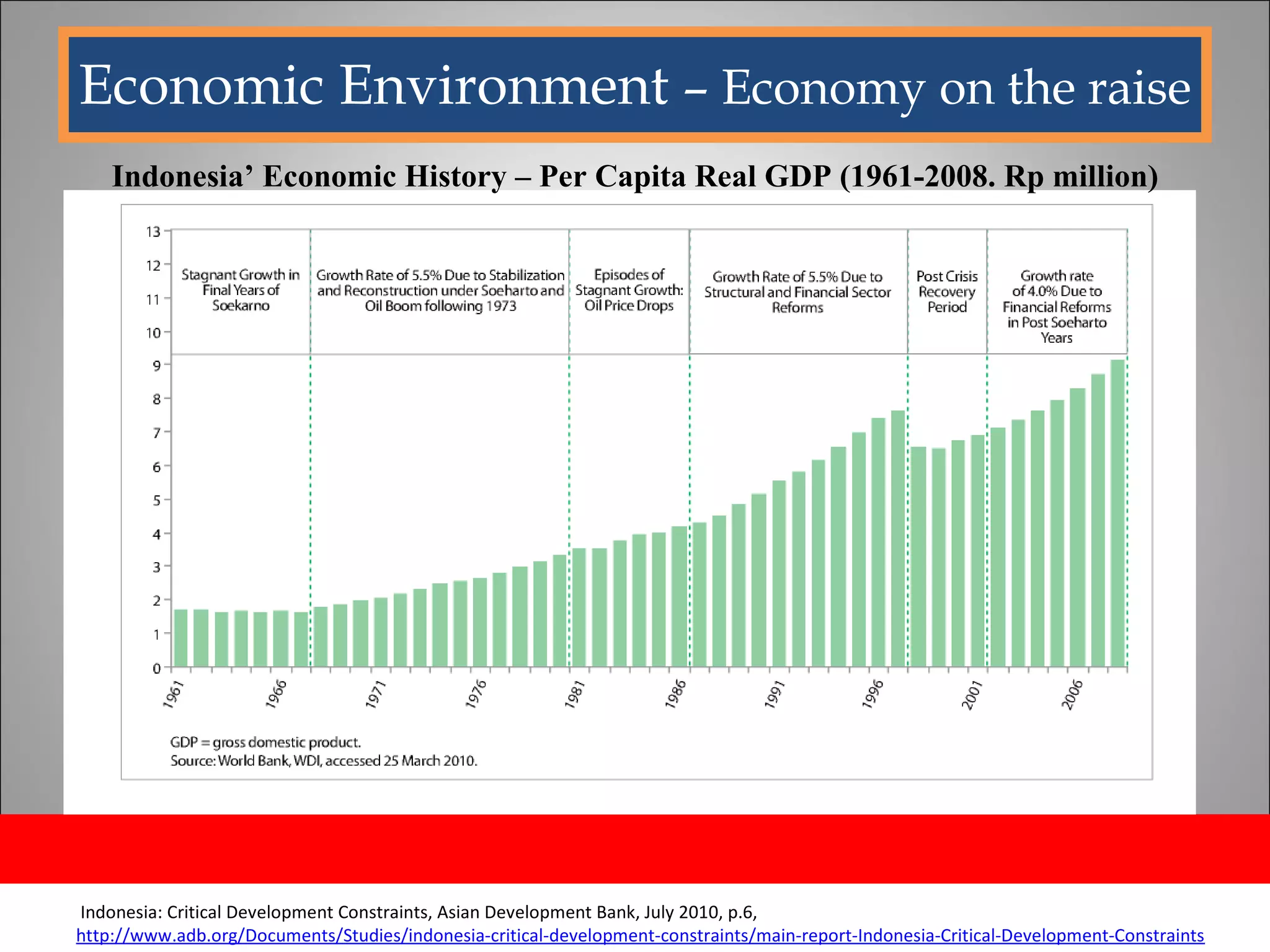
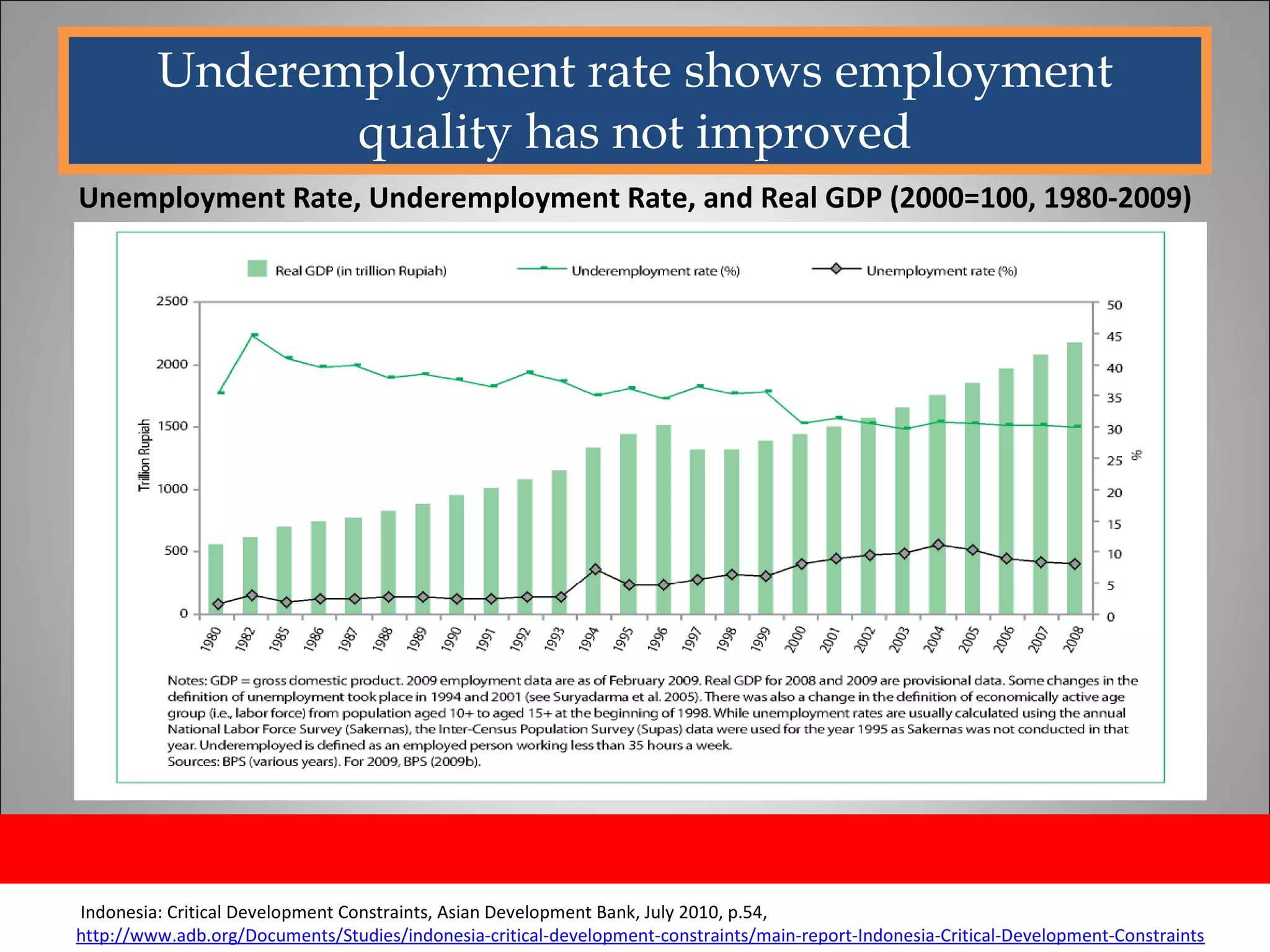
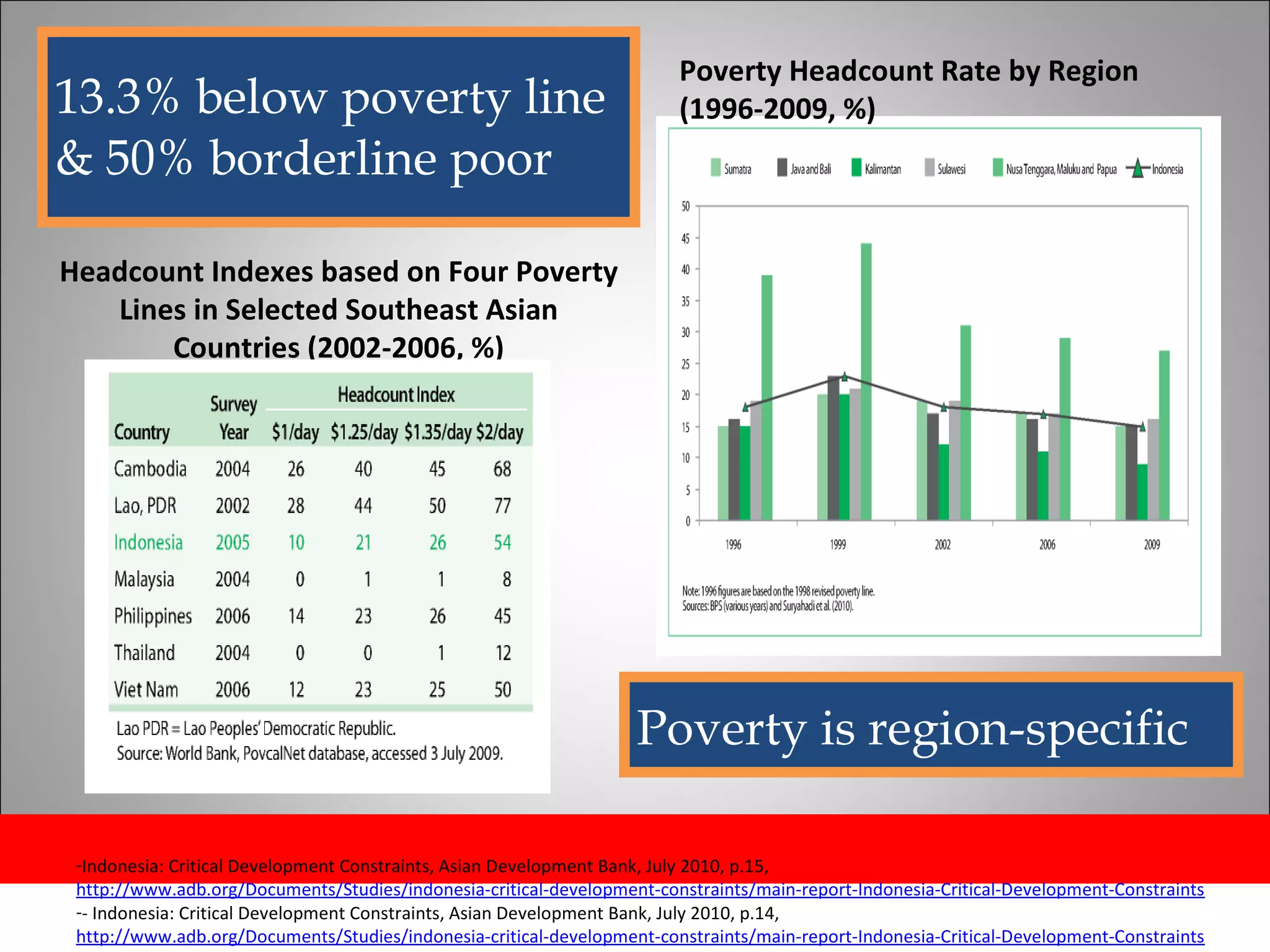
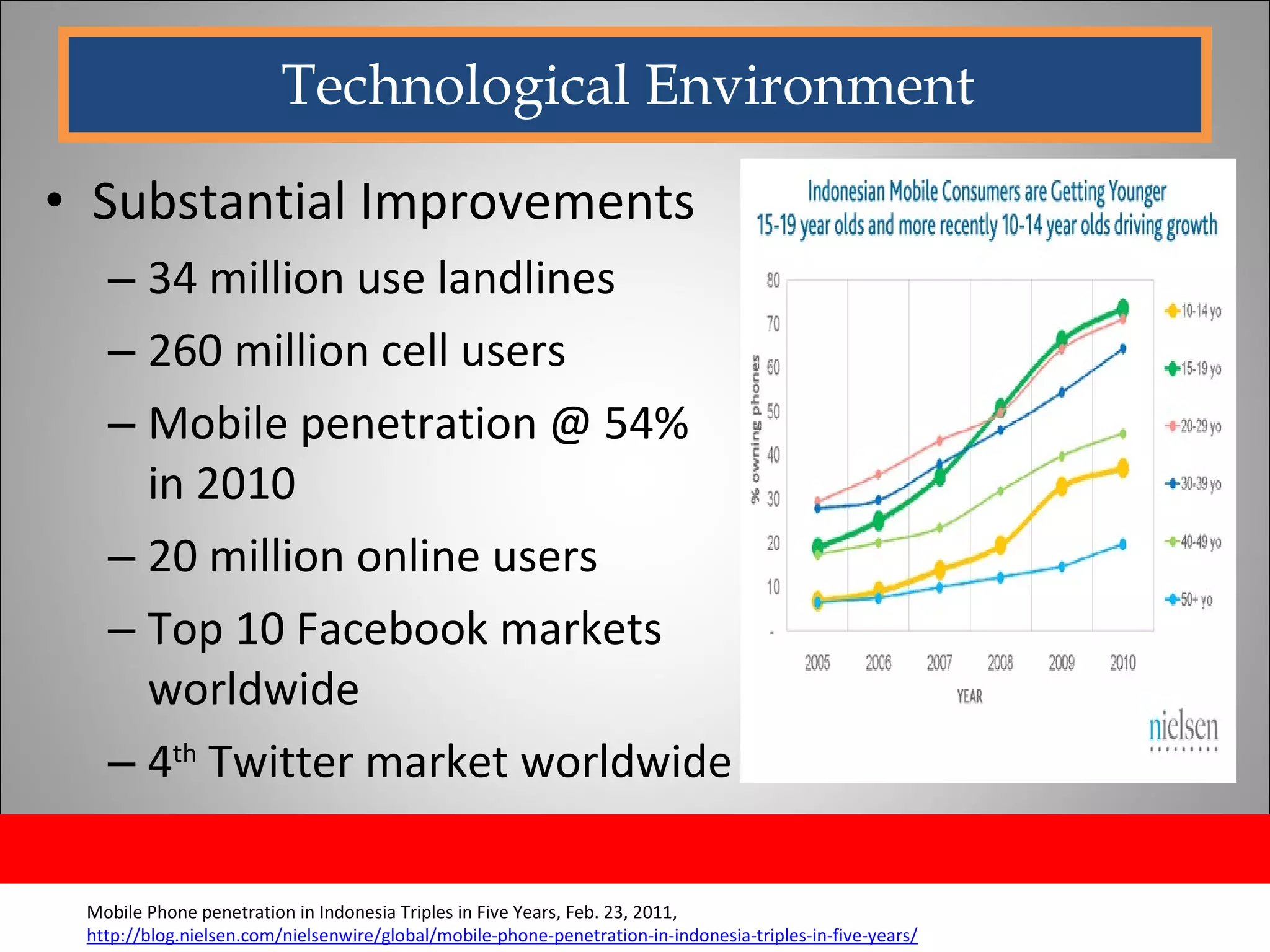
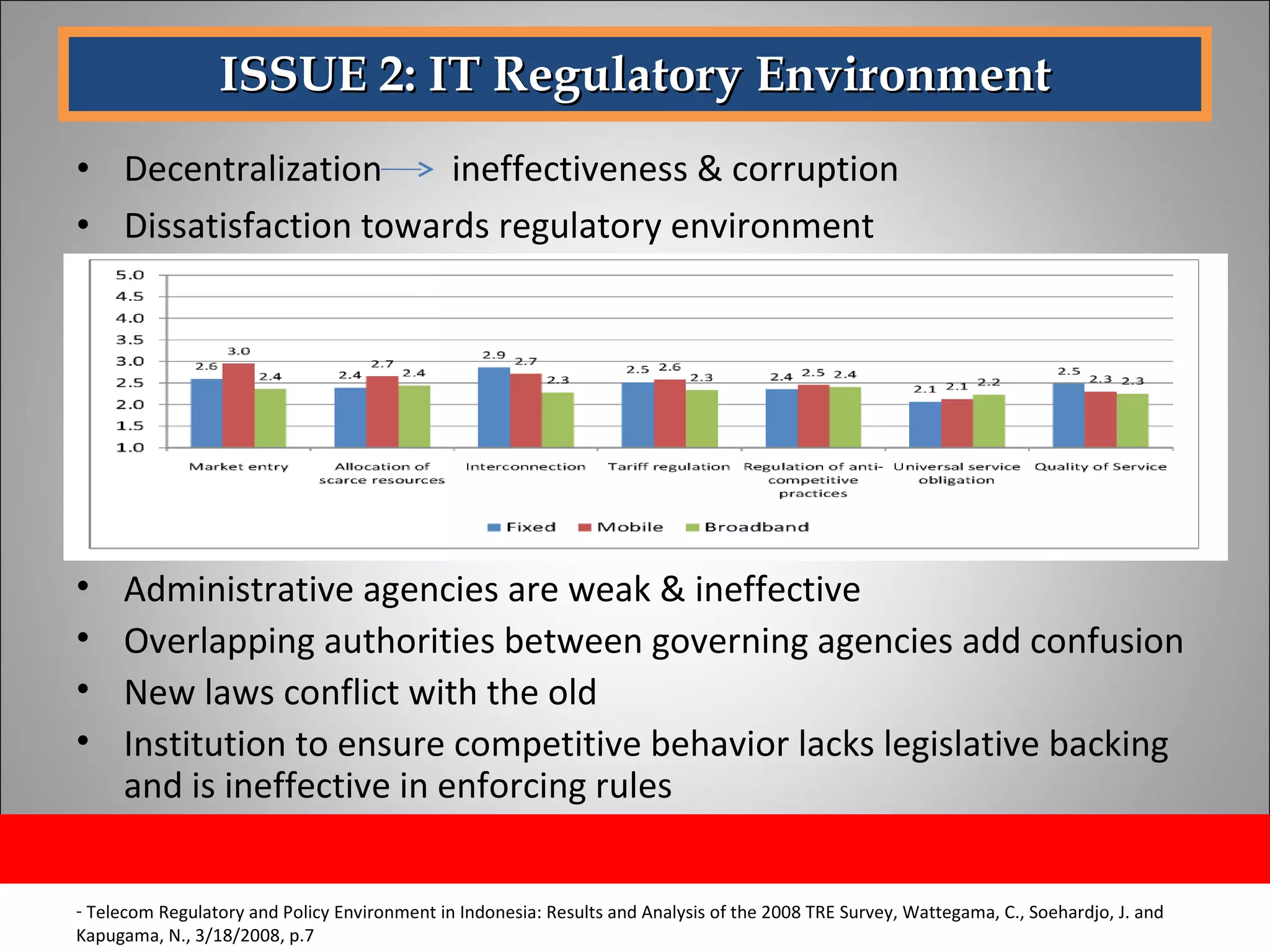
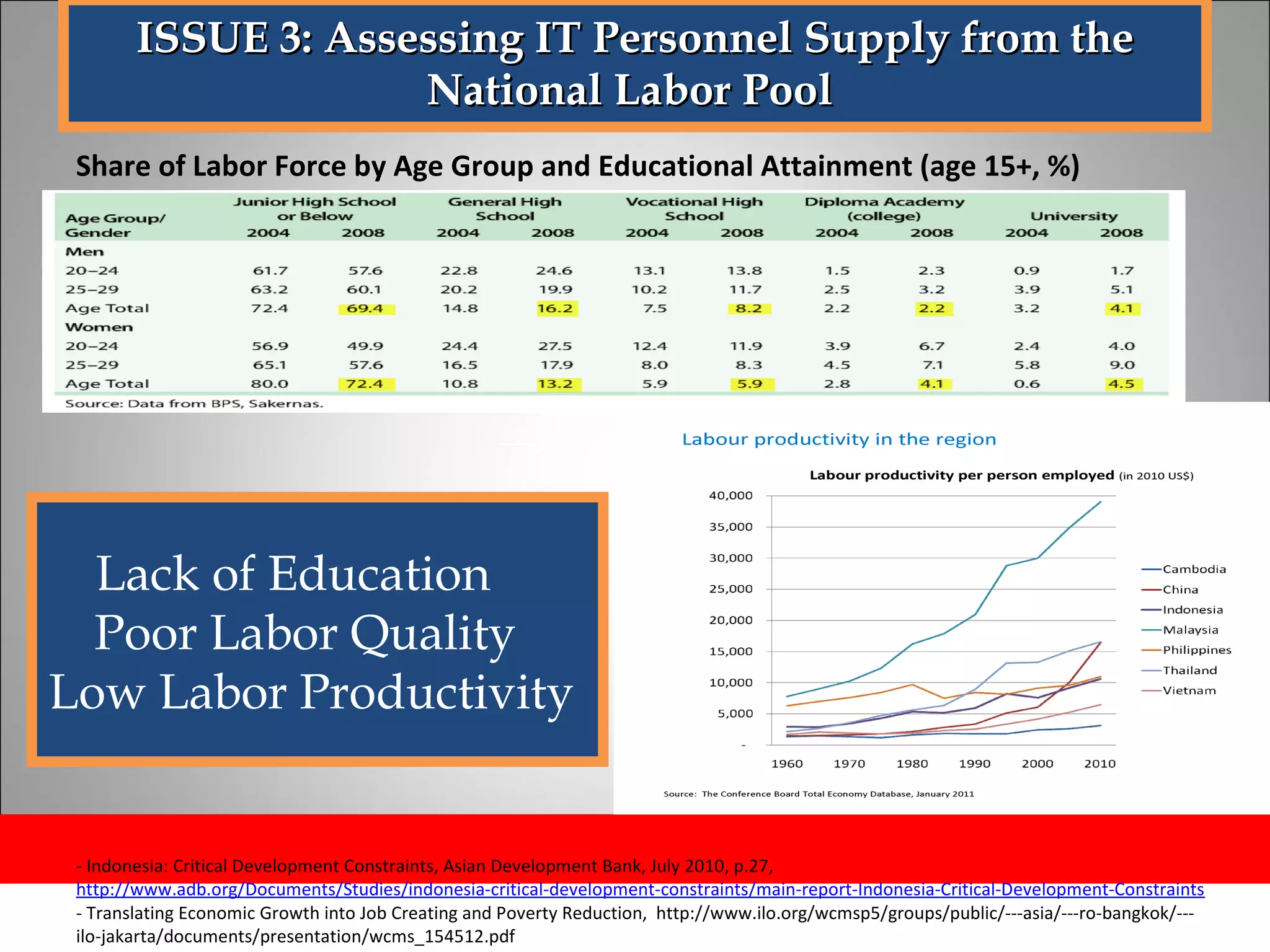
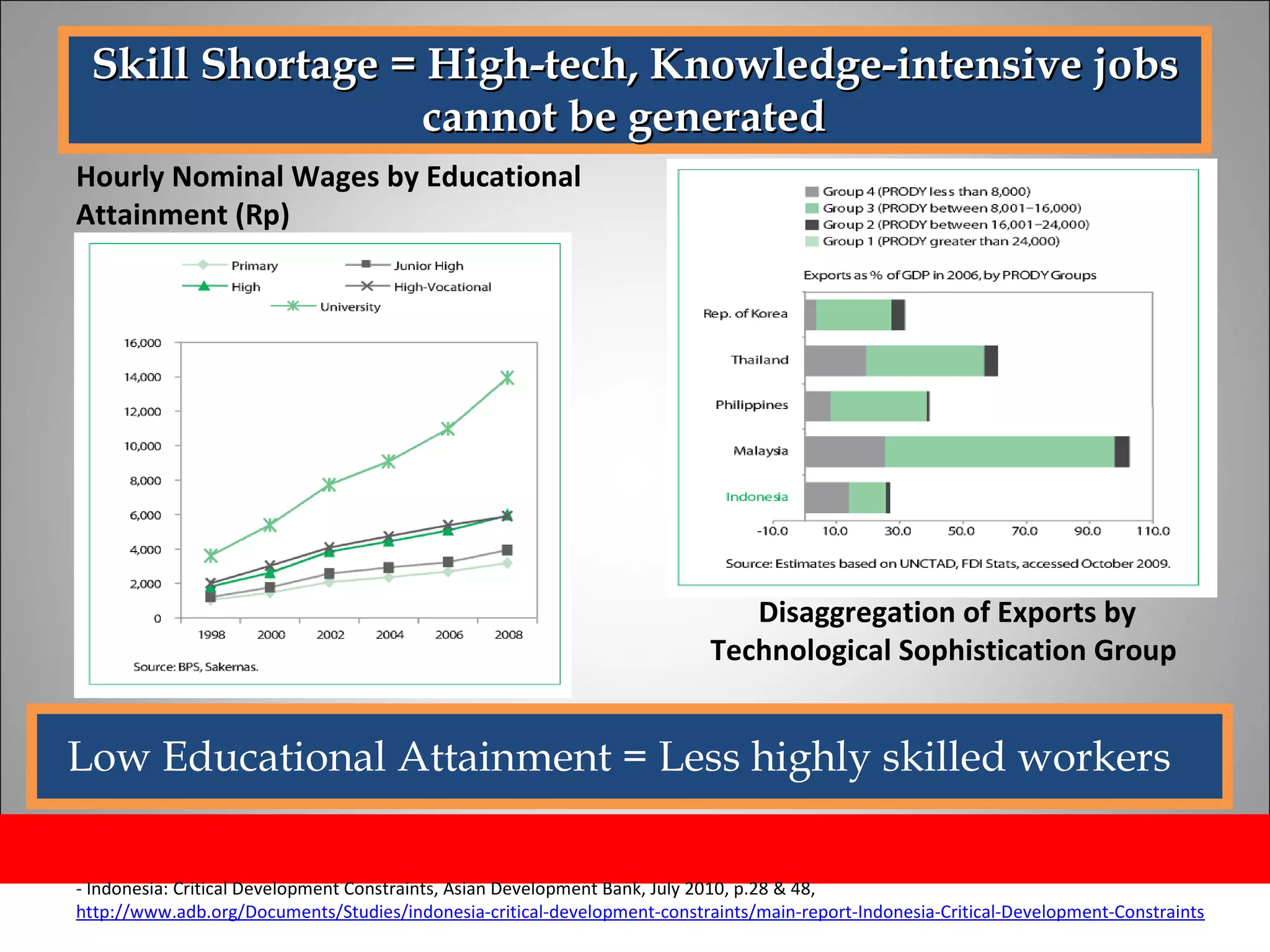
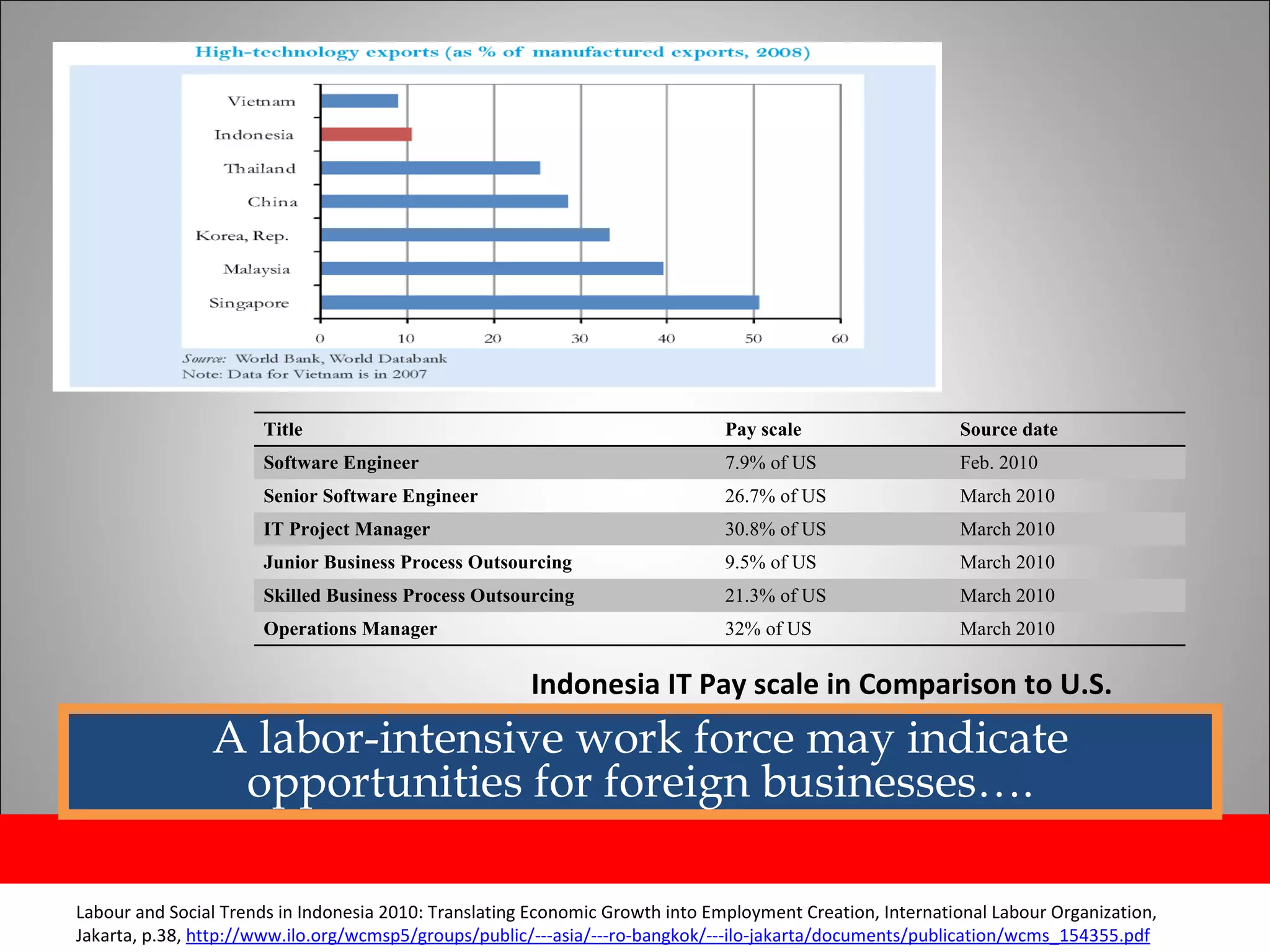
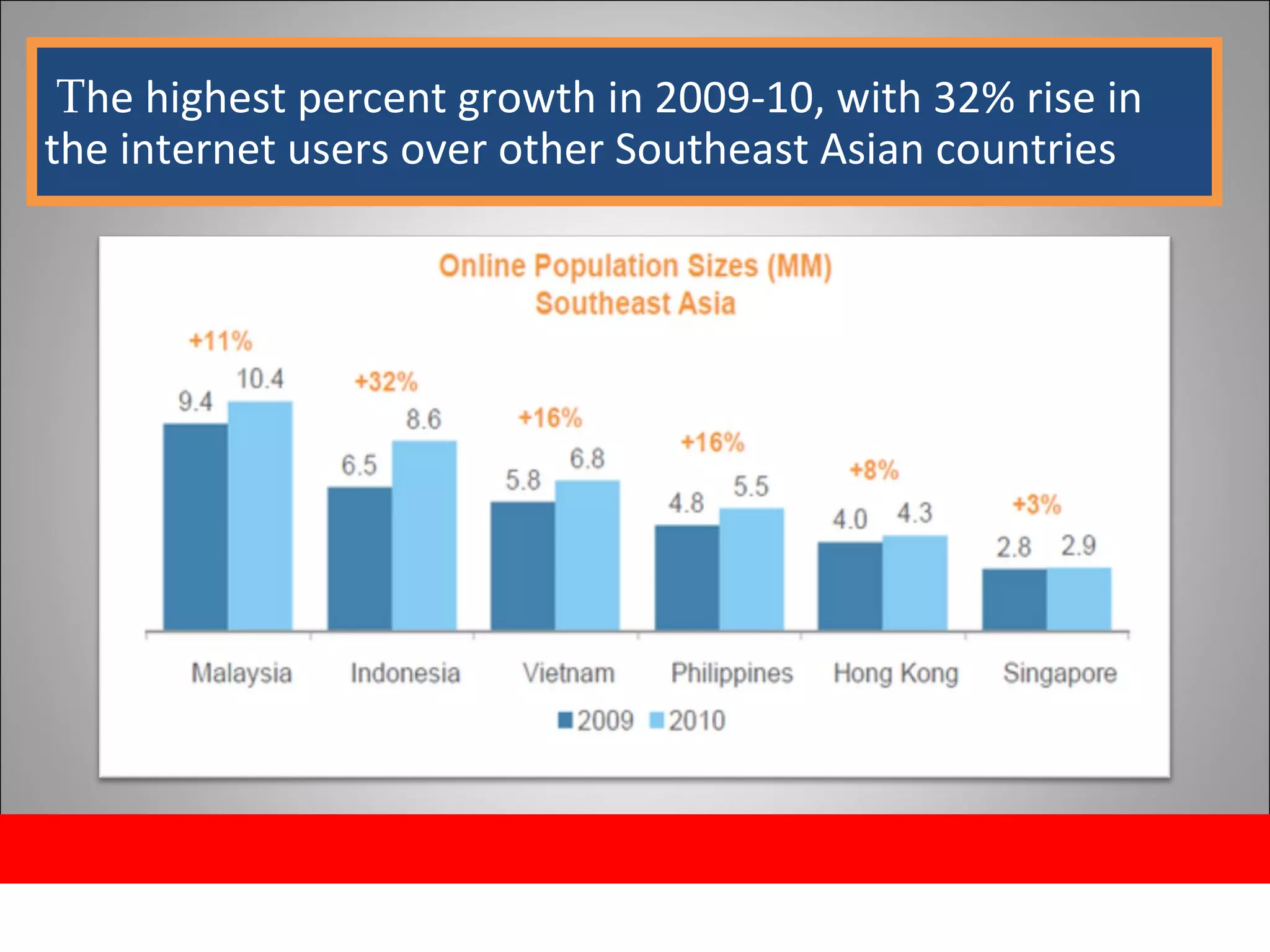
The document discusses opportunities and issues in Indonesia's IT sector. Key issues include poor telecommunication infrastructure quality, a weak regulatory environment, and lack of skilled IT personnel. Opportunities include growing internet usage, potential for IT outsourcing, and IT-enabled services. Recommendations to address issues and capitalize on opportunities are also discussed.