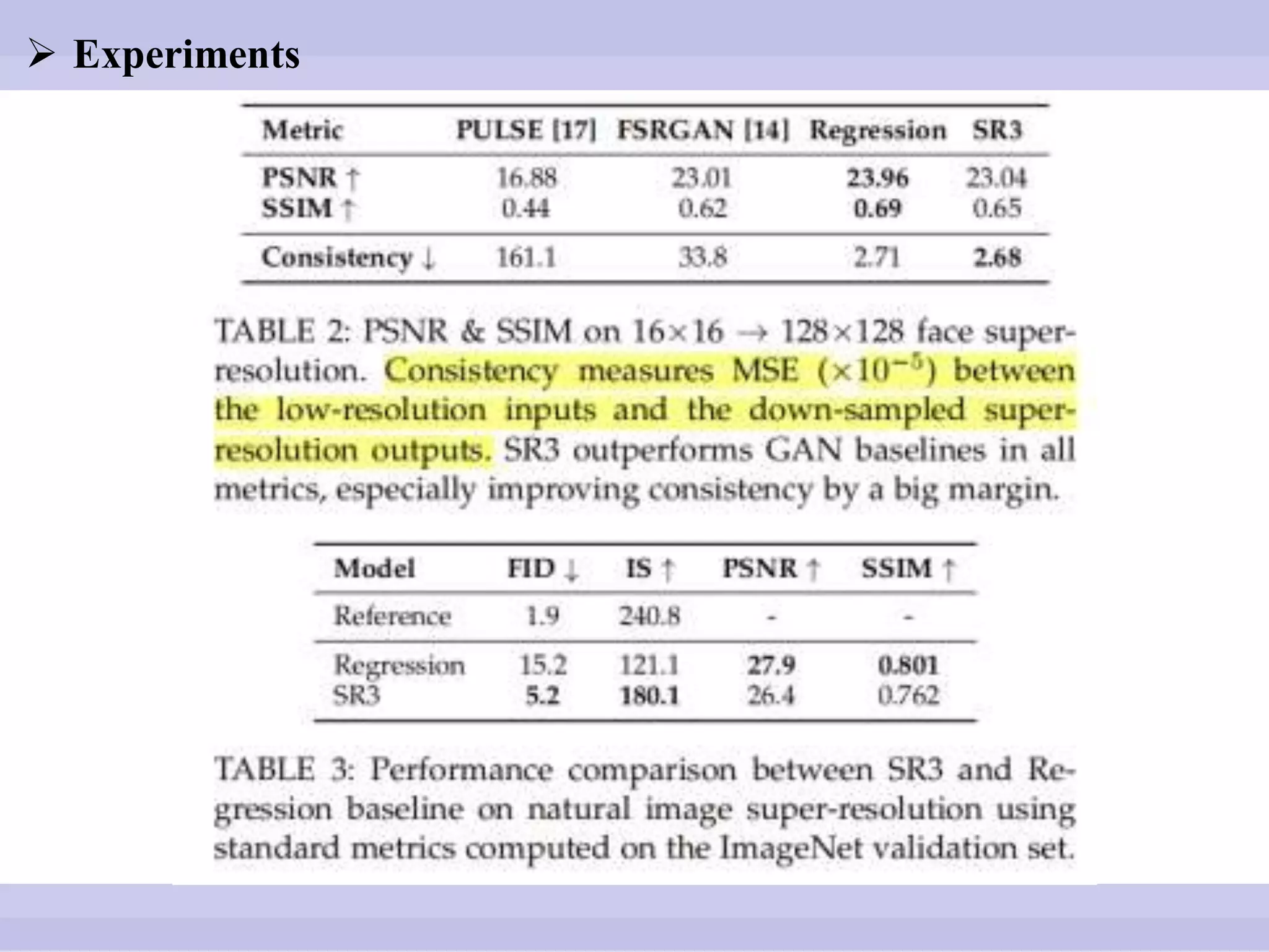
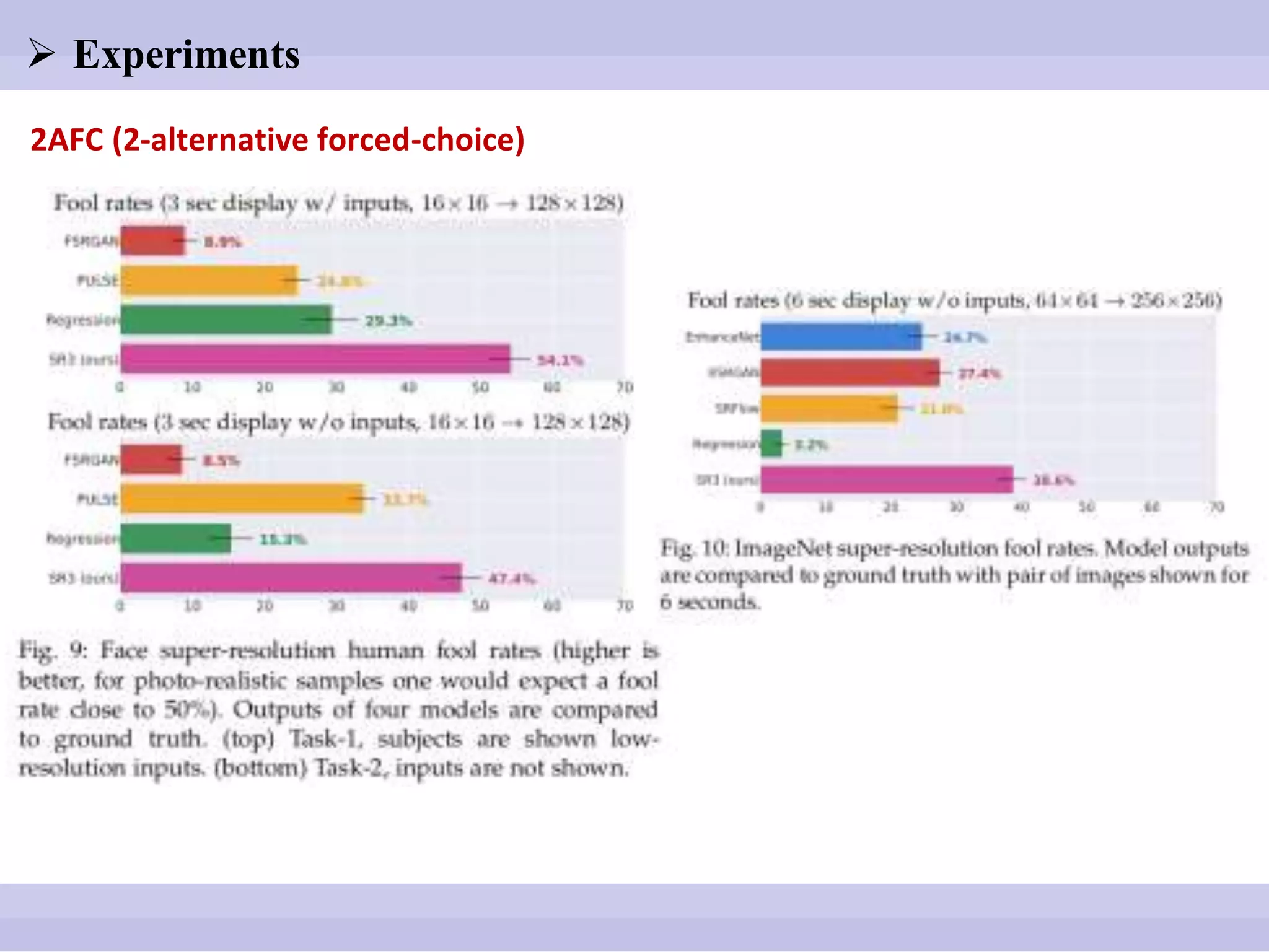
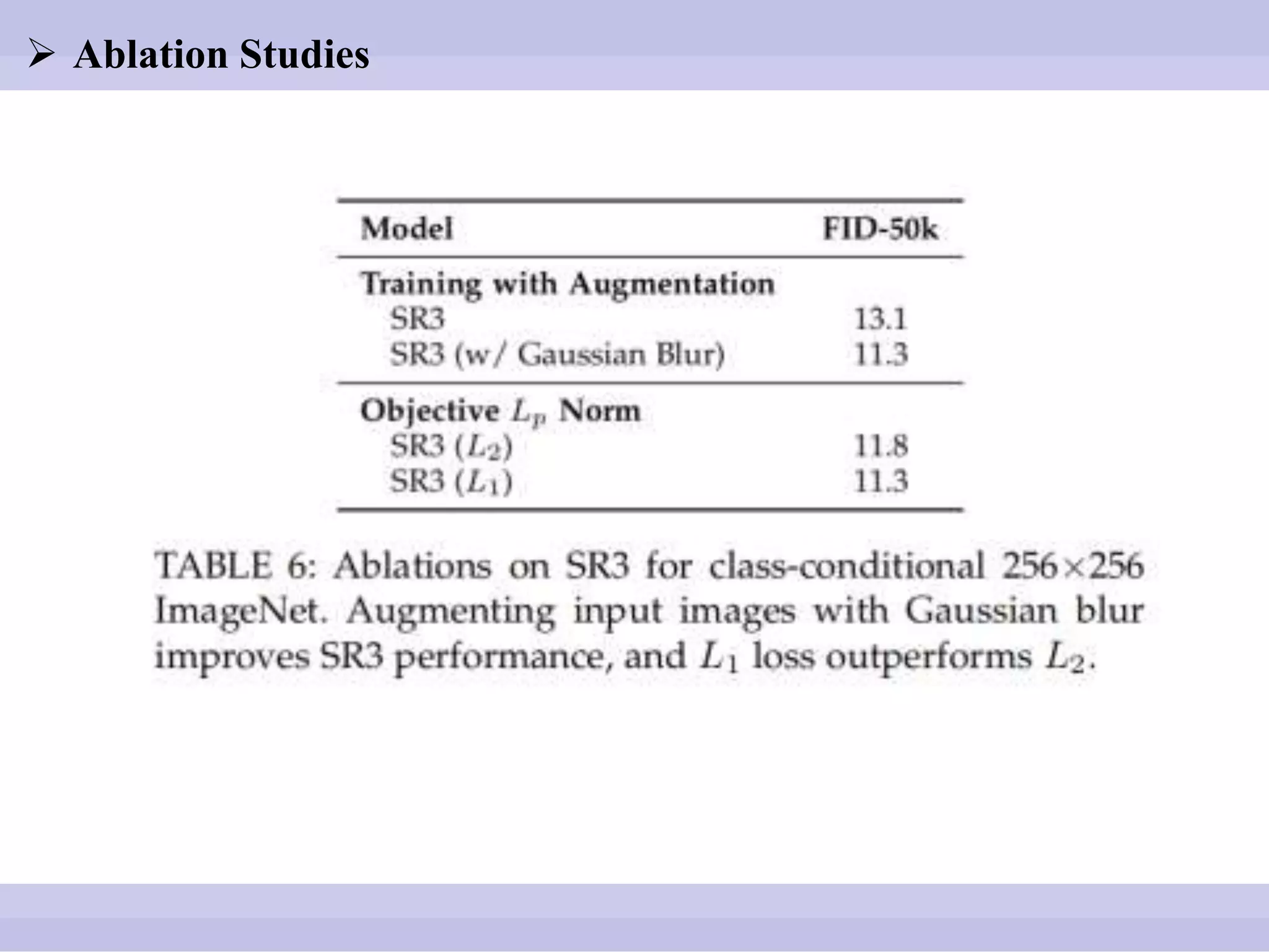
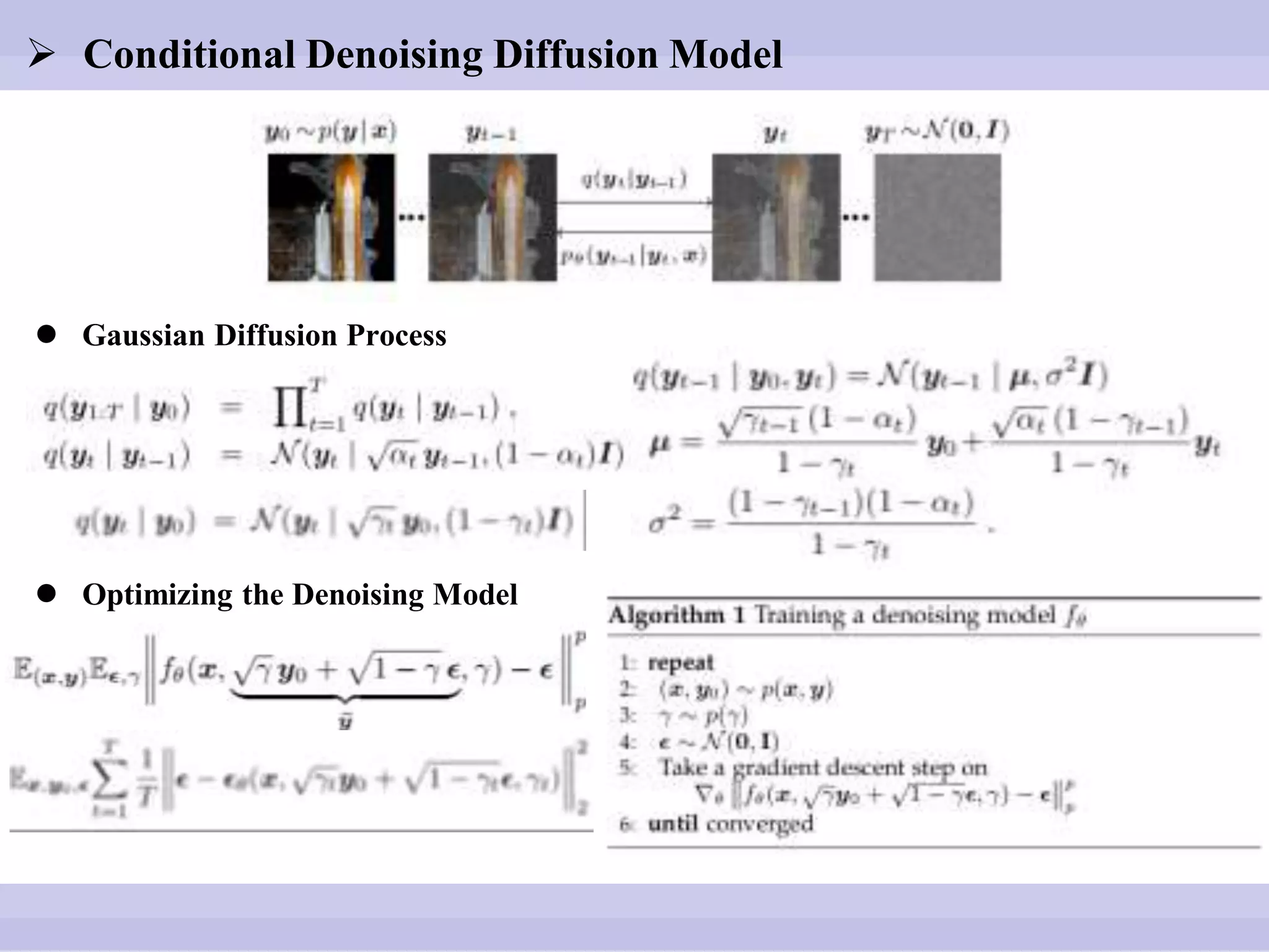
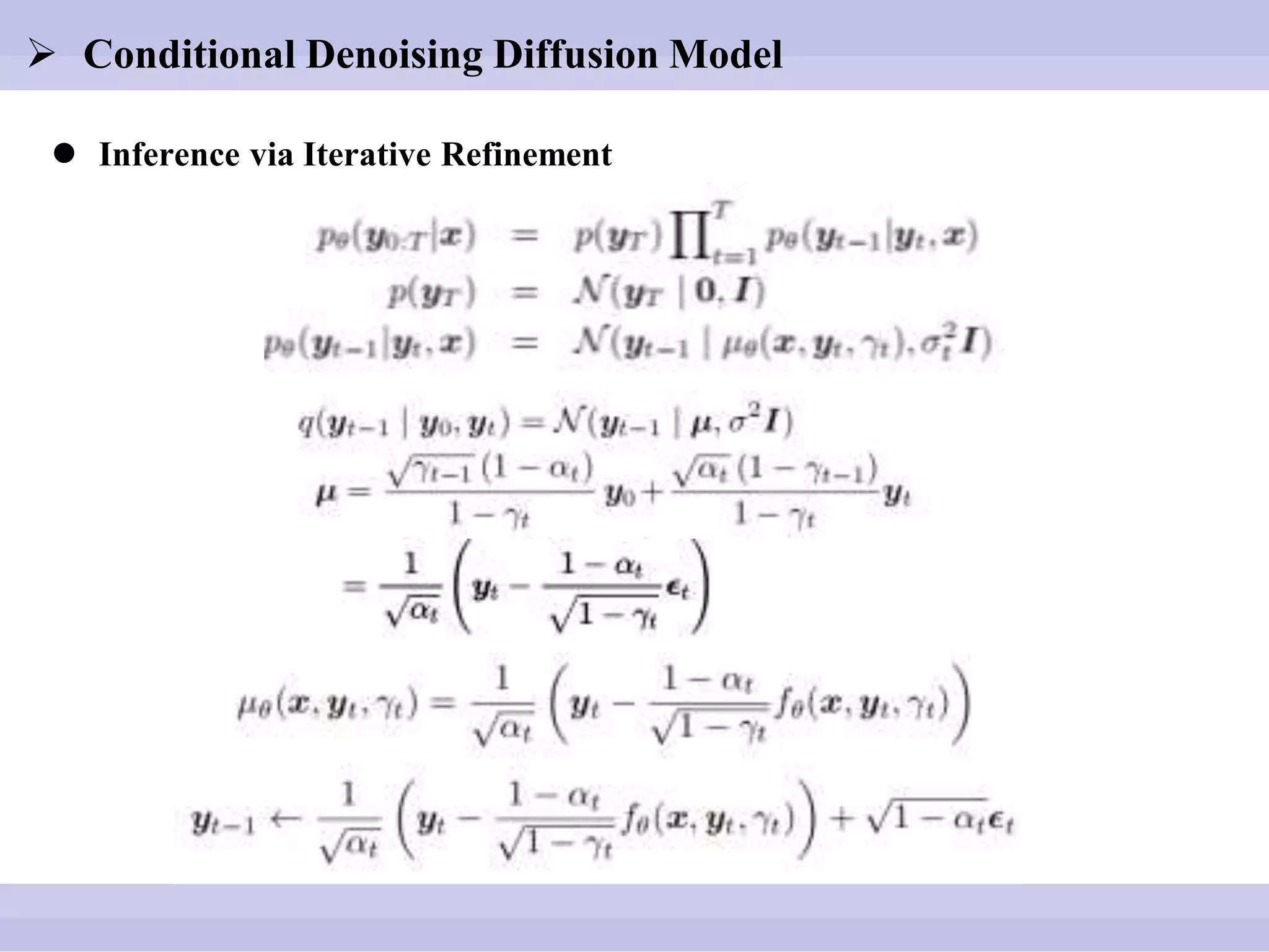
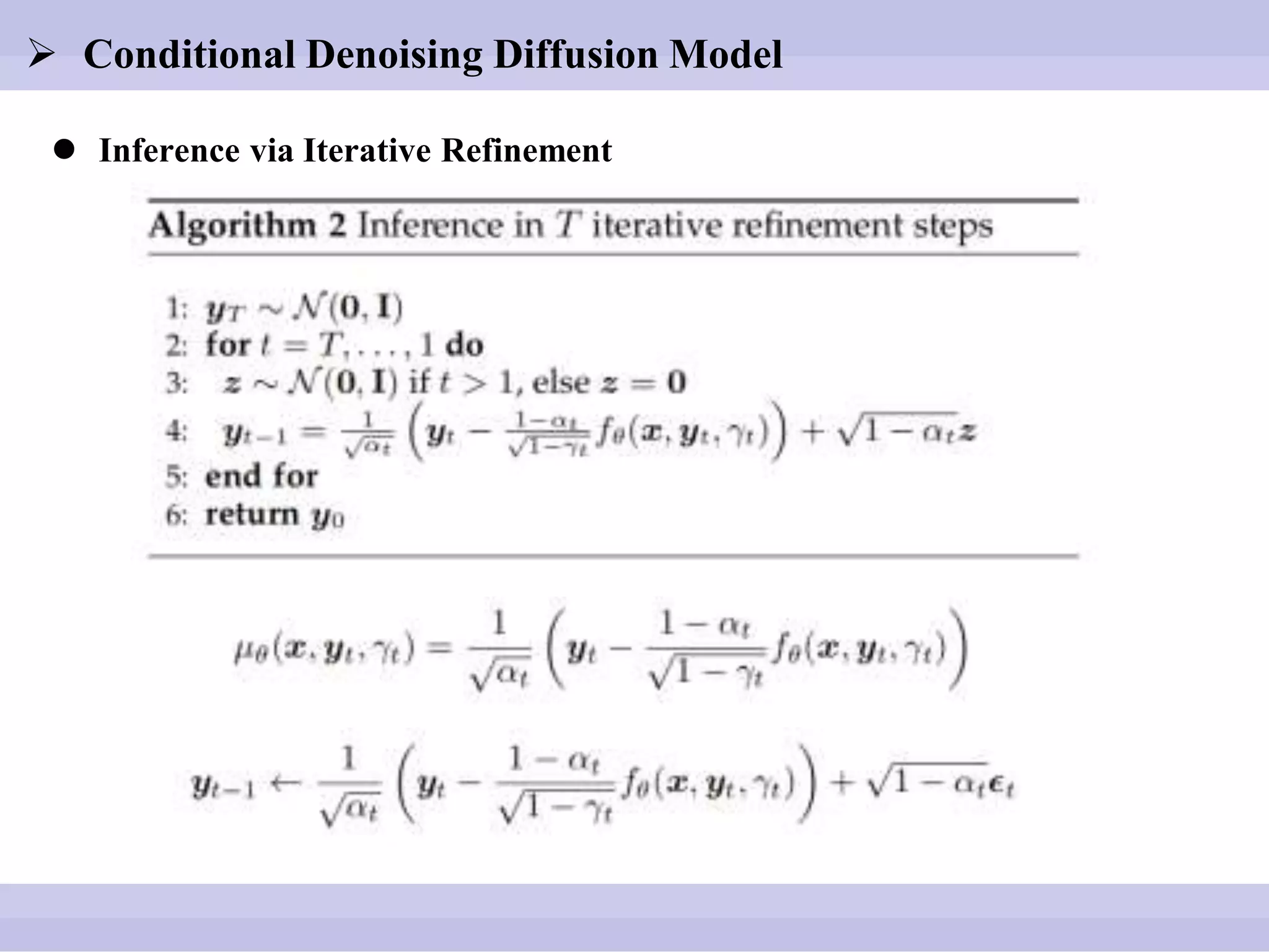
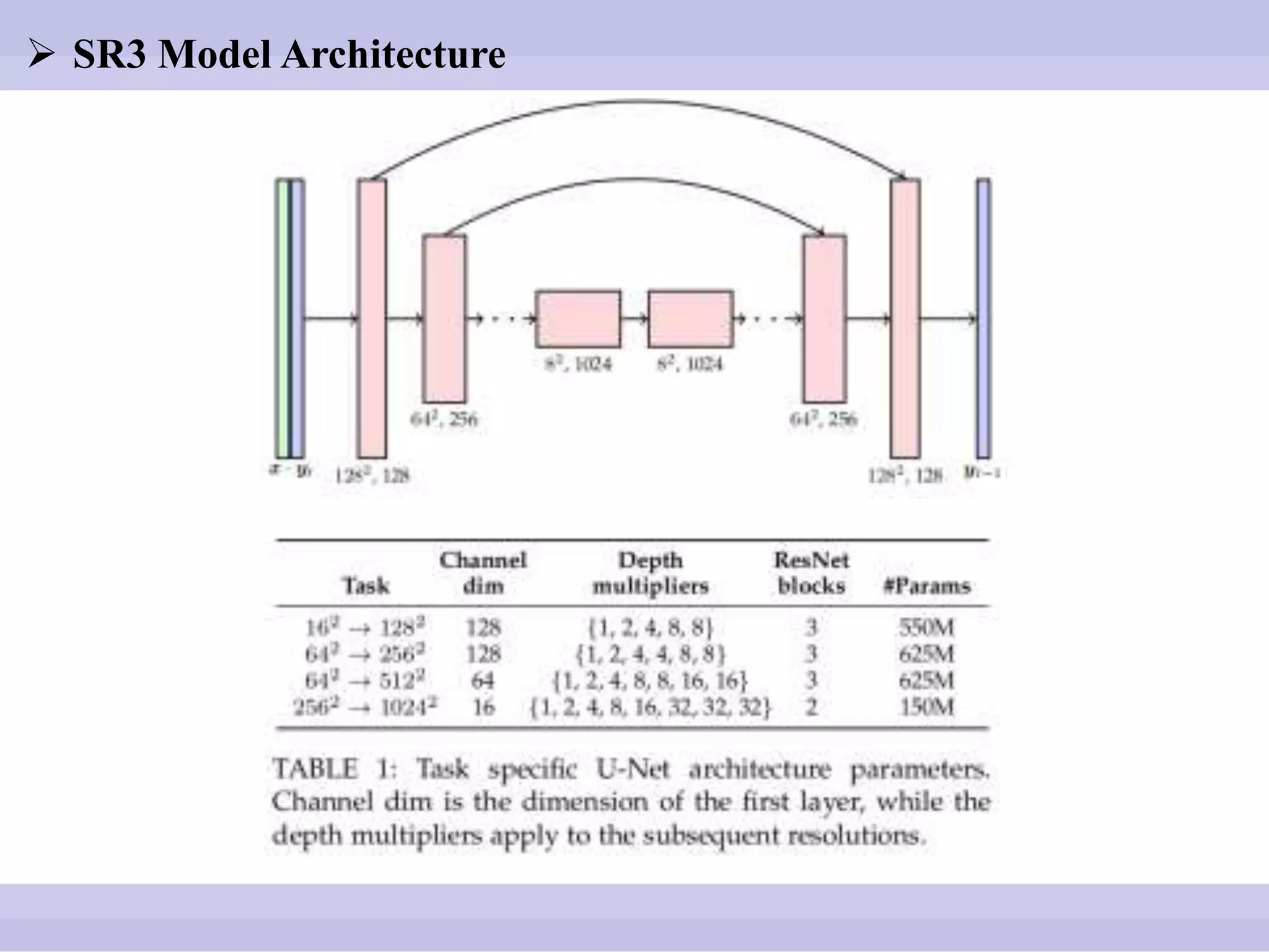
The document discusses diffusion models, outlining both the forward and reverse diffusion processes that involve noise addition and removal respectively. It highlights advancements in denoising diffusion probabilistic models and their improved performance through optimized noise schedules and architectures. The content also includes experimental results showcasing the capabilities of super-resolution models and various studies conducted.

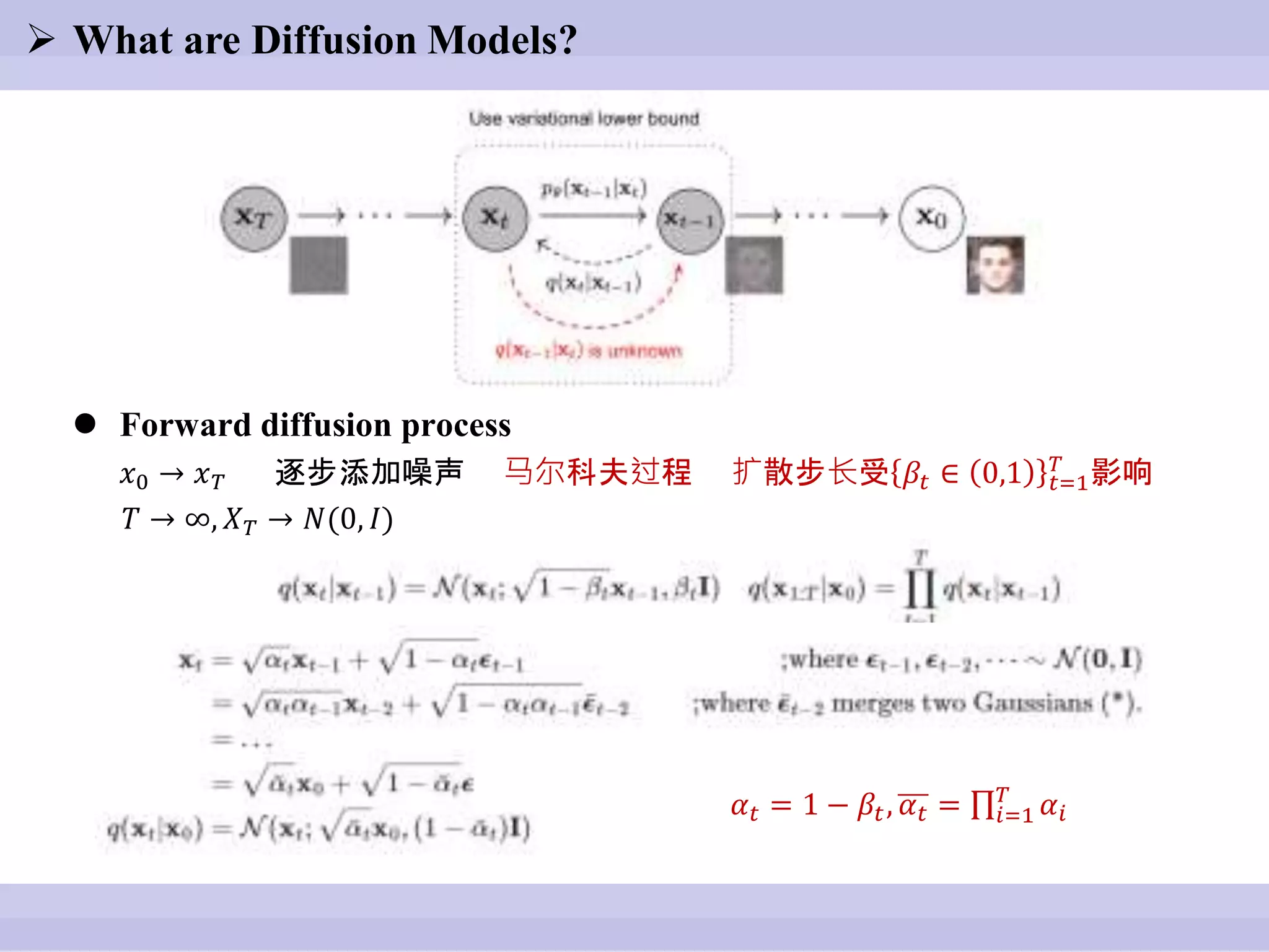
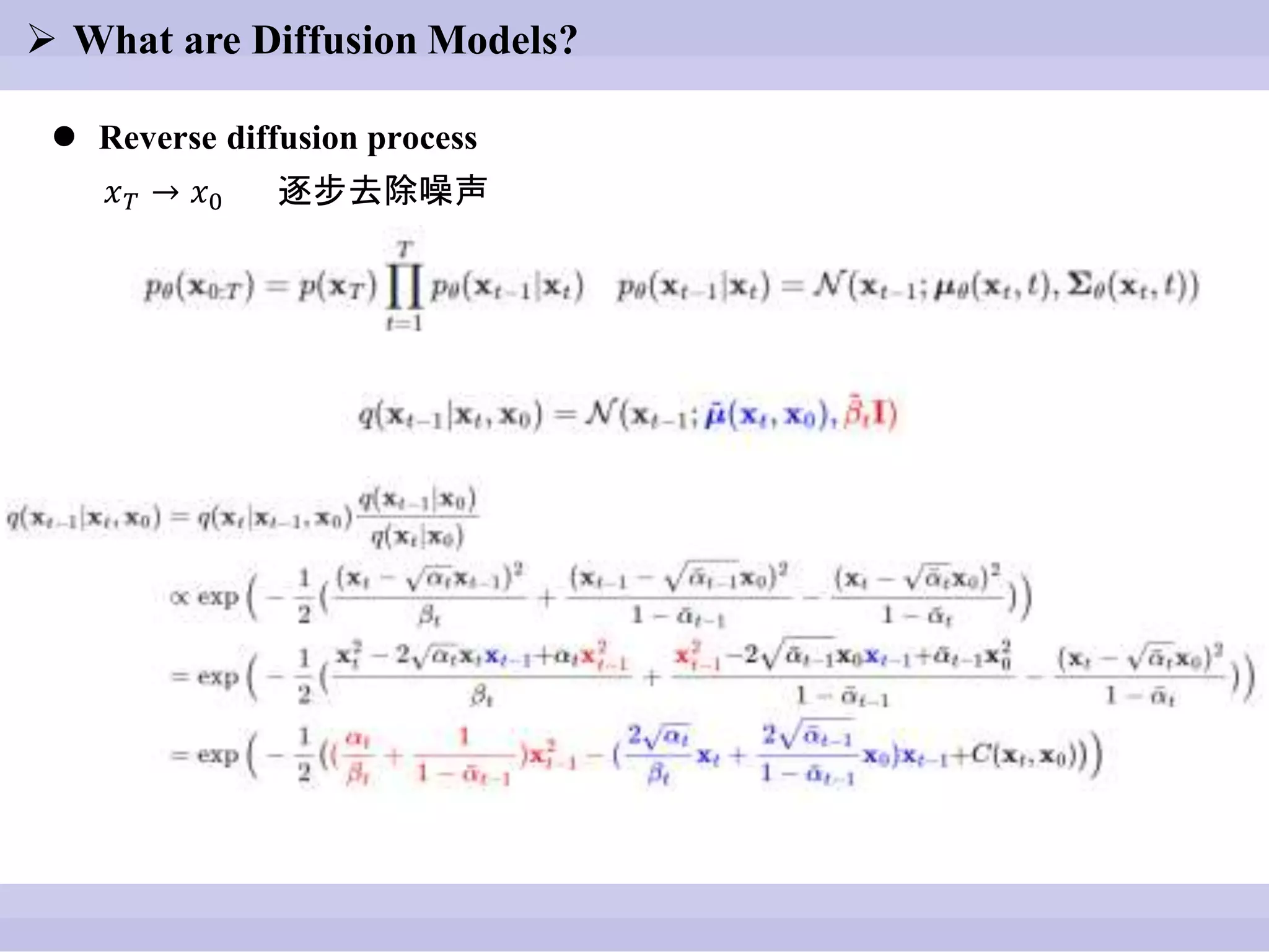
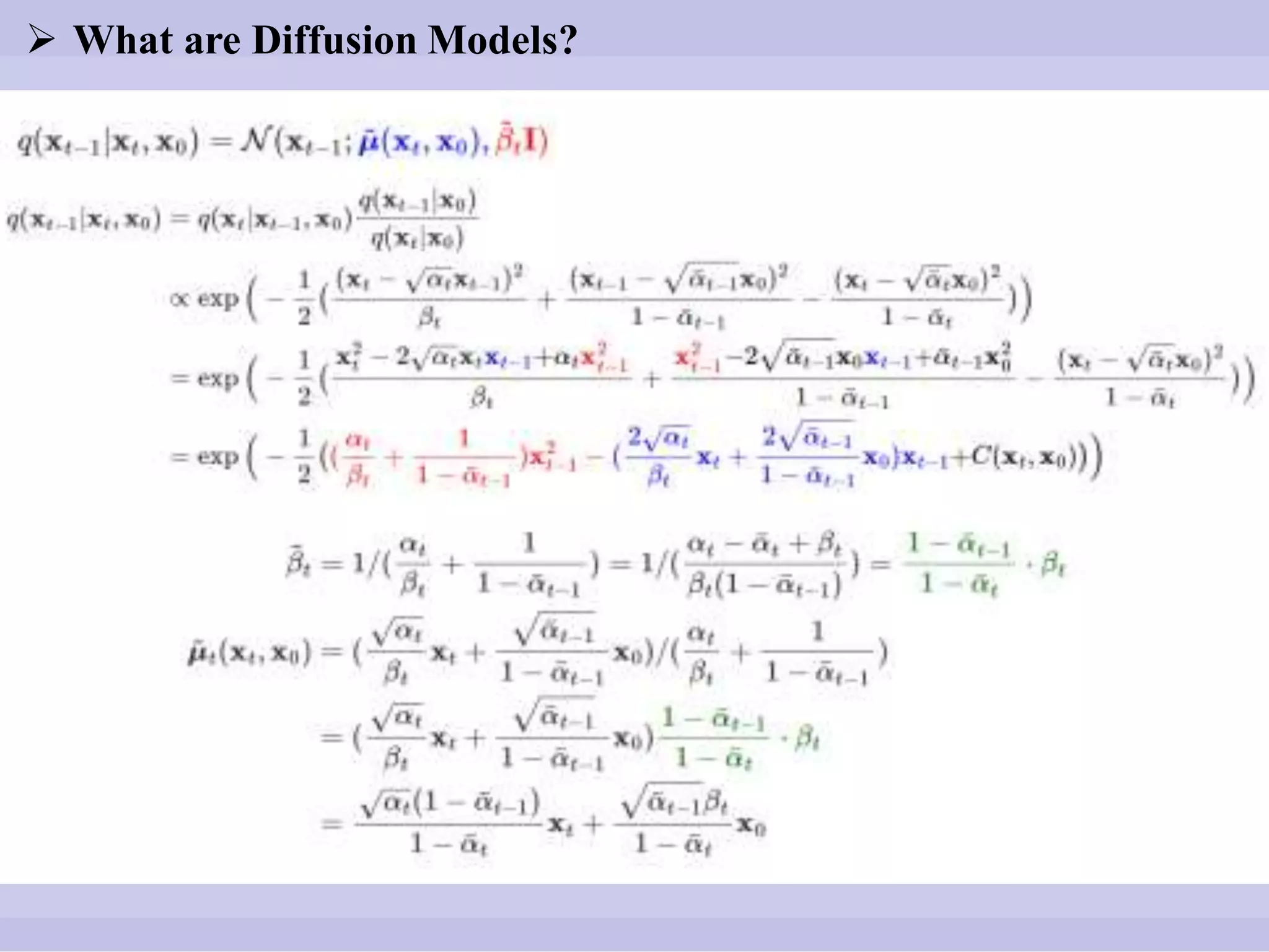
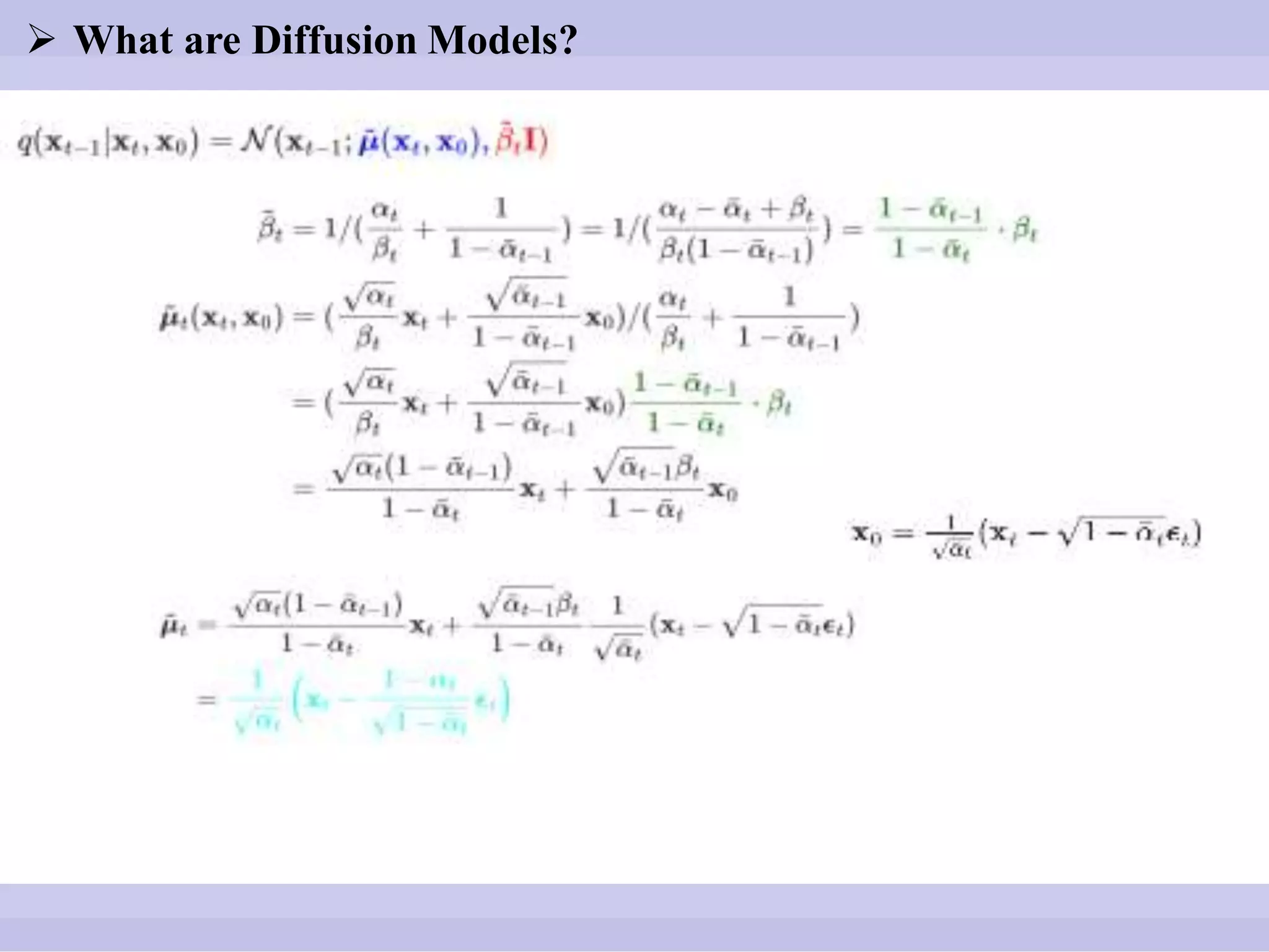
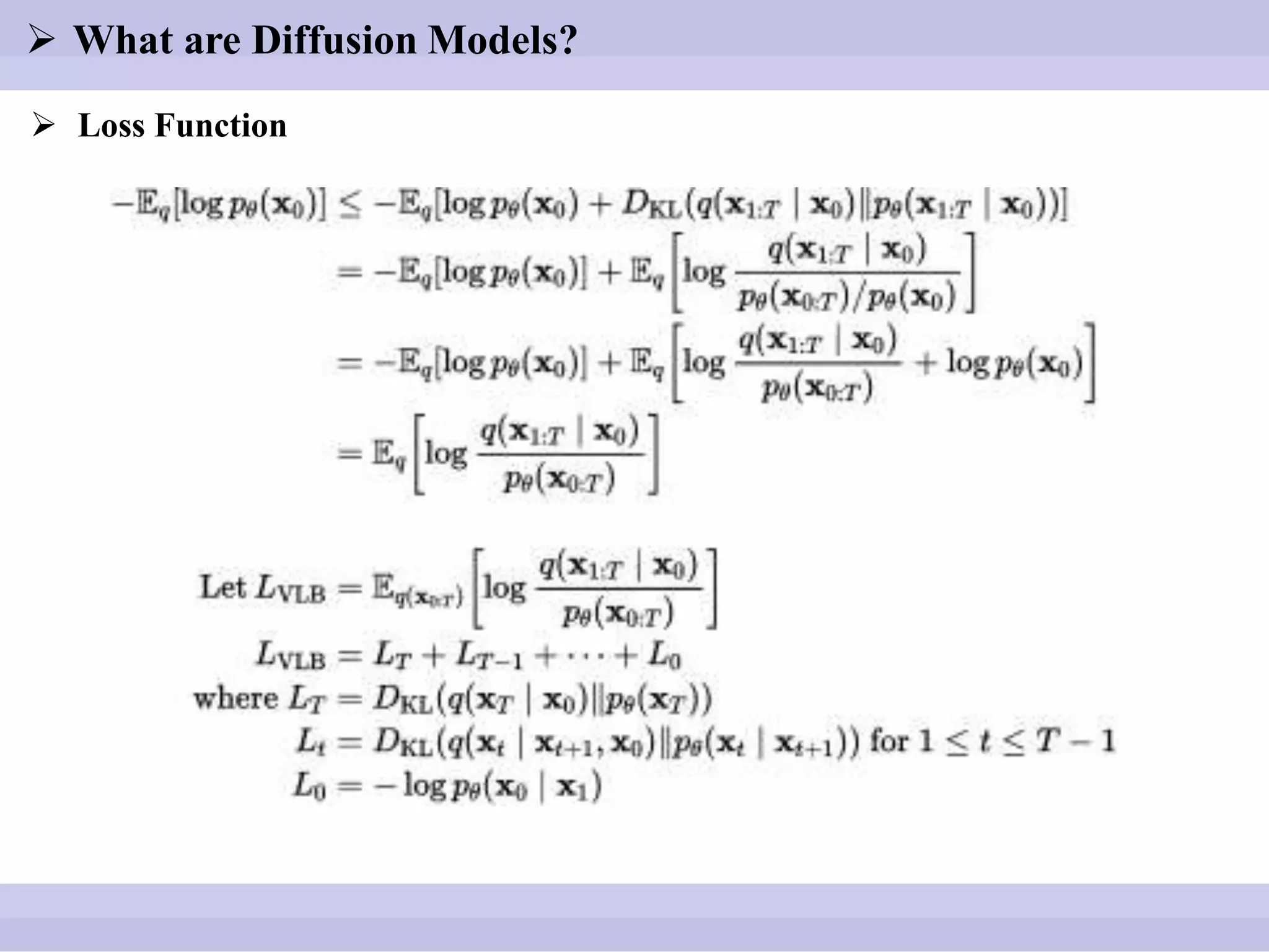
![ What are Diffusion Models?
( Ho J, Jain A, Abbeel P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models[J]. Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 6840-6851. )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1012presentation-221020011726-5a1d6b32/75/Image-super-resolution-via-iterative-refinement-pptx-7-2048.jpg)
![ Improved Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
( Nichol A Q, Dhariwal P. Improved denoising diffusion probabilistic models[C]//International Conference
on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2021: 8162-8171. )
Help diffusion models to obtain lower NLL
Improving the Noise Schedule 𝜷𝒕 cosine-based variance schedule
( a small offset s to prevent βt from being too small near t = 0 )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1012presentation-221020011726-5a1d6b32/75/Image-super-resolution-via-iterative-refinement-pptx-8-2048.jpg)
![ Improved Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
( Nichol A Q, Dhariwal P. Improved denoising diffusion probabilistic models[C]//International Conference
on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2021: 8162-8171. )
Learning 𝜽(𝒙𝒕, 𝒕)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1012presentation-221020011726-5a1d6b32/75/Image-super-resolution-via-iterative-refinement-pptx-9-2048.jpg)
![ Noise Schedules
( Chen N, Zhang Y, Zen H, et al. WaveGrad: Estimating gradients for waveform generation[J].
arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.00713, 2020. )
𝛾~𝑝(𝛾) 𝑝(𝛾) = 𝑡=1
𝑇 1
𝑇
𝑈(𝛾𝑡−1, 𝛾𝑡)
𝑡~𝑈({1,2, . . . , 𝑇}), 𝛾~𝑈(𝛾𝑡−1, 𝛾𝑡)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1012presentation-221020011726-5a1d6b32/75/Image-super-resolution-via-iterative-refinement-pptx-14-2048.jpg)