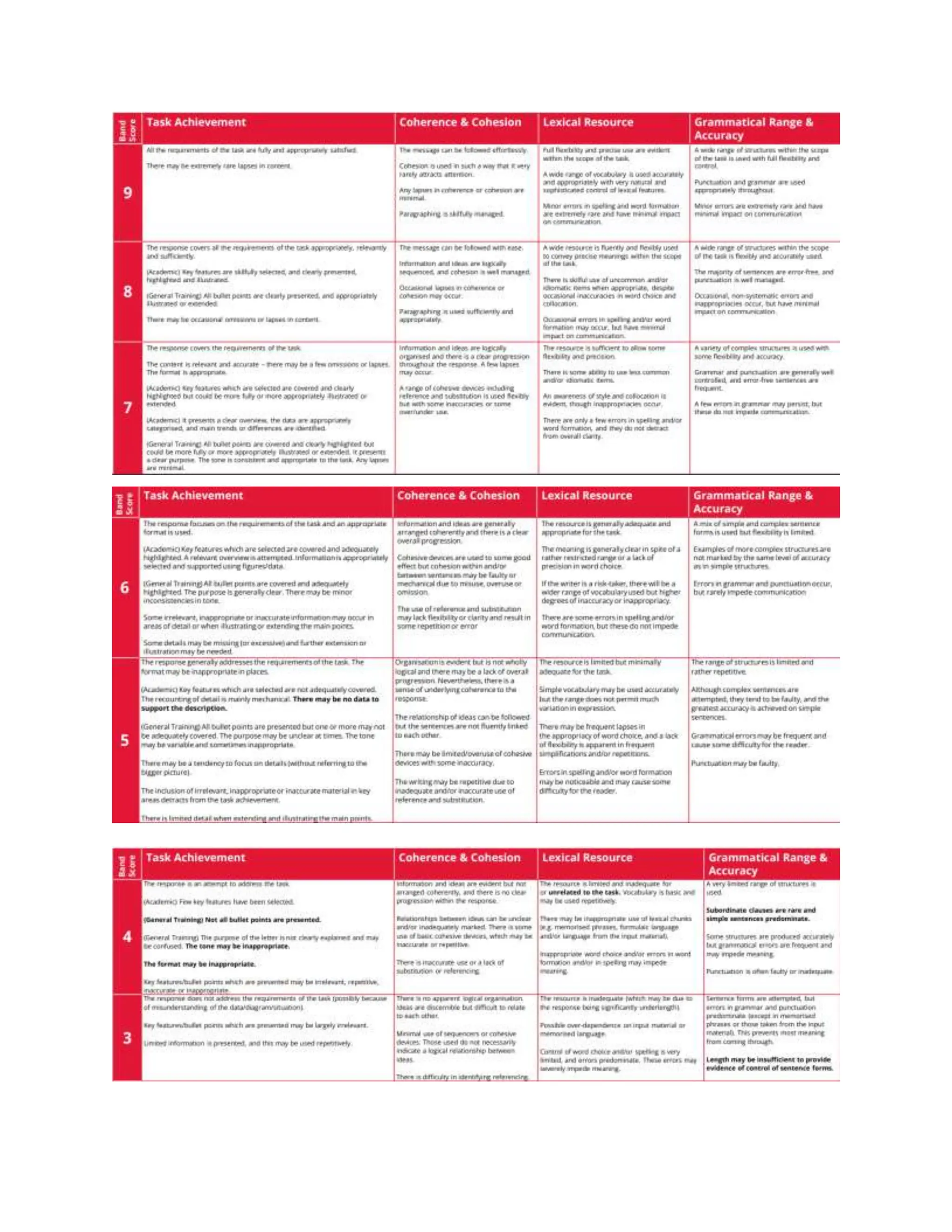
The document outlines a grading rubric for evaluating written responses across four main criteria: task achievement, coherence and cohesion, lexical resource, and grammatical range and accuracy, each ranging from scores of 4 to 9. It details the required characteristics for various scoring levels, emphasizing elements such as relevance, clarity, organization, vocabulary usage, and grammatical control. Each category provides specifics regarding what is expected at different performance levels, guiding evaluators in assessing written work effectively.