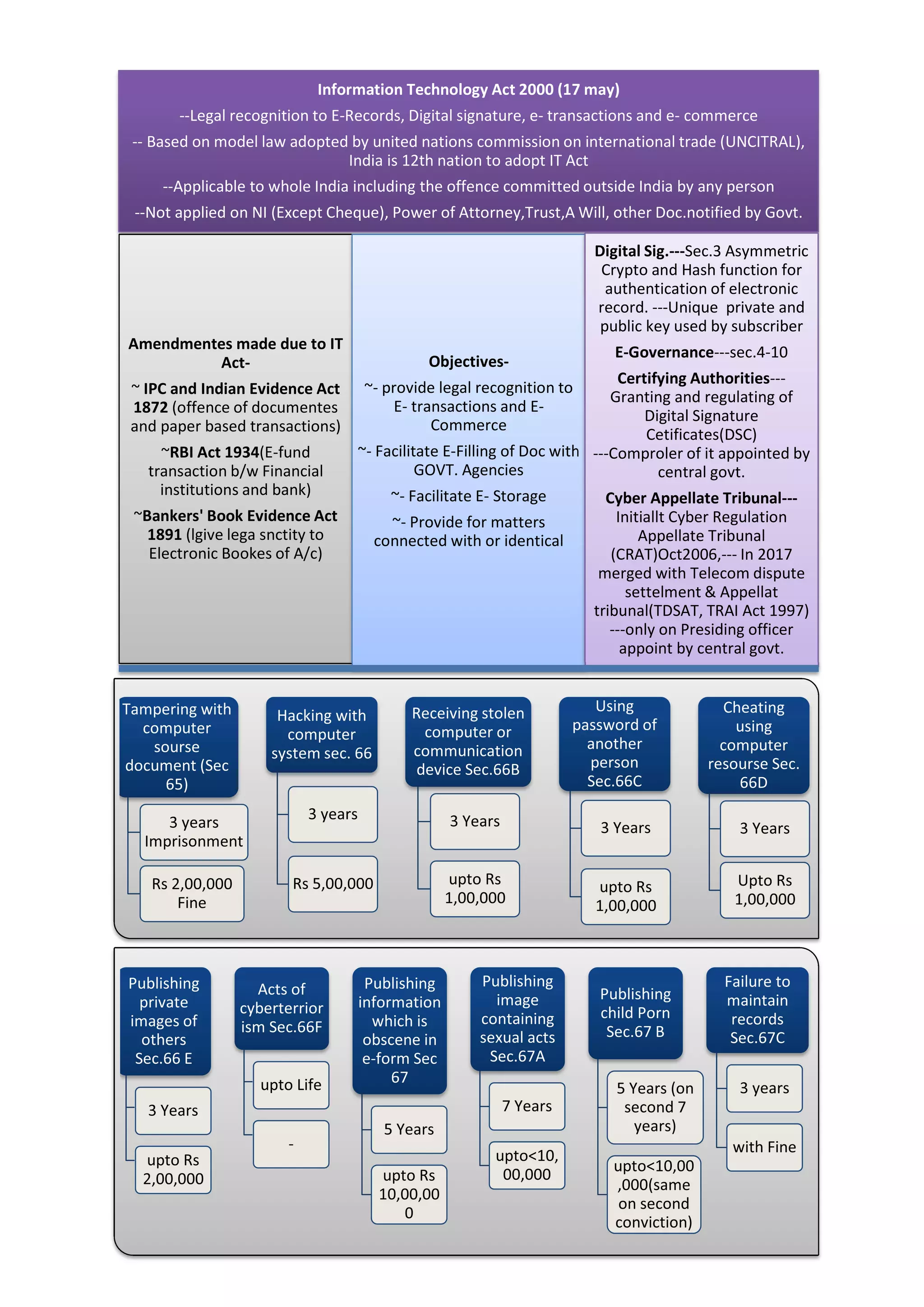
The Information Technology Act 2000 provided the legal framework for electronic records, digital signatures, e-transactions and e-commerce in India. It recognized electronic records and digital signatures as legally valid. India was the 12th country to adopt such a law based on a model adopted by the United Nations Commission on International Trade. The Act applies to the whole of India, including offenses committed outside India. It amended several other laws like the Indian Penal Code, Indian Evidence Act, and RBI Act regarding electronic transactions and records. The objectives of the Act were to provide legal recognition to e-transactions and e-commerce, facilitate e-filing with government agencies, and provide for matters relating to digital signatures and e-storage.