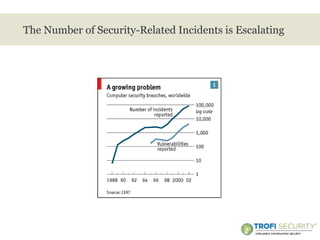
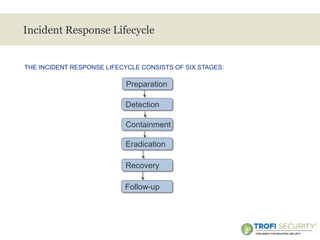
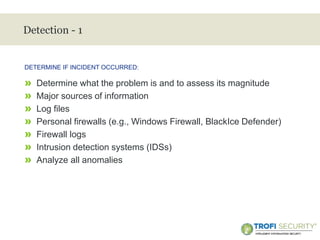
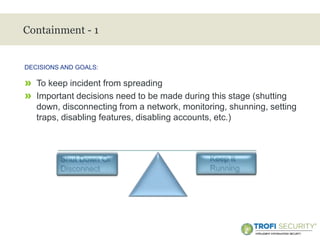
This document provides an overview of incident response handling and methodology. It discusses defining incidents, the goals of incident handling, and the incident response lifecycle which consists of preparation, detection, containment, eradication, recovery, and follow-up stages. It emphasizes the importance of having proper policies, procedures, training, and resources in place to effectively handle security incidents.