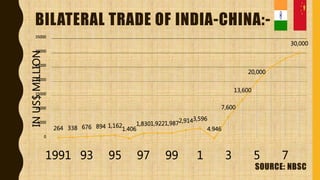
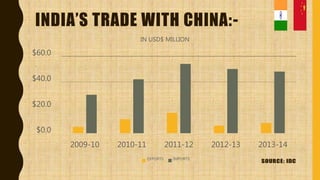
India and China have a 61-year economic relationship and are each other's largest trading partners. While China leads in manufacturing exports, India's economy relies more on services. Bilateral trade reached $71 billion in 2016, with China exporting electronics and machinery to India, and India exporting cotton and precious metals. However, India faces a large trade deficit due to higher imports from China and limited exports, which some argue is worsened by Chinese dumping of low-cost goods into India. Both countries aim to strengthen economic ties but India works to protect its domestic industries from unfair trade practices.