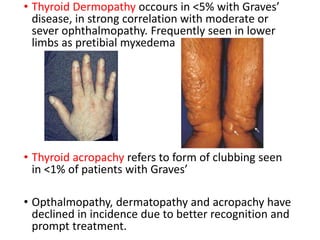
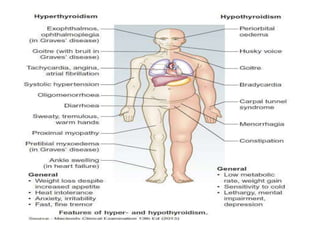
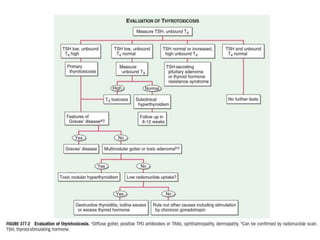
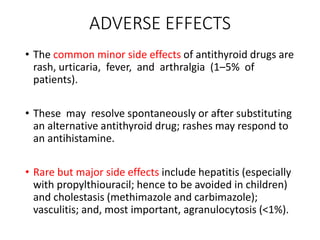
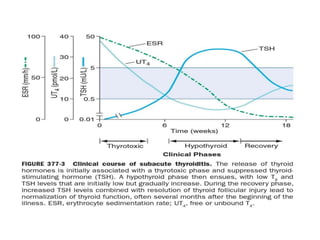
This document provides an overview of hyperthyroidism and its management. It discusses the main causes and clinical features of hyperthyroidism, focusing on Graves' disease which accounts for 60-80% of cases. The pathogenesis involves genetic and environmental factors leading to thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins that cause excessive thyroid hormone production. Management includes antithyroid medications, radioiodine therapy, or thyroidectomy. Antithyroid drugs are usually the first line treatment but have potential adverse effects. Radioiodine is an alternative that destroys thyroid tissue over time. Considerations for special populations like pregnant women are also covered.