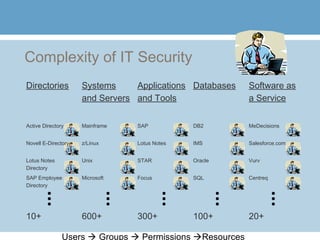
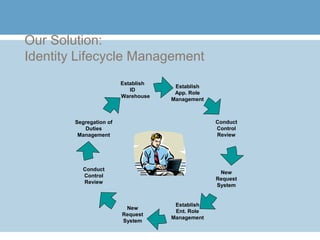
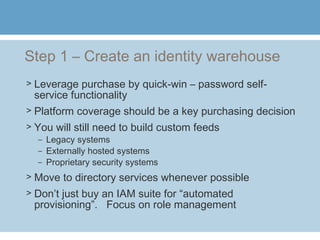
1) The document discusses 10 steps to implement role-based access control at an organization. The first step is to create an identity warehouse to consolidate user access credentials across different systems.
2) The second step is to establish enterprise role management by designing or purchasing a role management product to define people's access needs across all applications.
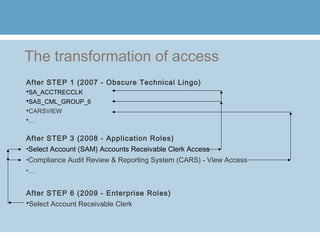
3) Additional steps include defining application roles, conducting online role attestation reviews, adjusting the access request system to use the new role terminology, creating enterprise roles, ongoing role attestation, adjusting the request system for enterprise roles, segregation of duties analysis, and leveraging role management for external users.