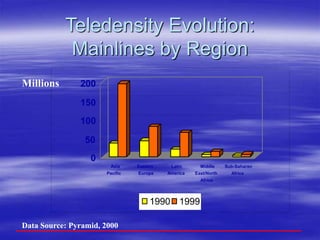
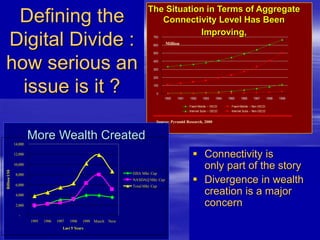
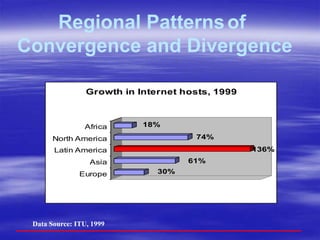
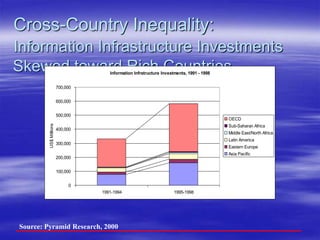
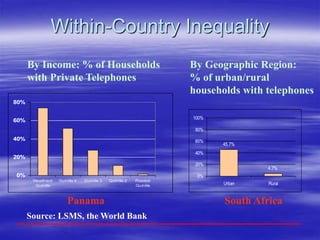
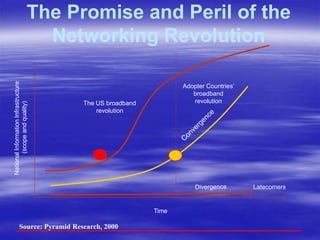
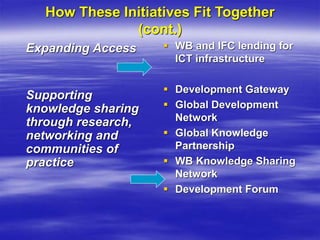
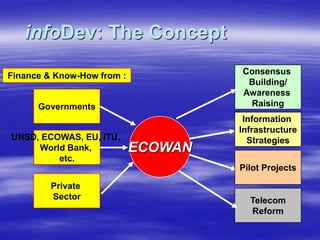
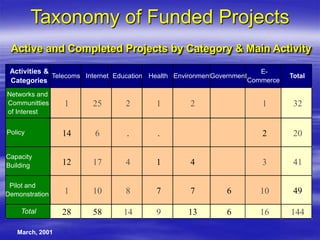
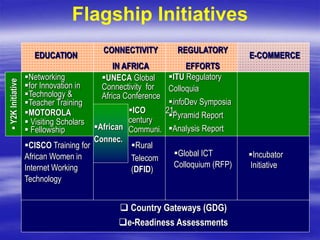
The document outlines ECOWAS's vision to leverage information and communication technologies (ICT) for knowledge development in developing countries, focusing on poverty reduction and economic growth. It emphasizes the risks of a growing digital divide due to disparities in access to knowledge and technology, while calling for strategies to enhance connectivity and support education and capacity building. Key initiatives include promoting competition, expanding access, and facilitating knowledge sharing through various global partnerships and programs.