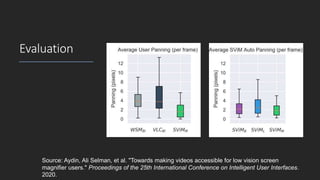
Vikas Ashok from Old Dominion University presented on using visual saliency models to improve web accessibility for people with visual impairments. He described two projects: SVIM, a saliency-driven video magnifier that tracks regions of interest in videos to aid low vision users, and SAIL, which automatically injects ARIA landmarks into webpages to streamline navigation for blind screen reader users. Both projects use deep learning models to detect salient regions and objects. SVIM clusters salient pixels to adjust the video viewport for magnification, while SAIL identifies salient areas to tag with landmarks. Evaluations found SVIM enhanced the video experience and SAIL reduced task completion times for screen reader users compared to manually landmarked pages.




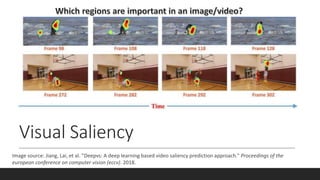



![Saliency Detection
DeepVS [1]
Trained on a video saliency dataset (LEDOV)
Object-to-motion CNN for incorporating objects and motion
ConvLSTM layers for incorporating temporal information
Image source: [1] Jiang, Lai, et al. "Deepvs: A deep learning based video saliency prediction
approach." Proceedings of the european conference on computer vision (eccv). 2018.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationmitre-200414185822/85/Improving-Web-Accessibility-Using-Visual-Saliency-9-320.jpg)







![Webpage
Saliency with
GANs
SalGAN [1] originally trained
for image saliency, re-trained
to predict web saliency
[1] Pan, Junting, et al. "Salgan: Visual saliency prediction with adversarial networks." CVPR
Scene Understanding Workshop (SUNw). 2017.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationmitre-200414185822/85/Improving-Web-Accessibility-Using-Visual-Saliency-19-320.jpg)





