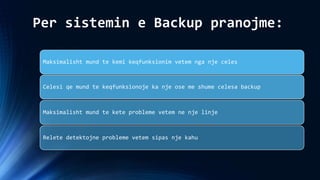
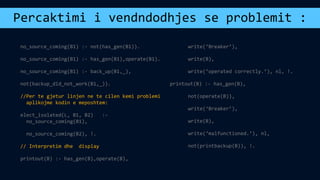
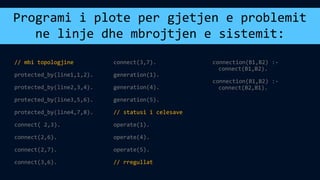
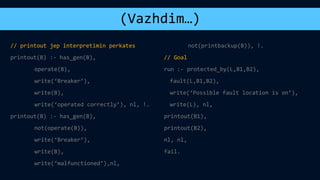
The document discusses several topics related to artificial intelligence including machine learning systems, artificial intelligence programming languages, and some concepts of artificial psychology. It provides an overview of machine learning concepts like self-improvement, adaptation to new situations, and behavior modification. It also describes different machine learning methods such as learning from external sources, exploring new information sources, and evaluating the consequences of past actions. Finally, it gives examples of logic programming in Prolog and using temporal logic to reason about time-based statements.