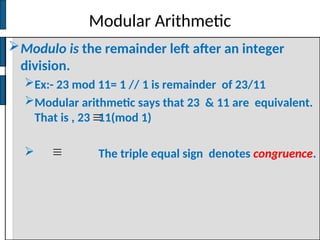
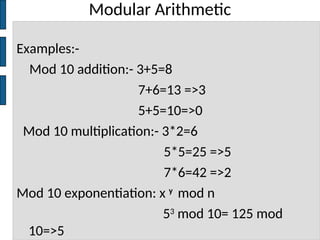
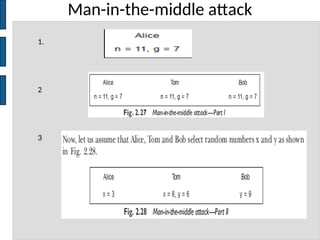
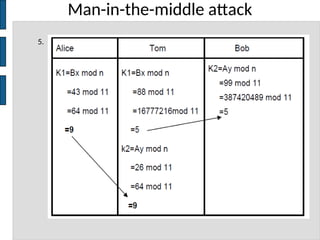
The document discusses key concepts in public key cryptography, including prime numbers, Euclid's algorithm, modular arithmetic, and the Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithm. It explains the basis of public key algorithms in modular arithmetic and details the processes of key generation and agreement, along with potential vulnerabilities like the man-in-the-middle attack. Additionally, it compares symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods and introduces digital signatures and envelopes.