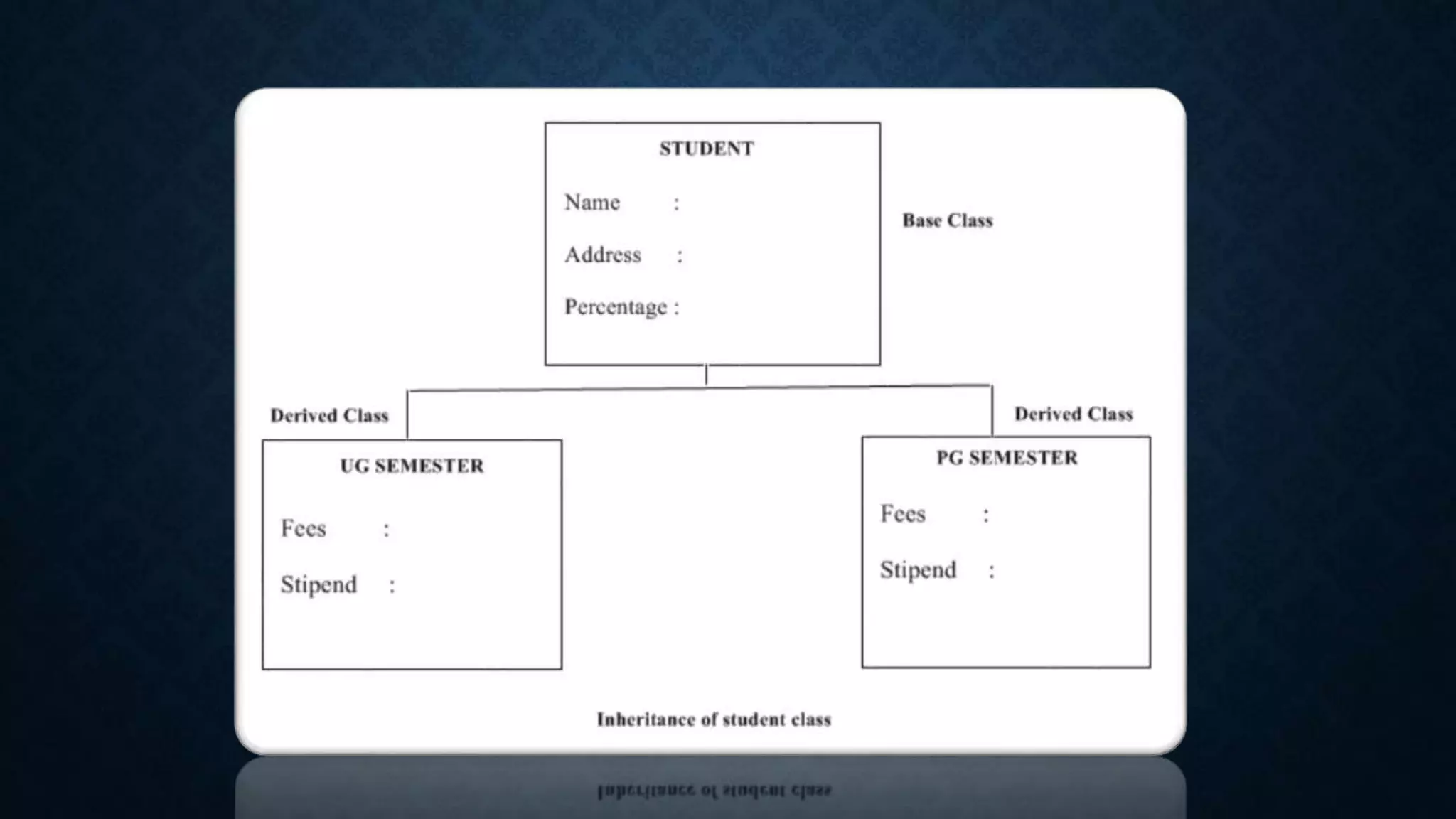
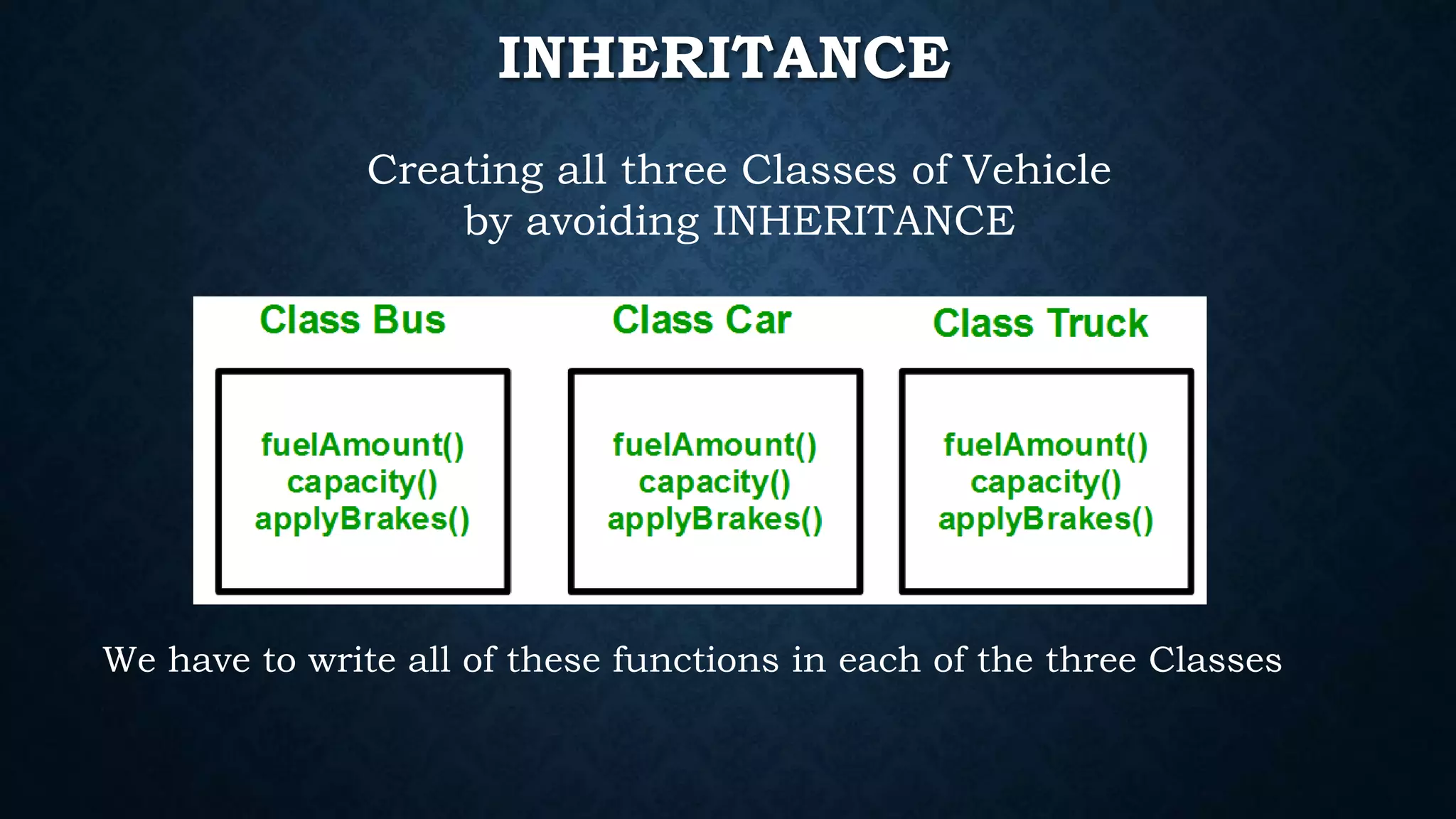
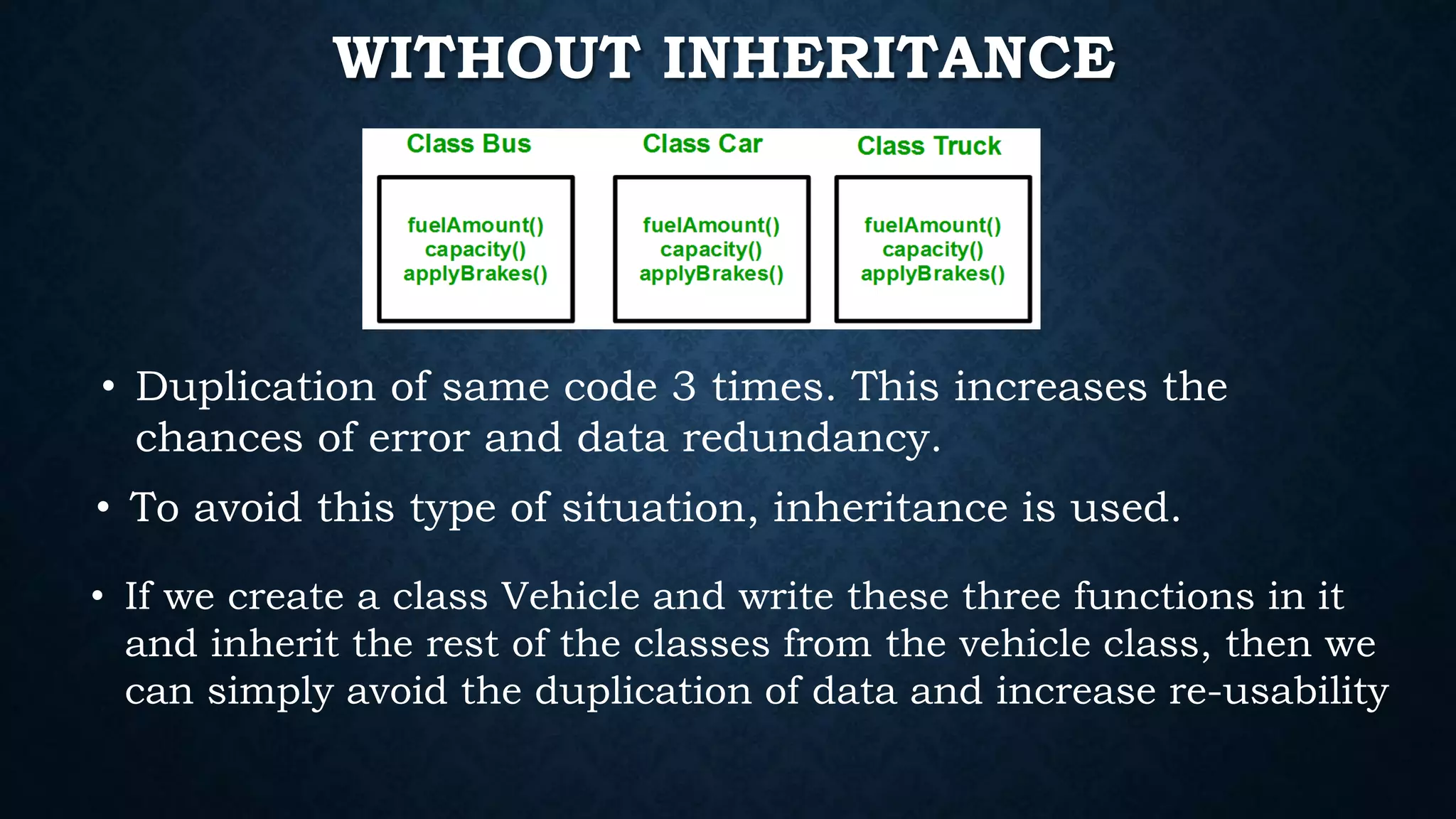
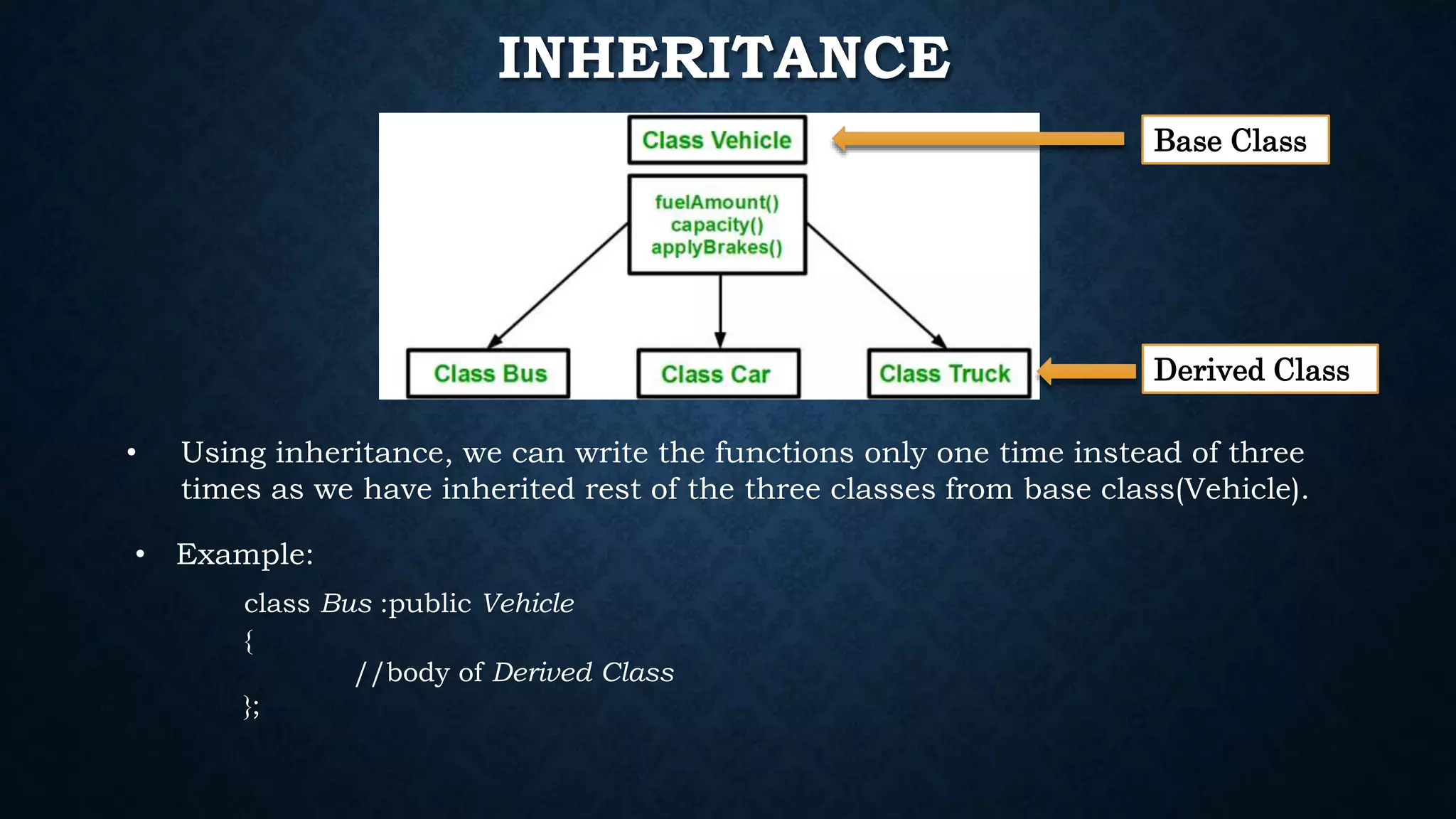
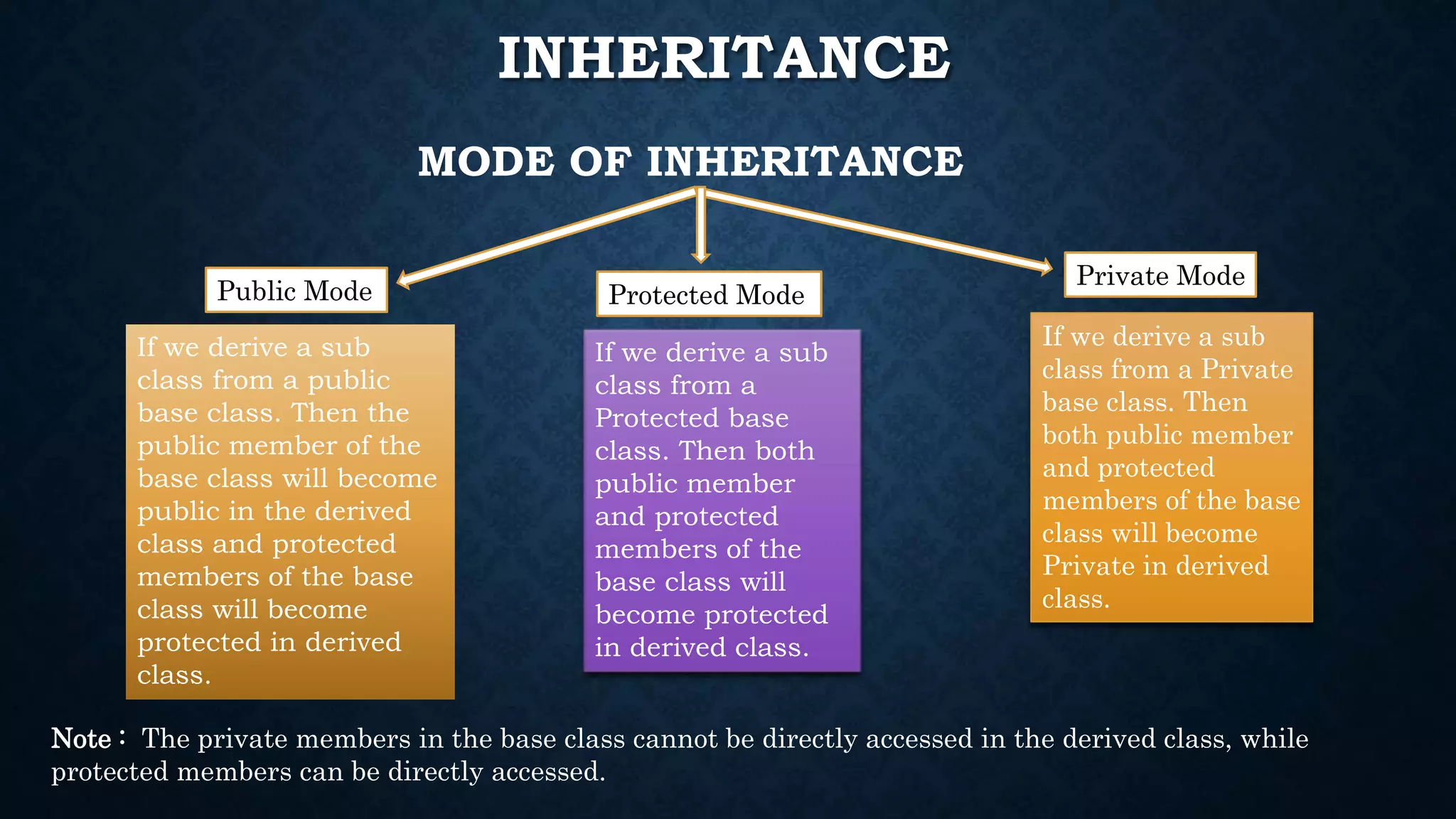
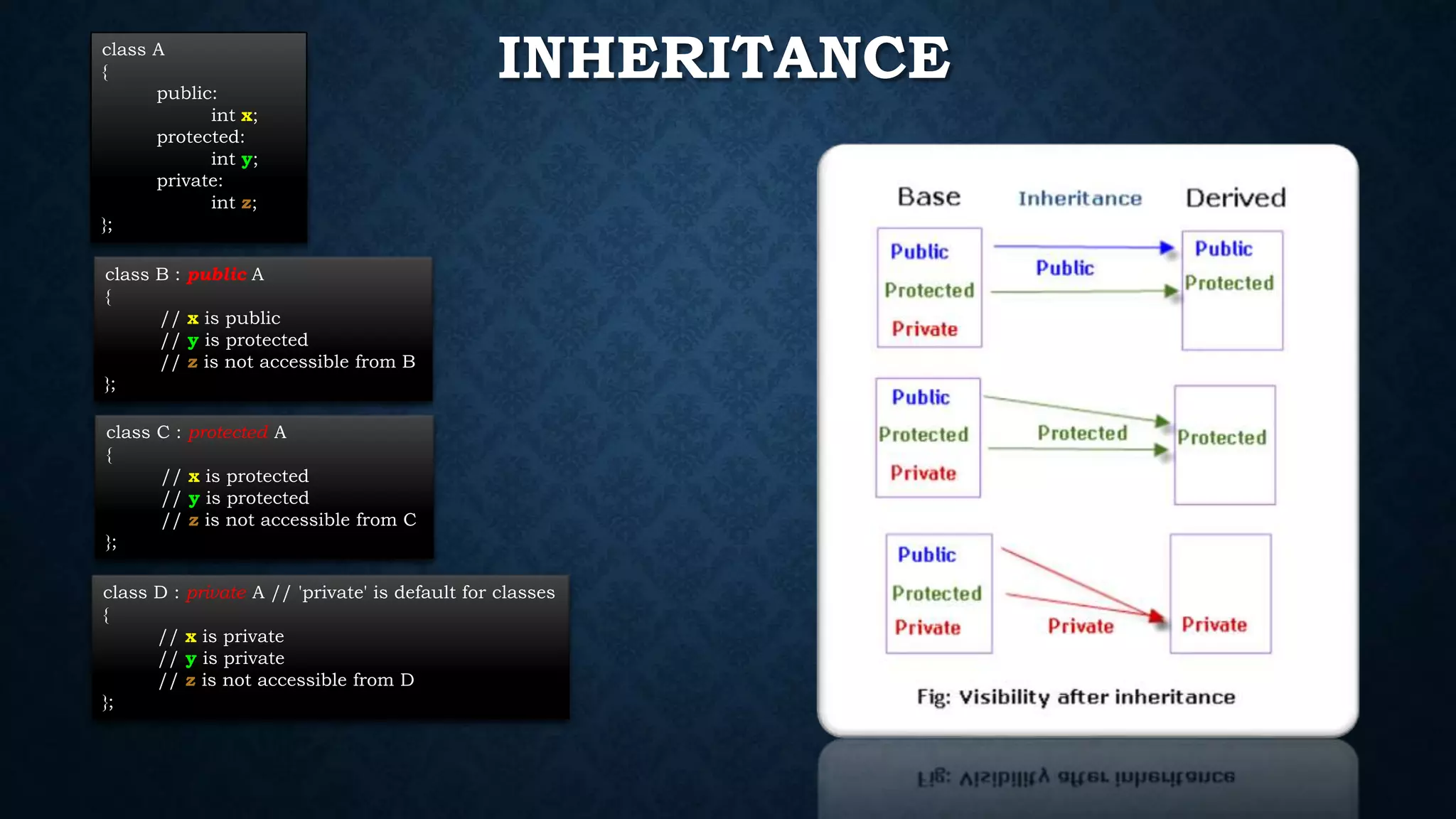
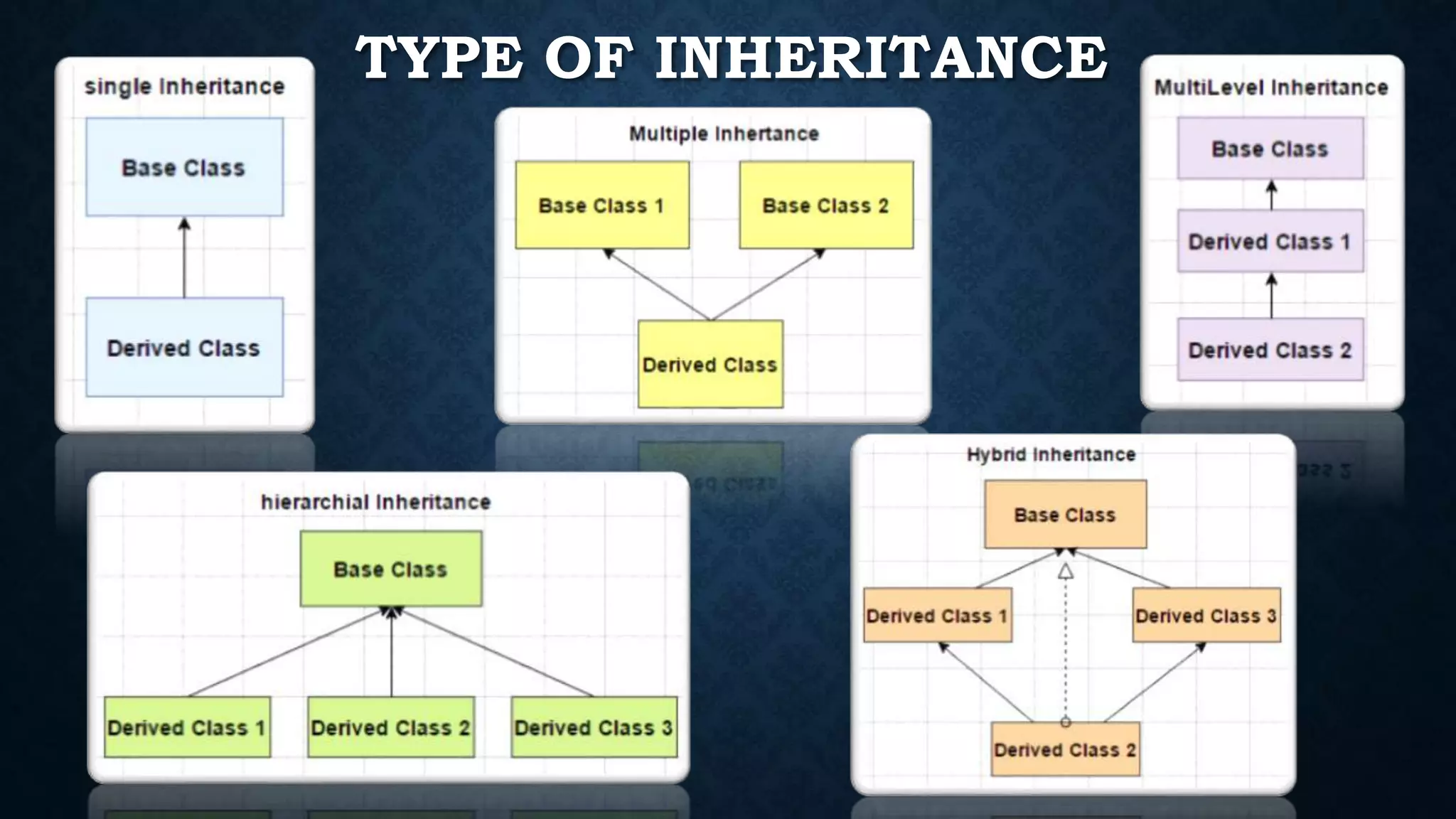
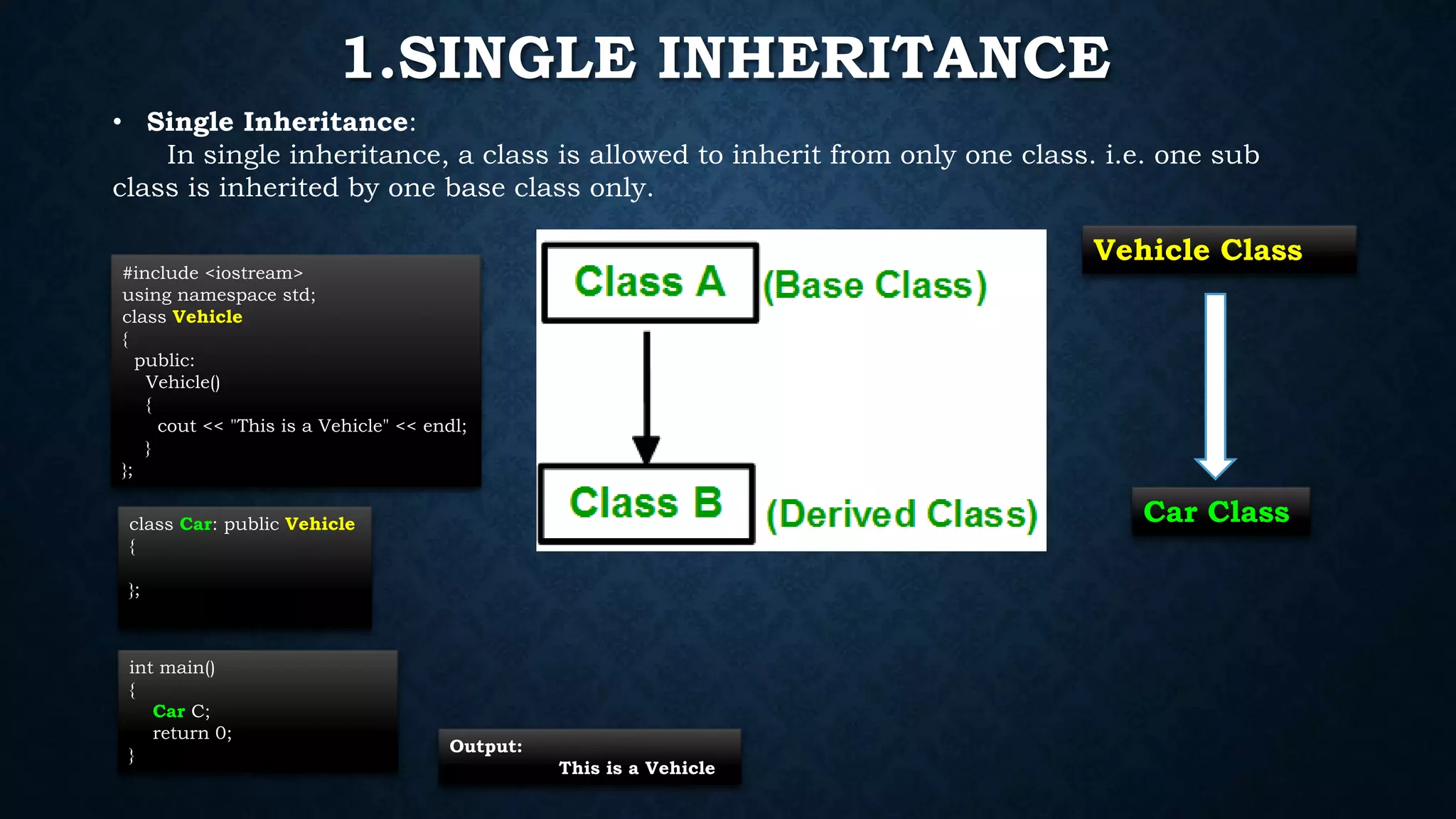
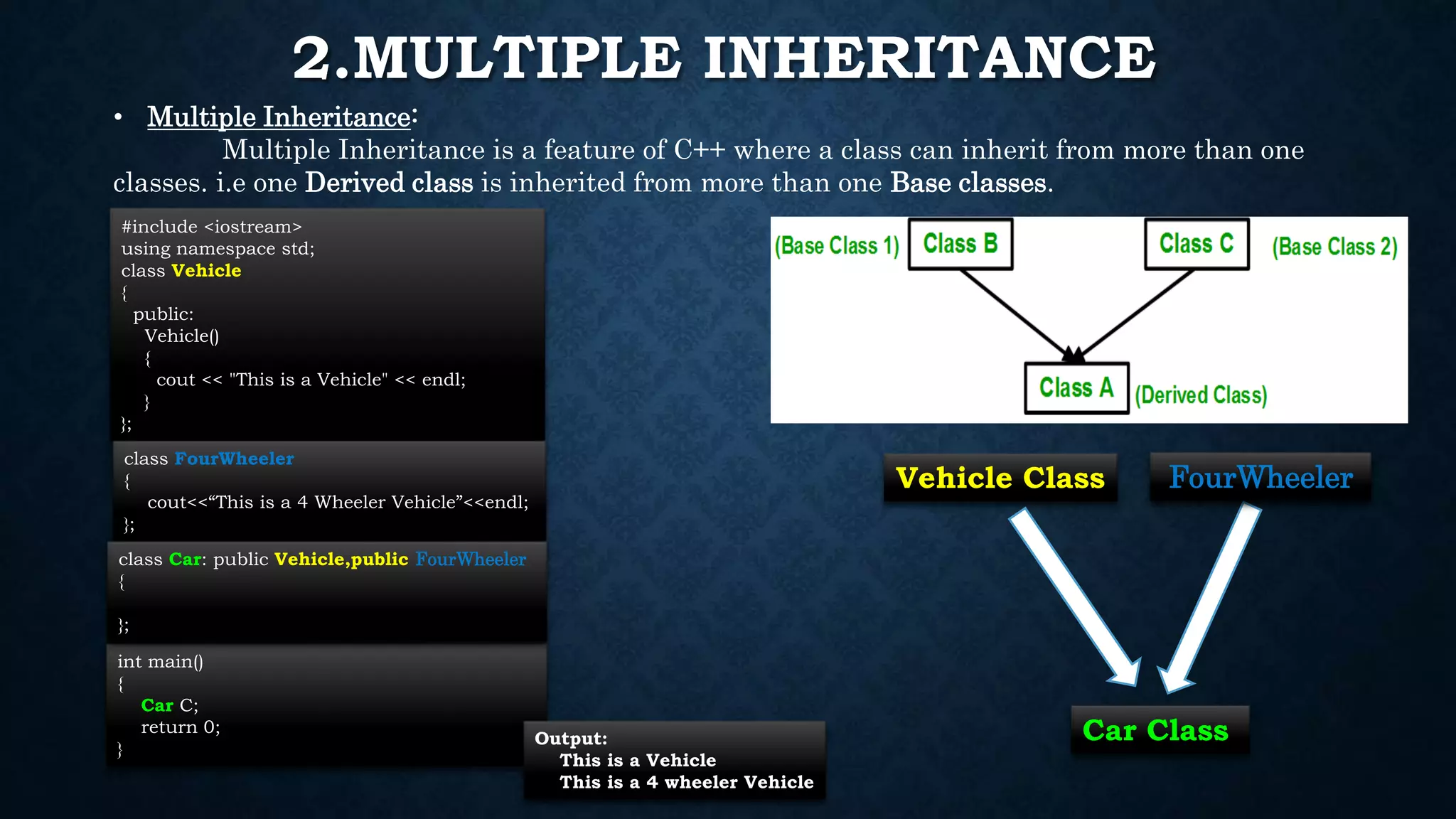
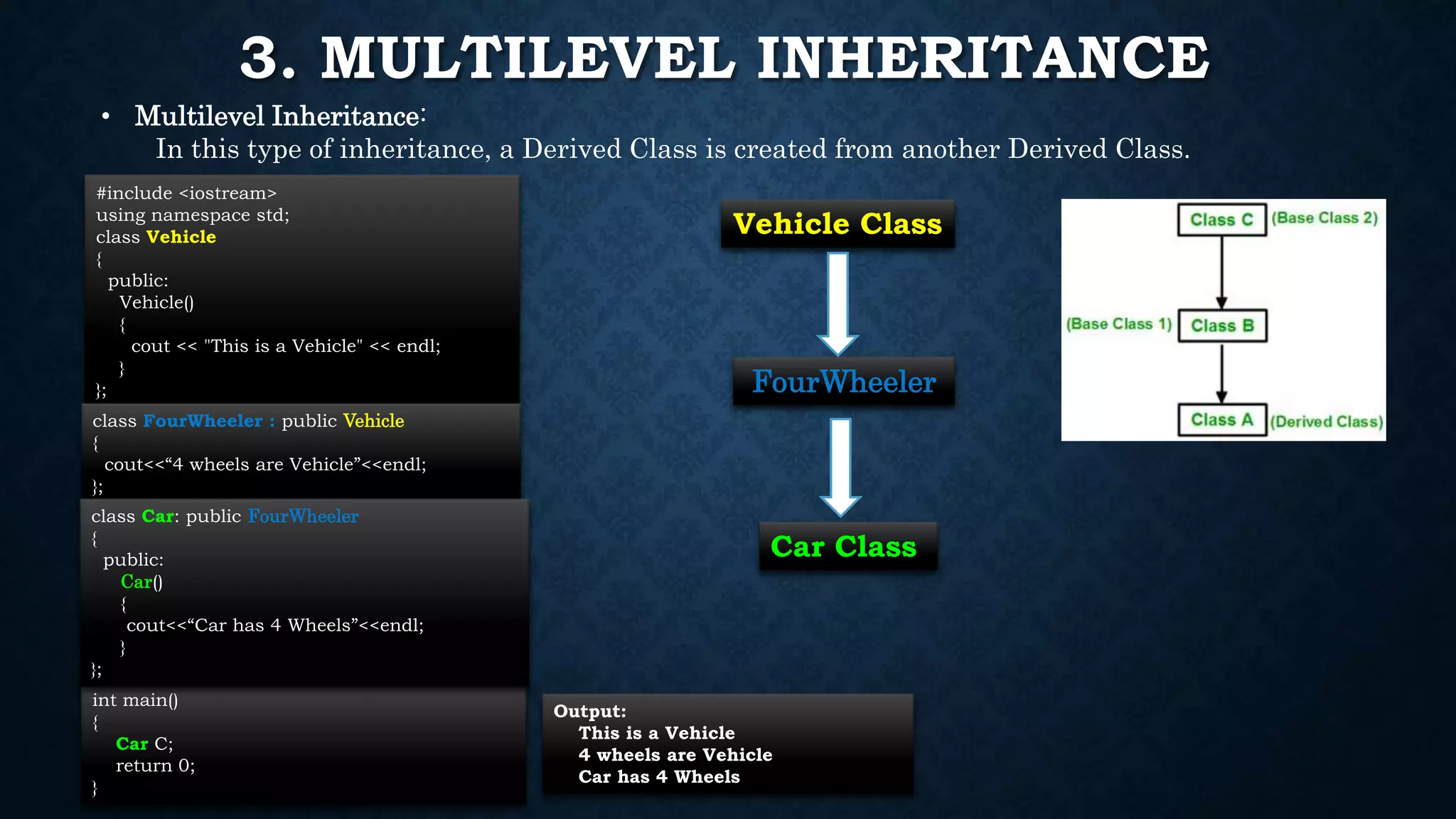
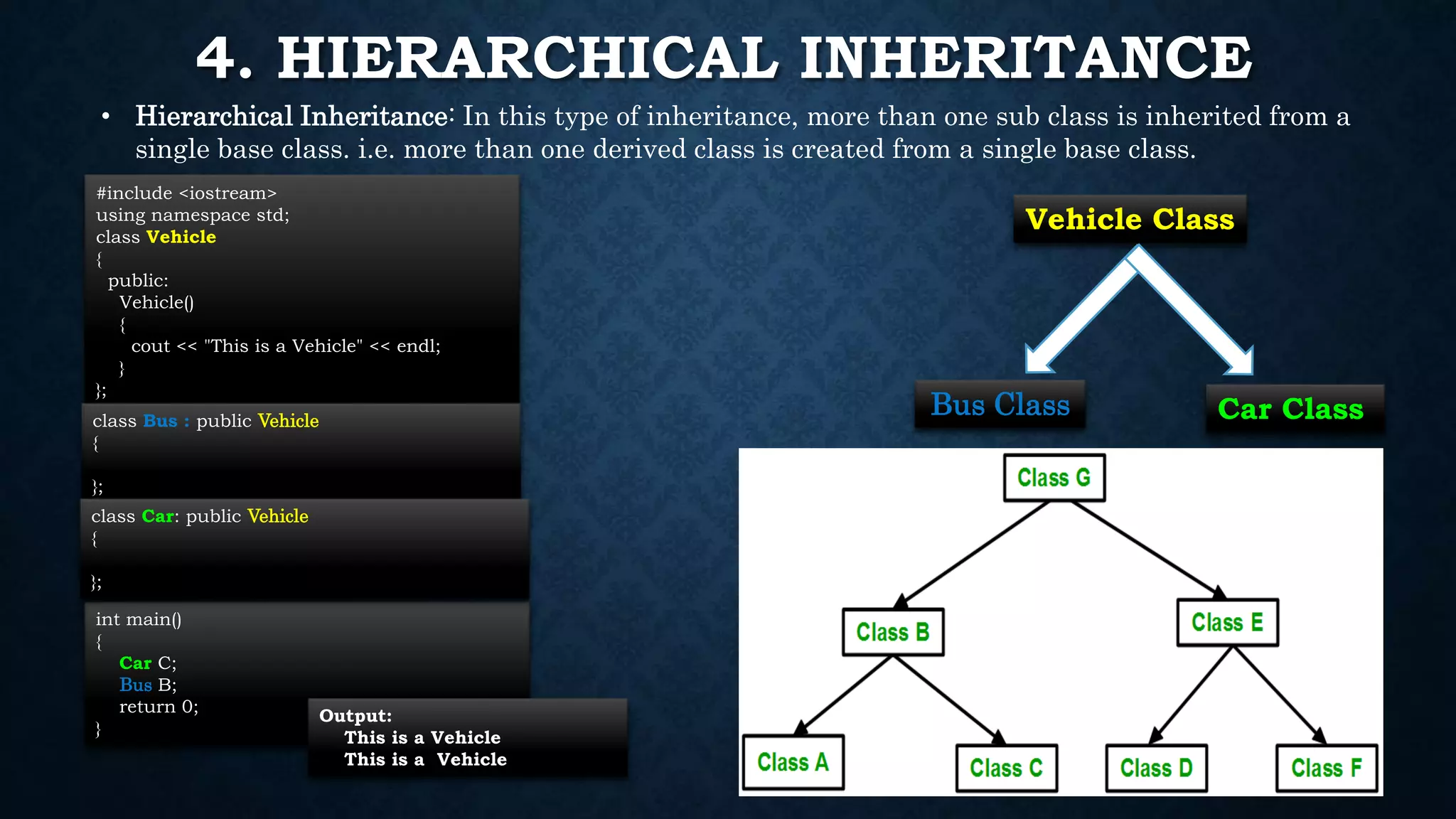
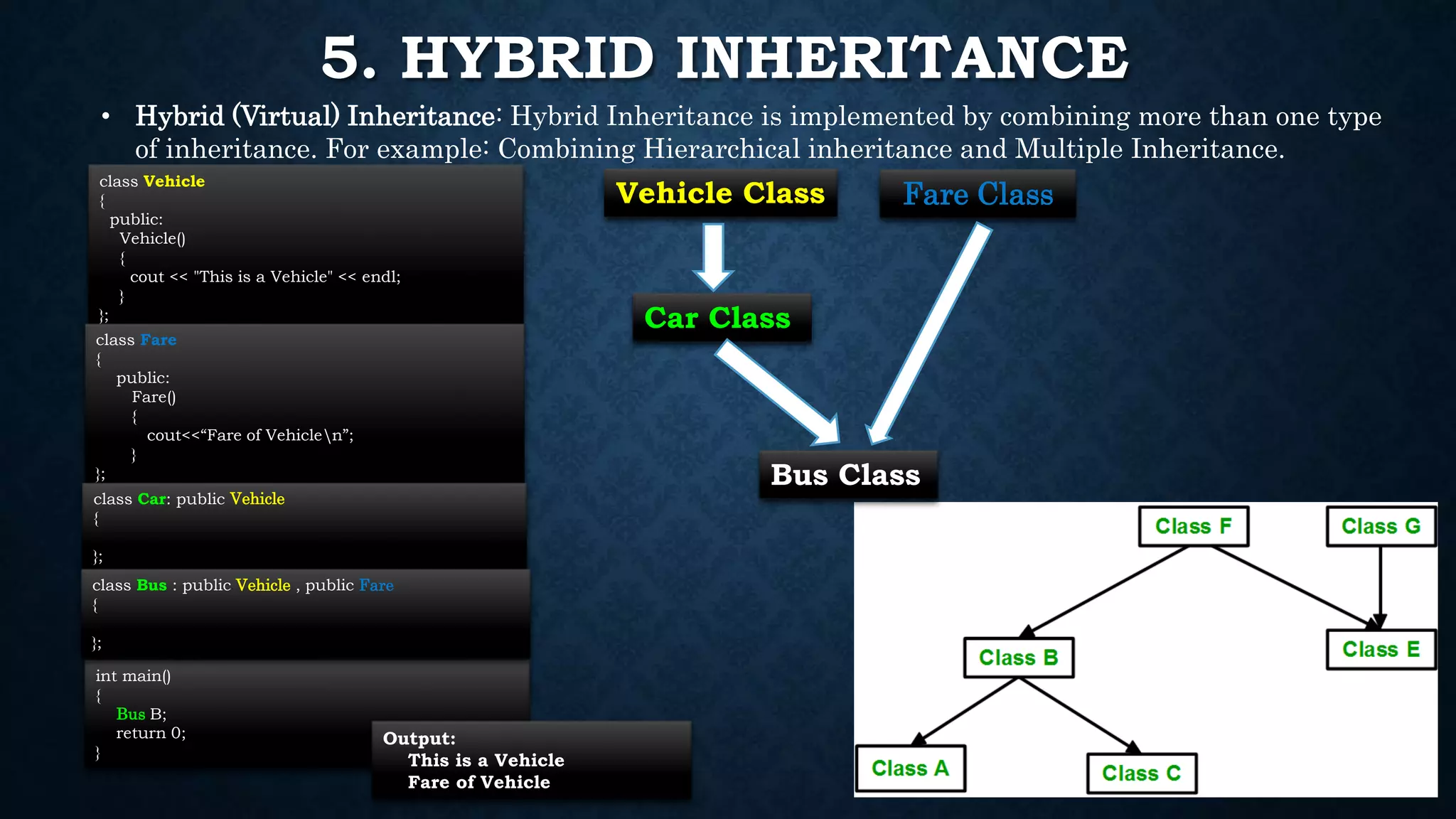
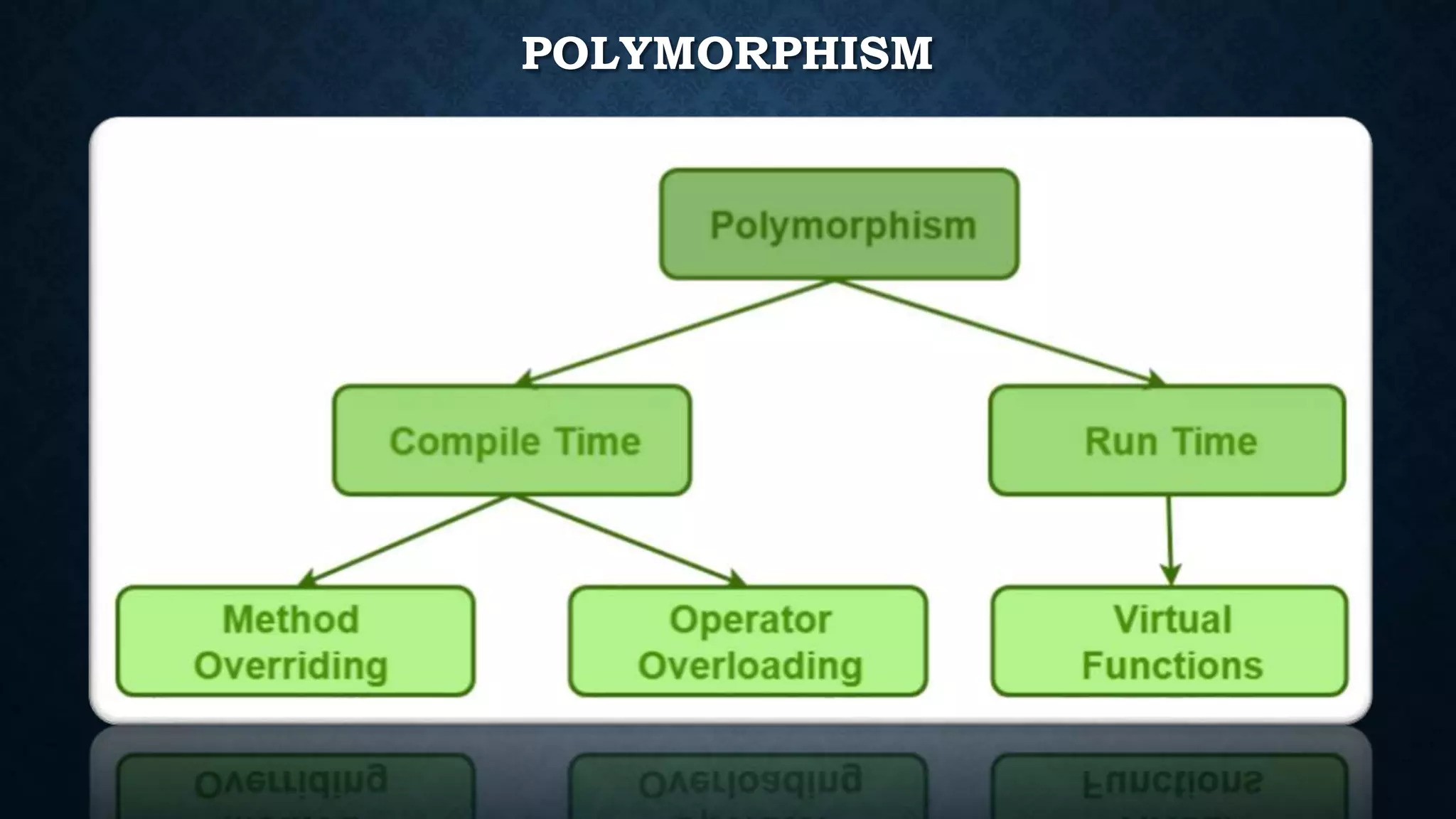
Inheritance allows classes to inherit properties and characteristics from other classes. This allows code reuse and avoids duplication. There are different types of inheritance in C++ including single, multiple, multilevel and hierarchical inheritance. Polymorphism means having many forms and allows functions or operators to work in different ways depending on the type of object. Compile time polymorphism is achieved through function overloading and operator overloading while runtime polymorphism is achieved through function overriding.