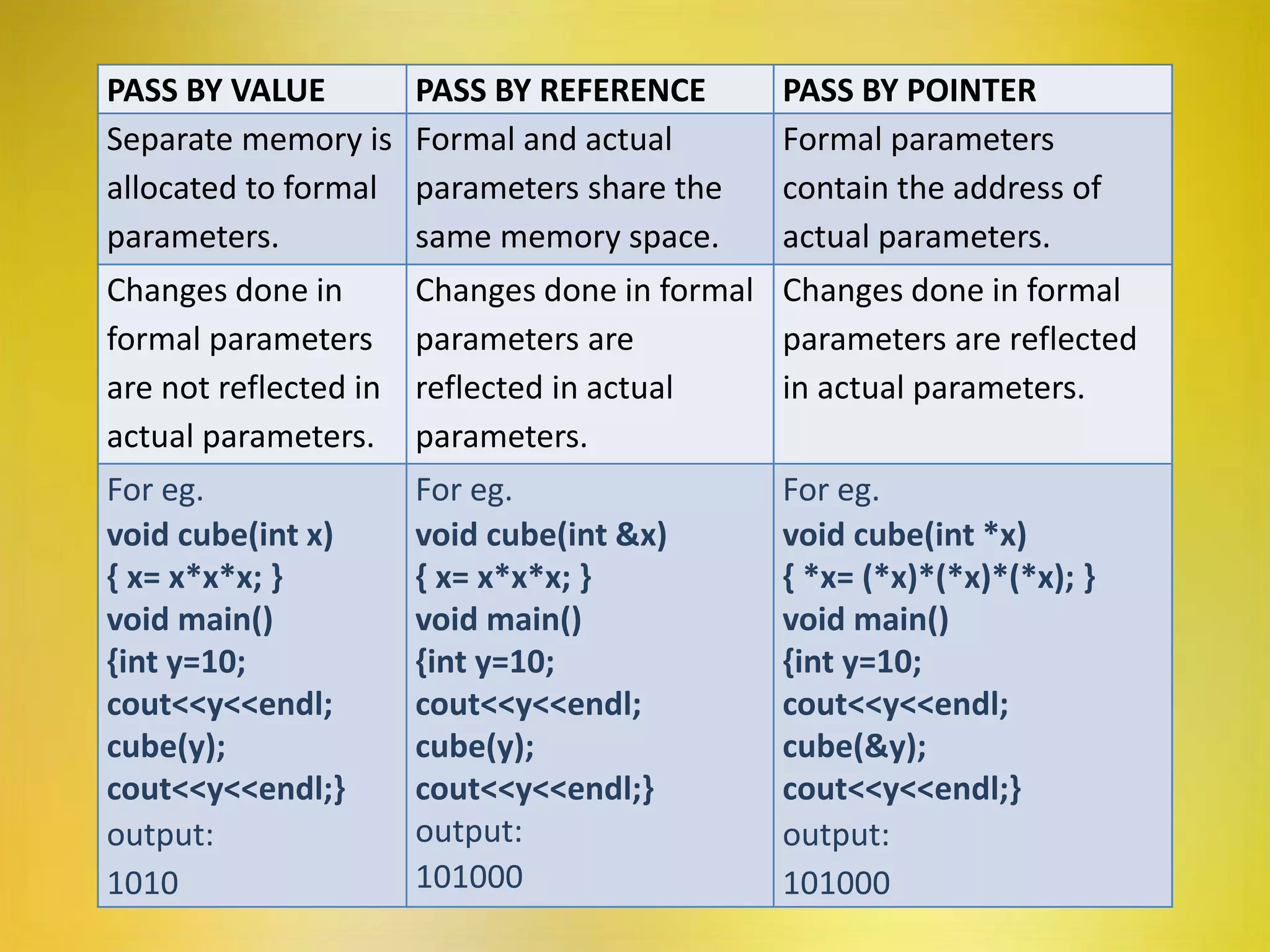
This document provides an overview of pointers in C++. It defines pointers as variables that store the memory address of another variable. It discusses declaring and initializing pointer variables, pointer operators like & and *, pointer arithmetic, passing pointers to functions, arrays of pointers, strings of pointers, objects of pointers, and the this pointer. Advantages of pointers include efficient handling of arrays, direct memory access for speed, reduced storage space, and support for complex data structures. Limitations include slower performance than normal variables, inability to store values, needing null references, and risk of errors from incorrect initialization.














![Array of Pointer
• Array is collection of similar data type.
• We can create pointer variable with array both
are similar data type.
• Using array of pointer searching, insertion,
deletion etc. operation we can perform.
• Syntax:
Data_type variable_name[size of array];
Data_type *pointer_variable;
pointer_variable=variable_name;
OR
pointer_variable=&variable_name[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointerinc-170318055024/75/Pointer-in-C-18-2048.jpg)
![• Example of pointer of array:
Void main()
{
int a[2],*ptr;
Ptr=&a[0];
Cout<<“Ptr :”<<ptr;
*Ptr++;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointerinc-170318055024/75/Pointer-in-C-19-2048.jpg)
![String of Pointer
• Array of character is called string.
• We can create pointer variable with string both
are similar data type.
• Using string of pointer searching, finding length ,
comparisons ,concatenation ,reverse etc
operation we can perform.
• Syntax:
Data_type variable_name[size of string];
Data_type *pointer_variable;
Pointer_variable=&variable_name[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointerinc-170318055024/75/Pointer-in-C-20-2048.jpg)
![• Example of string of pointer:
void main()
{
Char name[4]=“NEEL”,*ptr;
Ptr=&name[0];
While(*ptr!=‘0’)
{
Ptr++;
Cout<<*ptr;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointerinc-170318055024/75/Pointer-in-C-21-2048.jpg)







