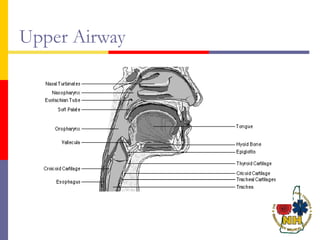
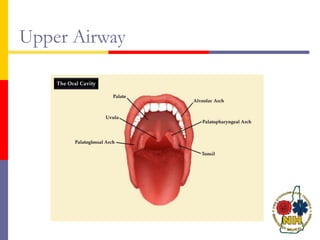
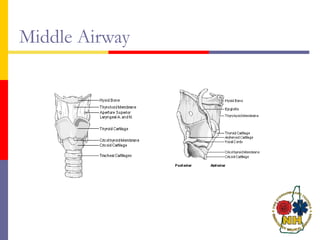
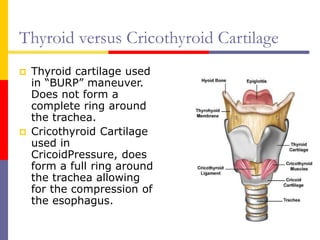
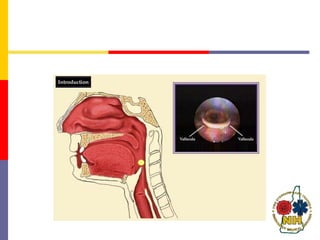
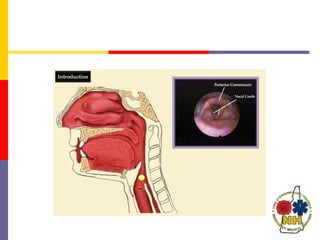
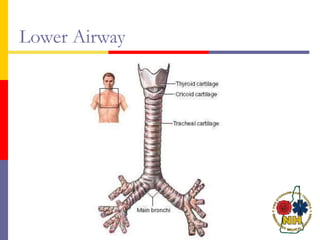
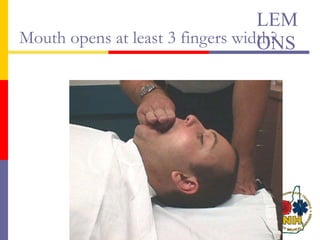
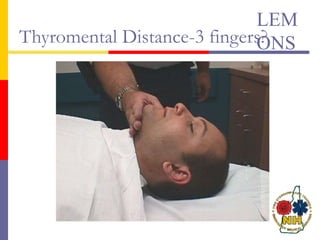
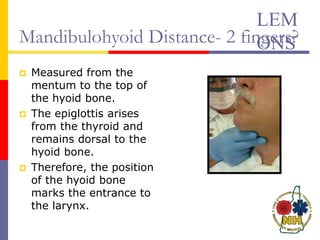
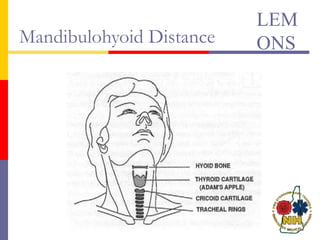
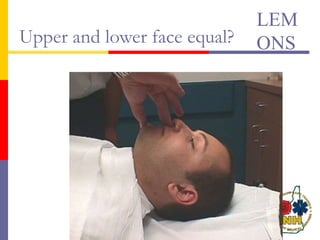
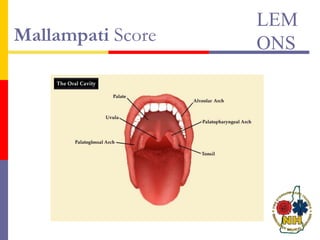
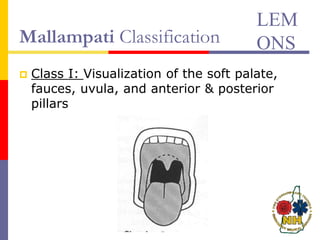
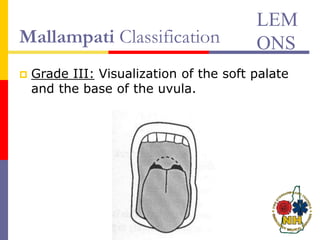
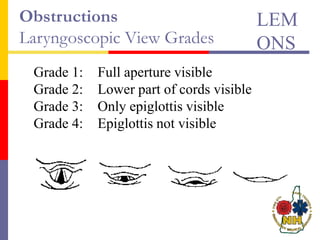
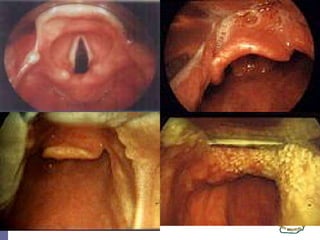
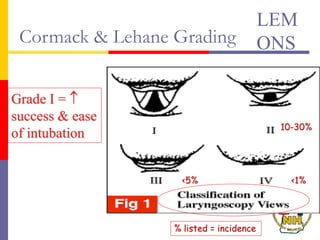
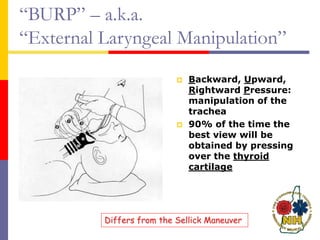
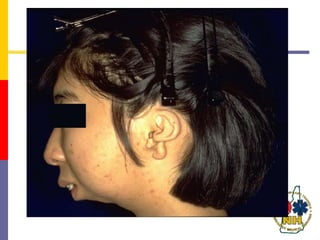
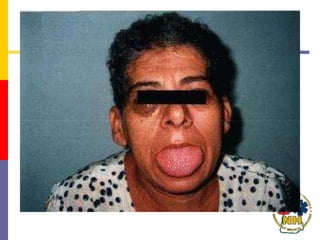
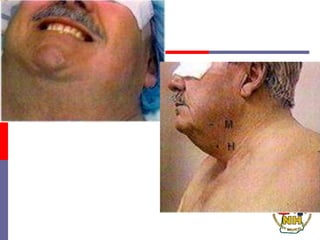
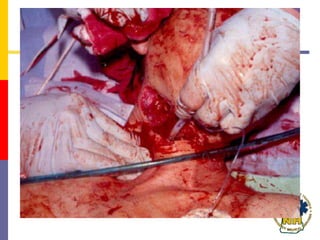
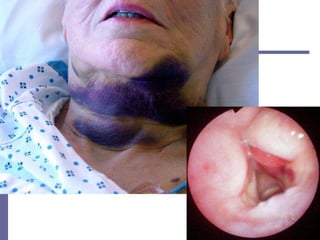
This document reviews techniques for advanced airway assessment. It discusses predicting difficult airways using the LEMOS, MOANS, and DOA mnemonics which evaluate factors like mouth opening, neck mobility, obesity, and obstructions. Grading scales for laryngoscopy views and Mallampati classifications are also covered. The document emphasizes properly assessing airway risks before performing endotracheal intubation to prepare for potential difficulties and have alternative plans.