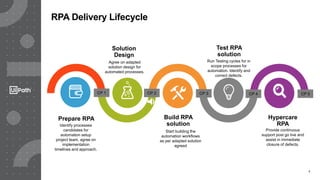
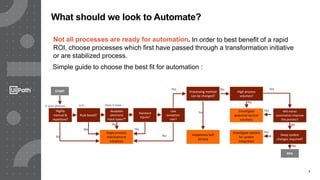
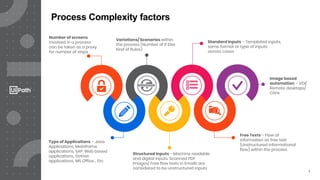
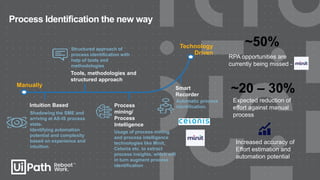
This document discusses best practices for identifying processes that are good candidates for robotic process automation (RPA). It outlines the RPA delivery lifecycle and provides guidance on assessing process characteristics, complexity factors, and aligning processes with estimated delivery timelines. The document recommends using process mining and intelligence technologies to augment traditional manual process identification methods and more accurately define processes, estimate efforts, and identify automation potential. This leads to improved documentation, relationships between teams, and a reduction in the effort required for process identification.