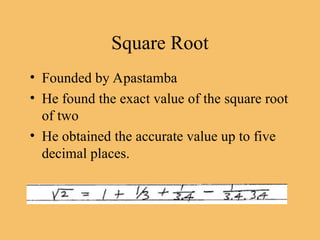
The document details the development of Indian mathematics from 1000 B.C. to 1000 A.D., highlighting key concepts such as the invention of zero, algebra, geometry, and the decimal system. It credits significant figures like Brahmagupta and Bhaskara for advancements in mathematical techniques and the accurate calculation of square roots. The document emphasizes the importance of Indian contributions to mathematics and discusses the historical timeline of these developments.