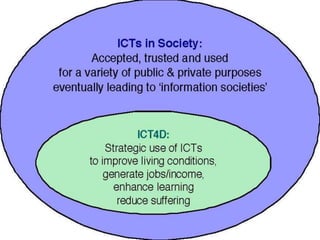
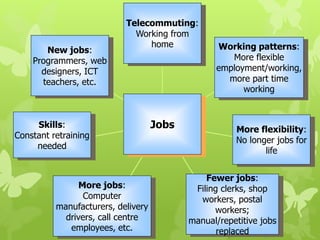
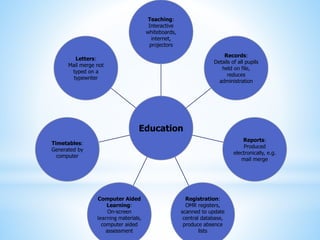
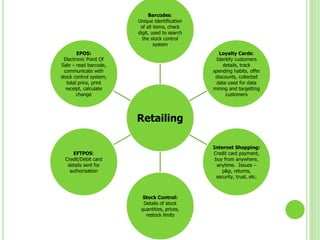
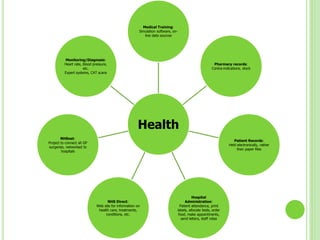
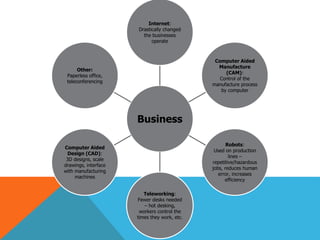
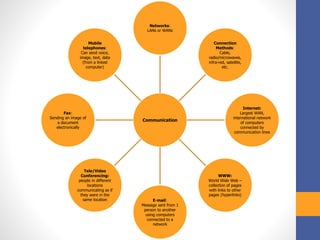
ICT stands for Information and Communication Technologies and focuses on telecommunications like the internet, cell networks, and satellites. Modern ICT allows users worldwide to communicate in real-time through tools like instant messaging, video chat, online games, and social media. ICT has impacted society in many ways by changing jobs, education, crime fighting, retail, health, banking, and communication.