## Explanation of the Math Behind Stable Diffusion (DDPMs)
Stable Diffusion is based on **Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPMs)**, which generate images by gradually removing noise.
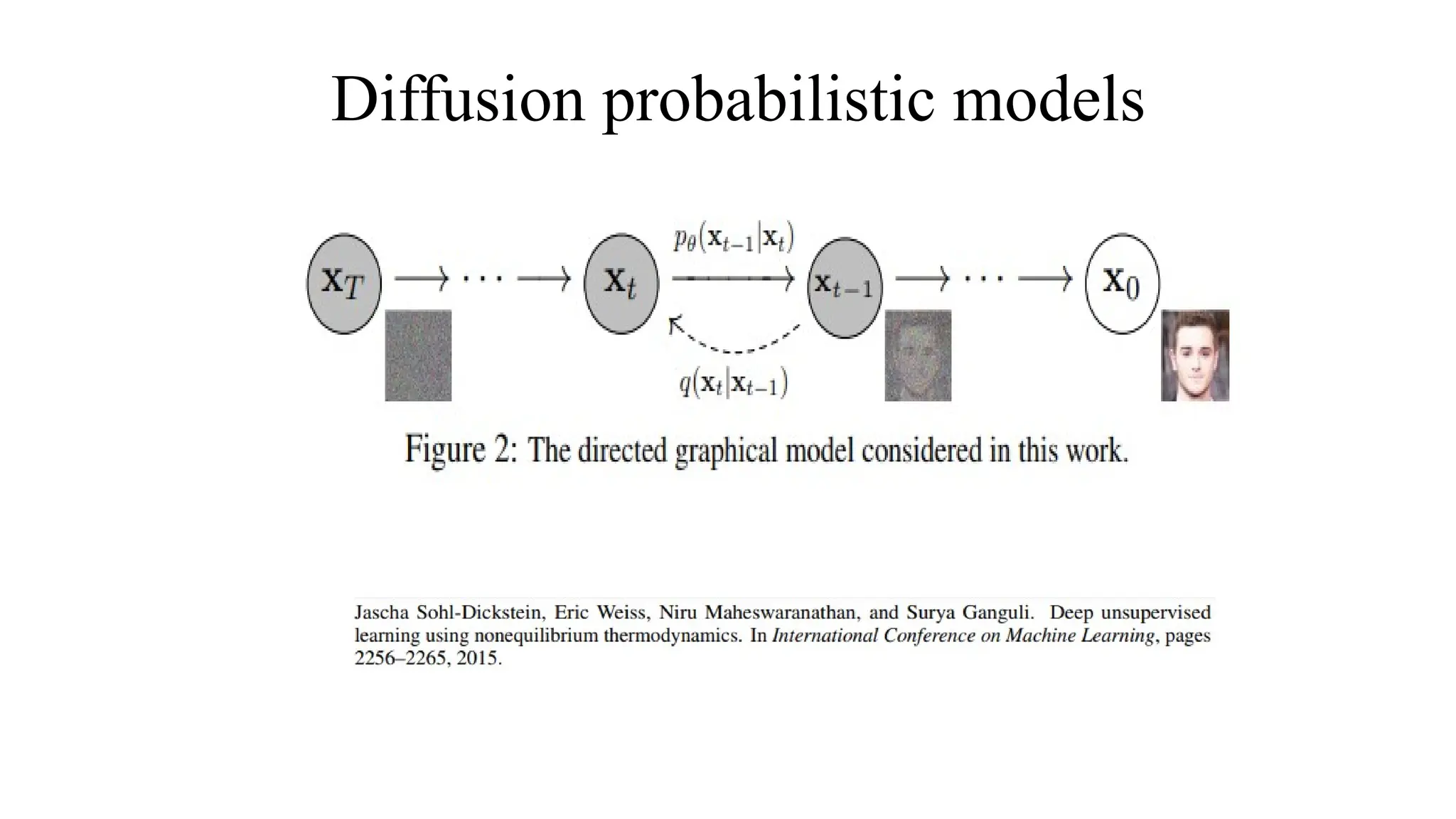
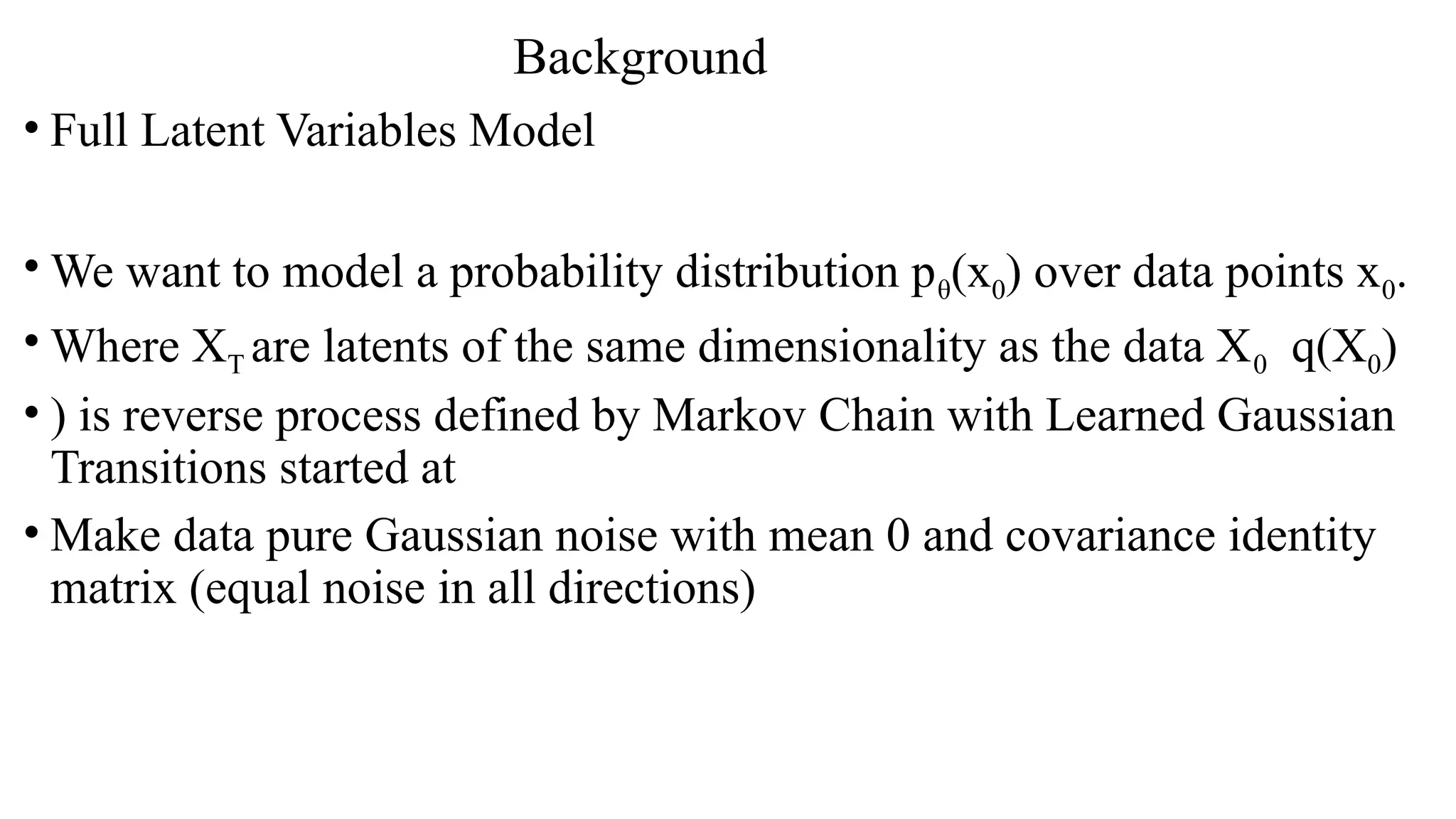
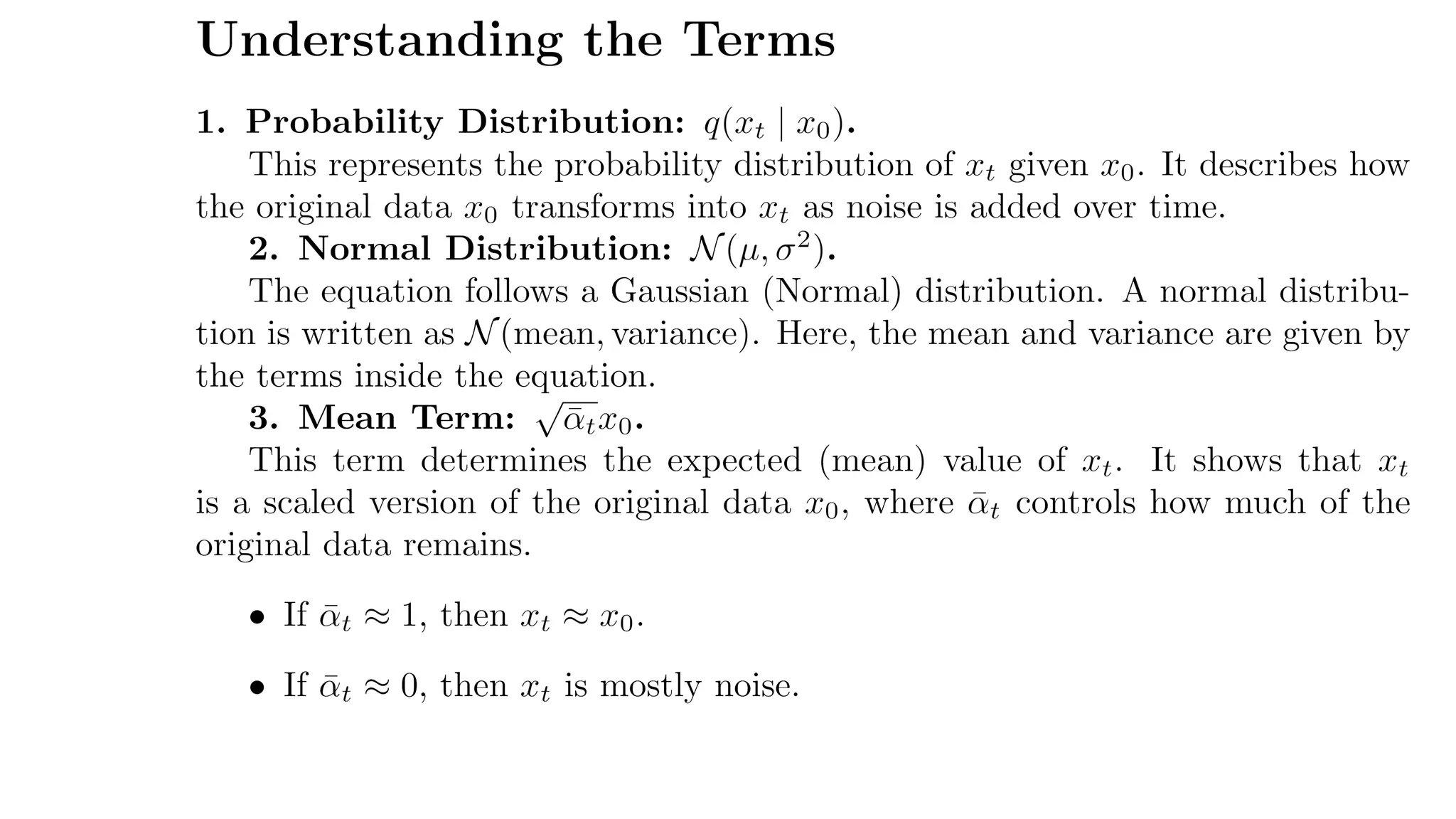
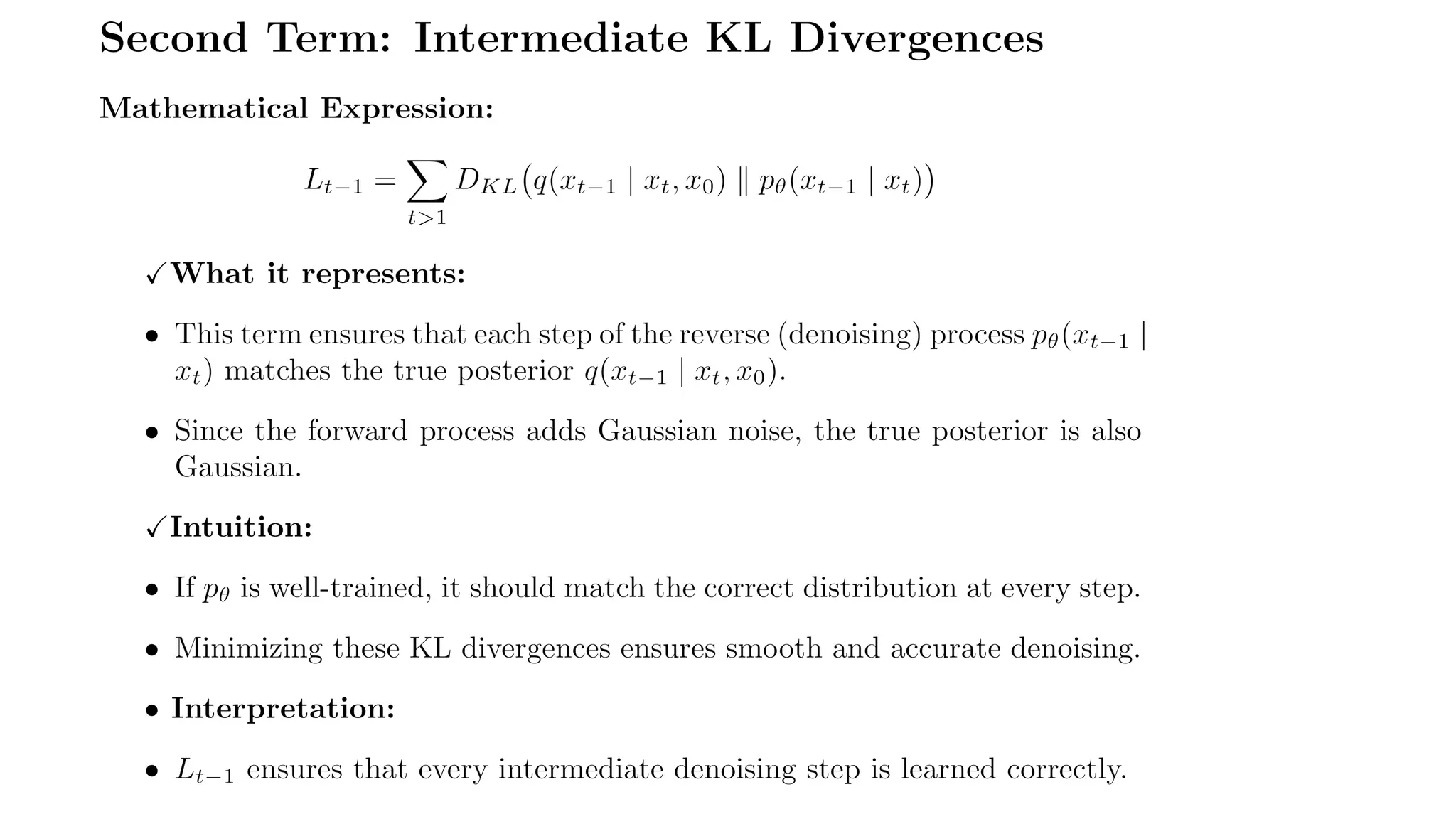
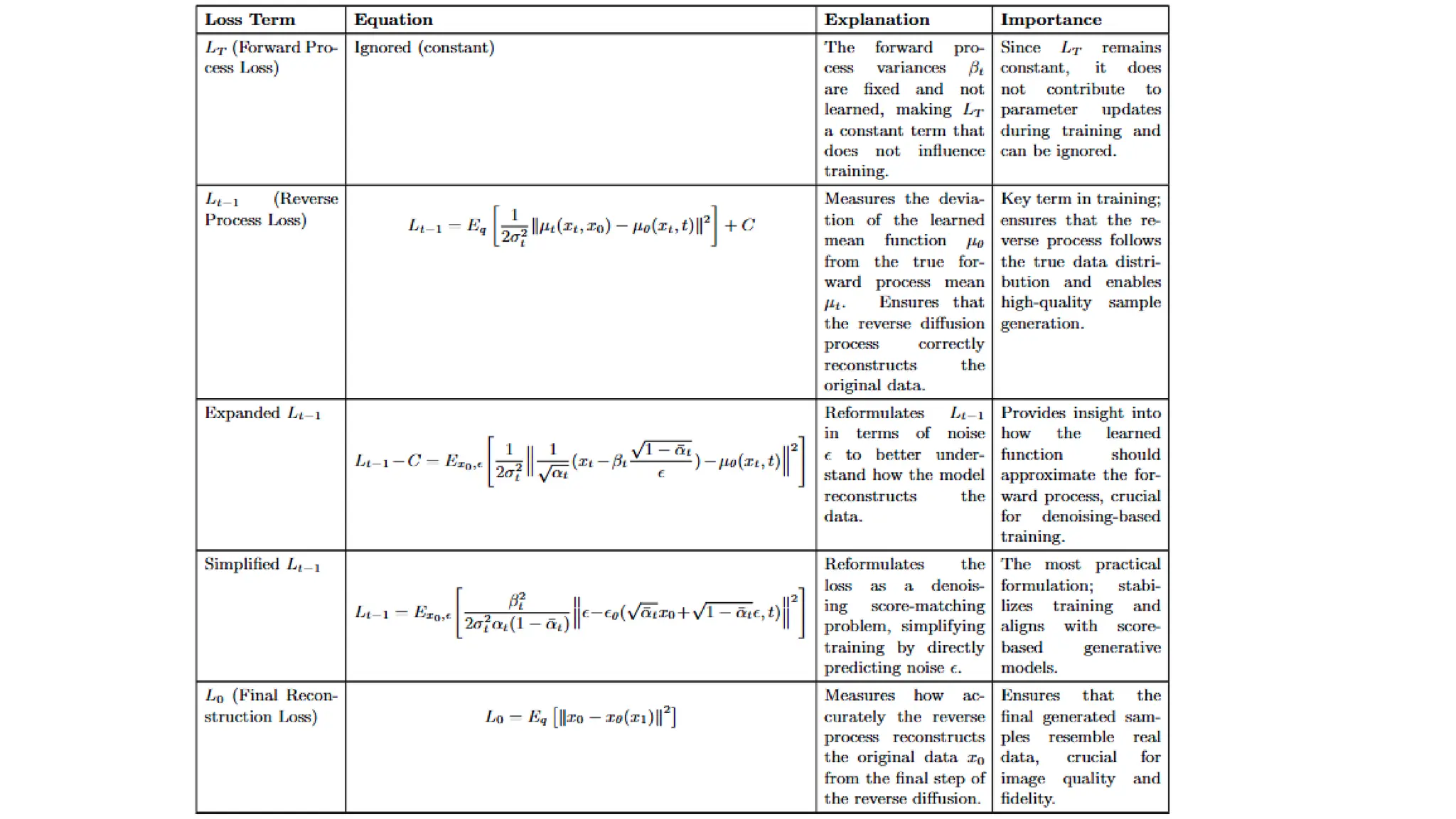
1. **Forward Process:** Noise is added to an image step by step until it becomes pure noise.
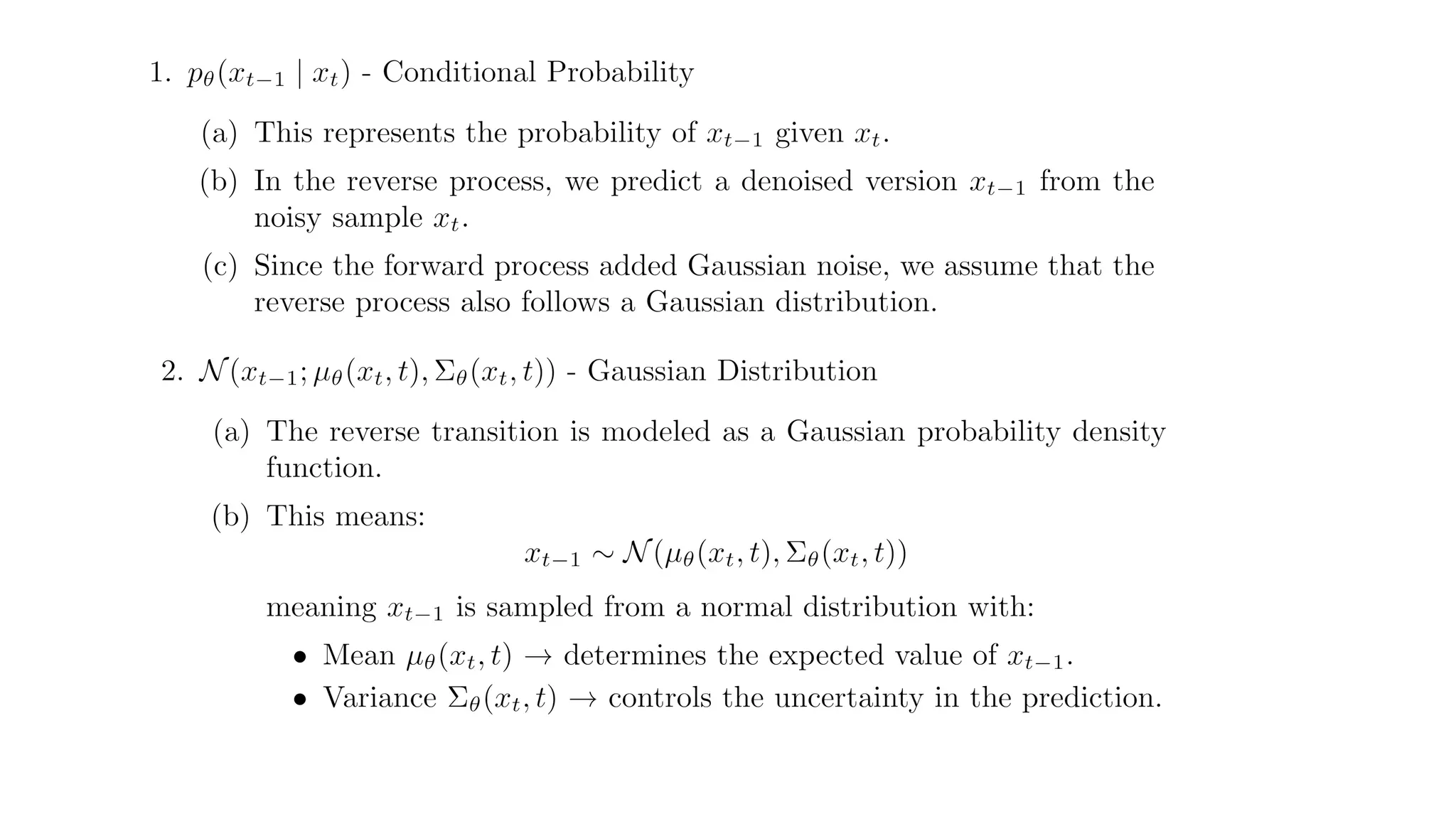
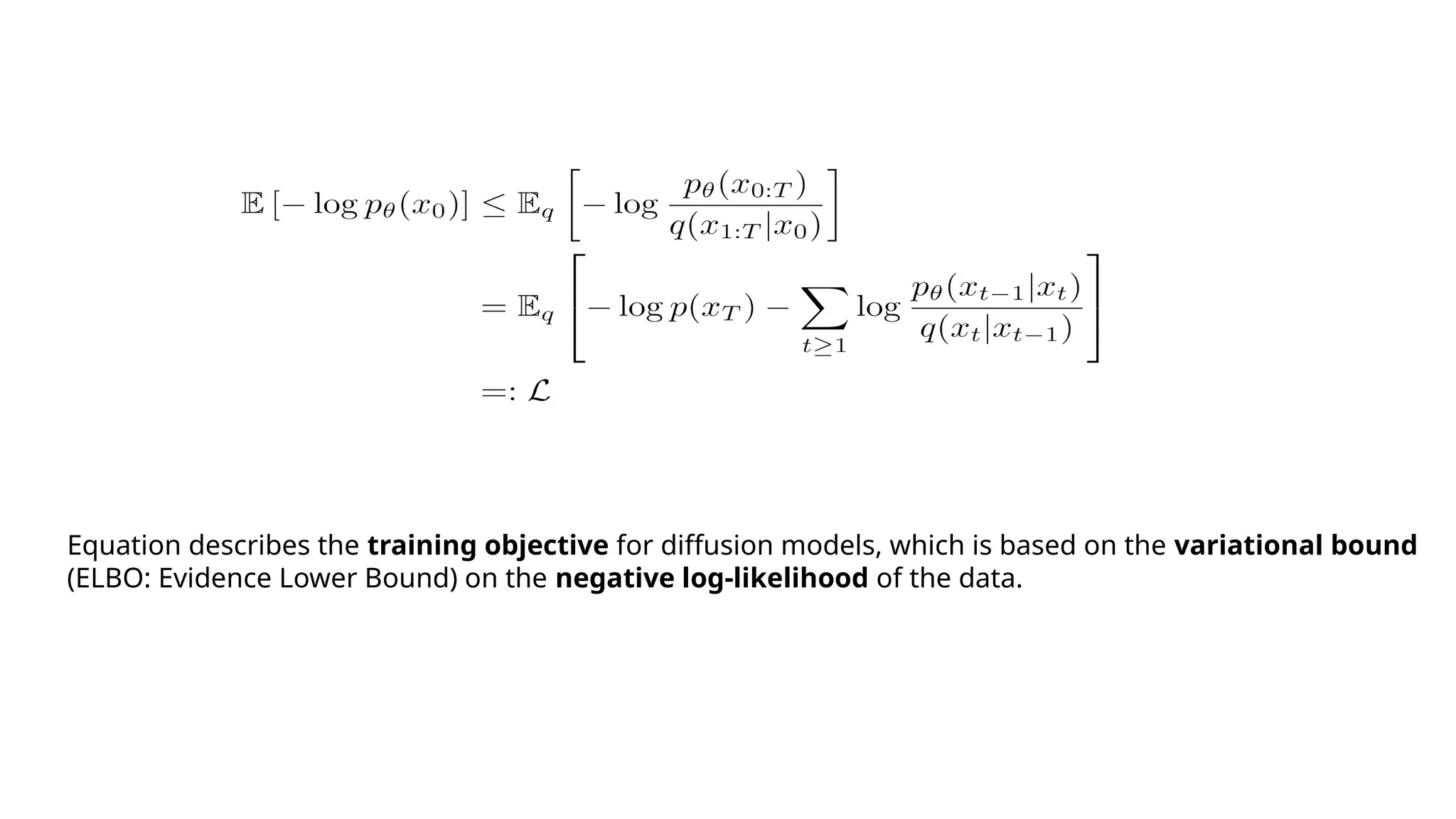
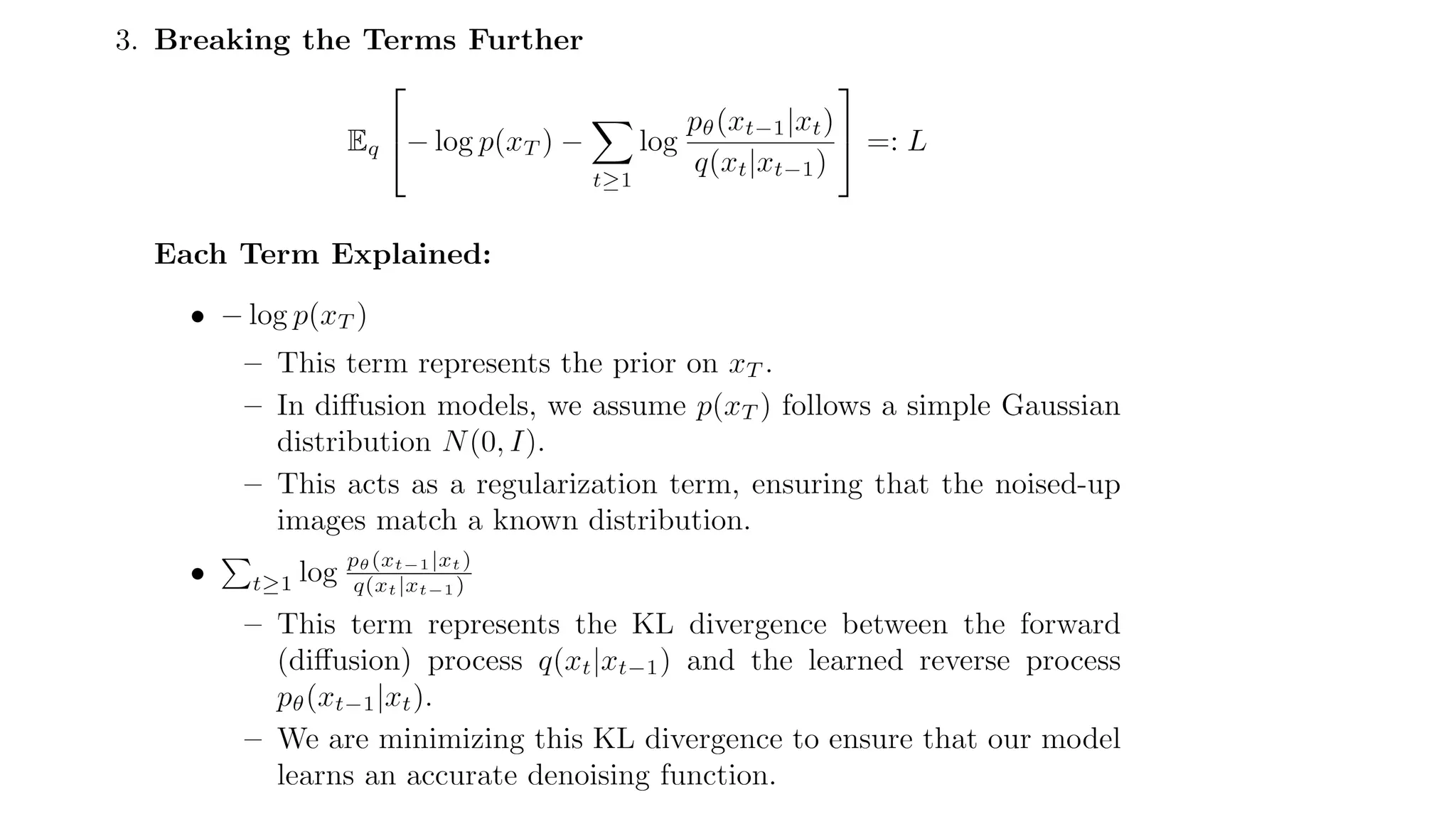
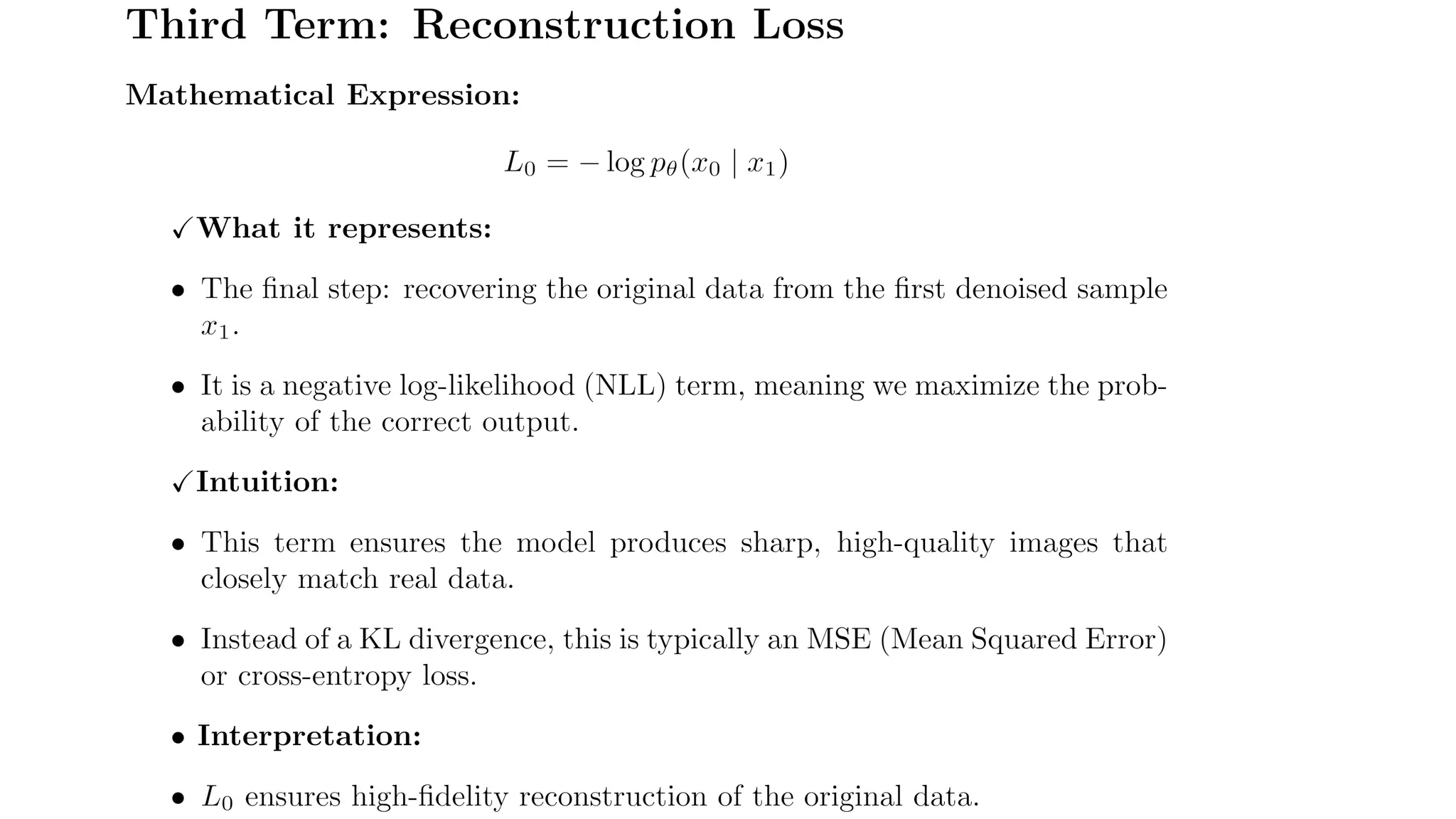
2. **Reverse Process:** A neural network learns to remove this noise, reconstructing a clear image.
3. **Training:** The model is trained to predict and remove noise efficiently.
4. **Image Generation:** Starting from random noise, the model gradually refines the image until it looks realistic.
















![Image Data Scaling
•Original Image Data: The image pixels are represented as integer values in the range {0, 1, ..., 255}.
•Scaled Data Representation: These pixel values are linearly scaled to [-1,1] using:
Why Scale to [-1,1]? Ensures that the input distribution to the neural network remains consistent.
•Helps in better training stability and convergence.
•Standardizes input for the reverse process.
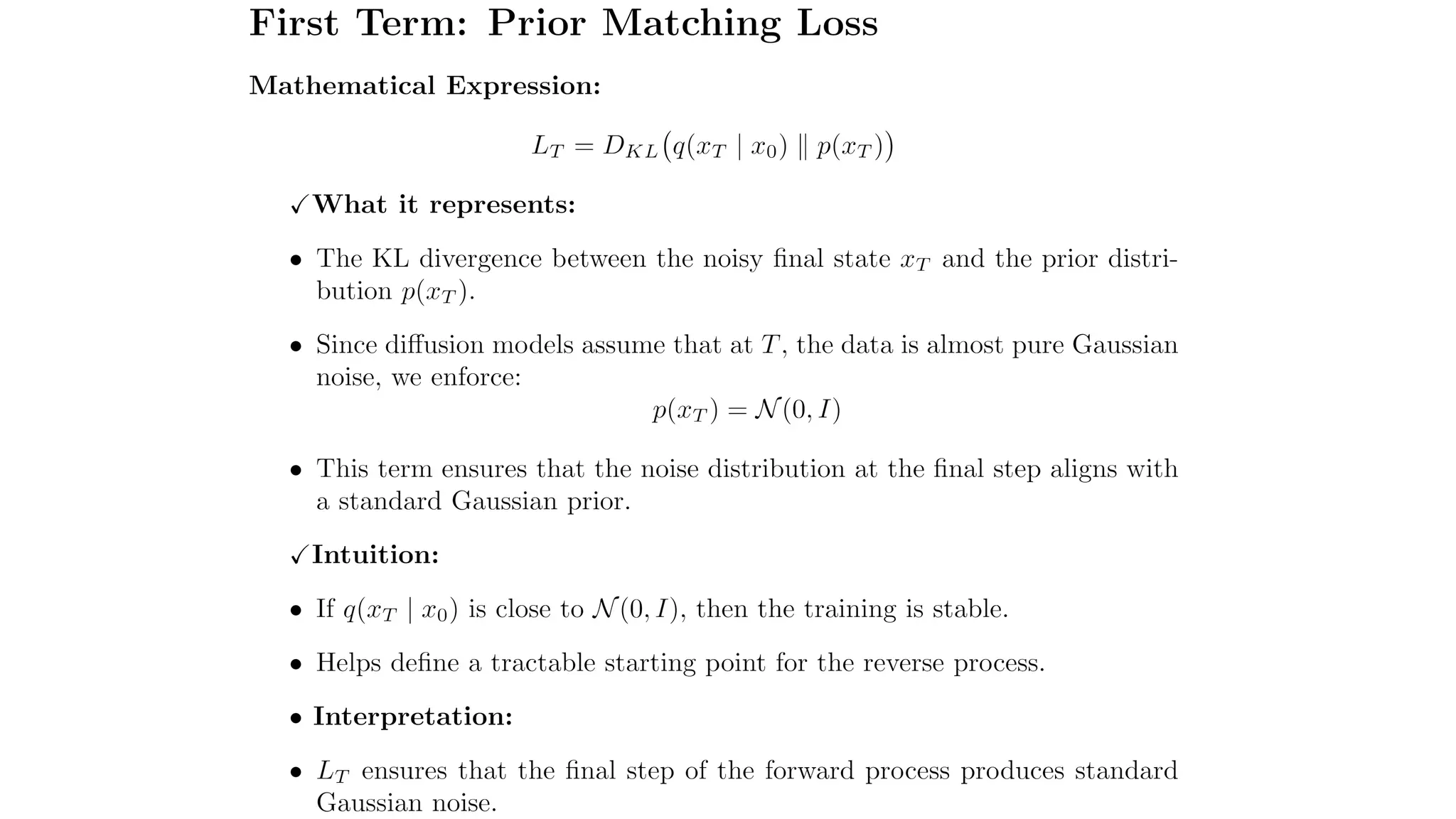
Standard Normal Prior in Reverse Process
•The reverse process begins with a standard normal prior p(xT), meaning that at the final step of the
forward diffusion, the image data follows a normal distribution:
• The goal of the reverse process (decoder) is to gradually denoise this distribution and reconstruct the original
data.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/denoisingdiffusionprobabilisticmodelsppt-250313135611-47a76145/75/Explanation-of-the-Math-Behind-Stable-Diffusion-DDPMs-27-2048.jpg)