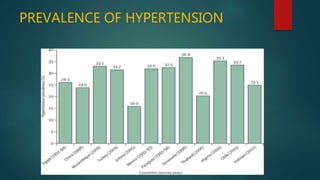
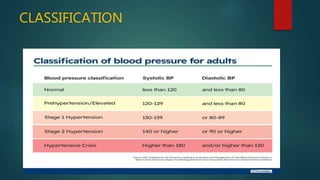
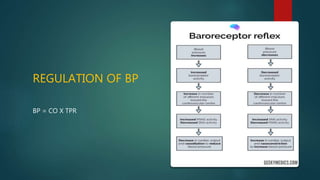
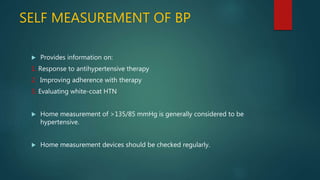
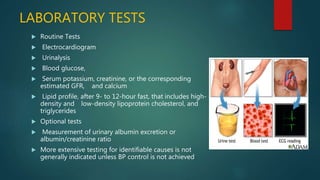
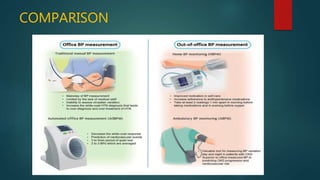
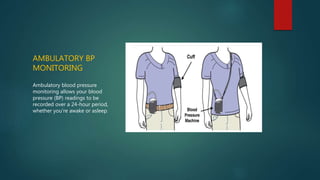
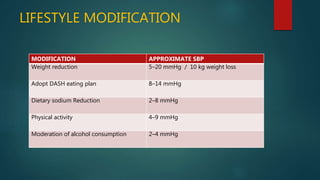
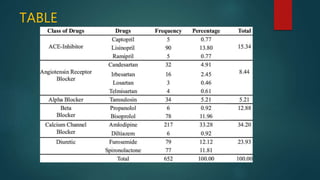
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common condition where the force of blood against artery walls is too high. It is defined as a systolic pressure over 140 mm Hg or diastolic over 90 mm Hg. Nearly 1 billion people worldwide have hypertension, which is poorly controlled. Risk factors include family history, stress, smoking, diet, alcohol, and other conditions like diabetes. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications like losing weight, reducing sodium, and medication. The goals of treatment are to reduce cardiac and renal risks and achieve a blood pressure under 140/90 mm Hg or 130/80 mm Hg for those with related conditions.