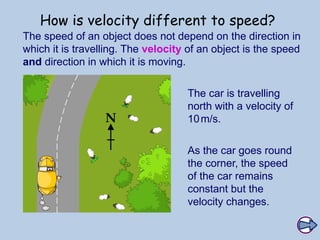
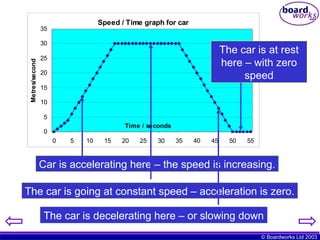
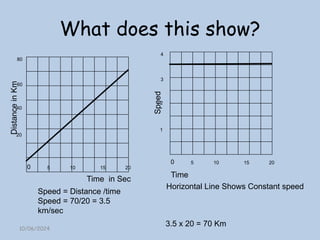
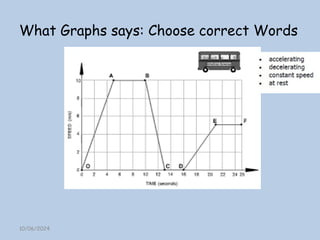
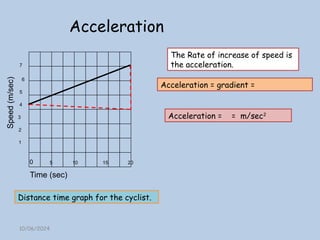
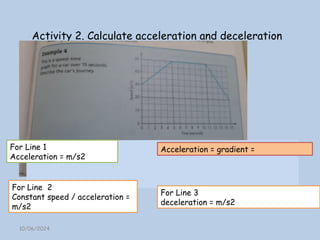
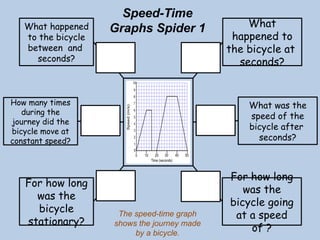
The document explains the concepts of speed, velocity, acceleration, and deceleration using speed-time graphs. It differentiates between speed and velocity, highlighting that speed does not depend on direction while velocity does, and includes activities for calculating acceleration. Additionally, it provides examples of interpreting graphs to analyze motion over time.