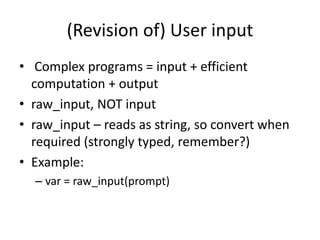
This document is a compilation of Python programming concepts covered in a class, including user input handling, basic control structures, string manipulation, and functionalities of loops. It outlines assignments aimed at enhancing practical programming skills, such as creating a simple calculator and handling user authentication. The document emphasizes the importance of understanding the principles of coding while providing references and revision notes for further learning.




![Obligatory xkcd reference[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class2-151002103744-lva1-app6892/85/if-while-and-for-in-Python-6-320.jpg)



![(Revision of)Strings
• Immutable
• Single or double, they don’t care
• Raw strings
• Escape sequences
• String slicing – string[start:stop:step]
• We count from 0 (why?)
• String methods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class2-151002103744-lva1-app6892/85/if-while-and-for-in-Python-10-320.jpg)


![In-class assignment[2]
Write a program that takes input of the form
‘num1,num2,[any one of +-*/]’ as a string
and performs the given operation. In other
words, your program is a simple calculator
which can perform floating point arithmetic.
Try making improvements like asking for no.
of decimal digits to be displayed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class2-151002103744-lva1-app6892/85/if-while-and-for-in-Python-13-320.jpg)




![for loops can do more!
• What is this ‘in’ anyway? (different time
complexity for different cases)
• for char in string
• for line in text
• for item in sequence
–Example: for i in [1,’a’,3]:
print i
# output: 1nan3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class2-151002103744-lva1-app6892/85/if-while-and-for-in-Python-18-320.jpg)


![In-class assignment
• Input an angle as degrees. And find a
trigonometric ratio based on users choice[out of
sin, cos and tan]. Do this ‘n’ times, where ‘n’ was
entered by the user initially.
HINT : import math. (what is import,
from..import .. ?) [3]
• Input two strings. One takes in login_ID and
other password. It prints “login_ID is successful”
if password is password. Else should show a fail
message and keep prompting user for
password.[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class2-151002103744-lva1-app6892/85/if-while-and-for-in-Python-21-320.jpg)
![In-class assignment
Find the factorial of a given number. Don’t
import math. Try to make your program break
and fix all those cases. (recursive vs.
iterative)[2]
Note that I said ‘number’. What if it user enters
a string and then it leads to a TypeError?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class2-151002103744-lva1-app6892/85/if-while-and-for-in-Python-22-320.jpg)


![References
• All “(Revision of)” slides were taken from class
1 presentation made by me on 11-9-15
• [1] – xkcd webcomic - https://xkcd.com/1425/
• [2] – idea by Tarun Verma
• [3] – modified form of something Tarun Verma
said](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class2-151002103744-lva1-app6892/85/if-while-and-for-in-Python-25-320.jpg)