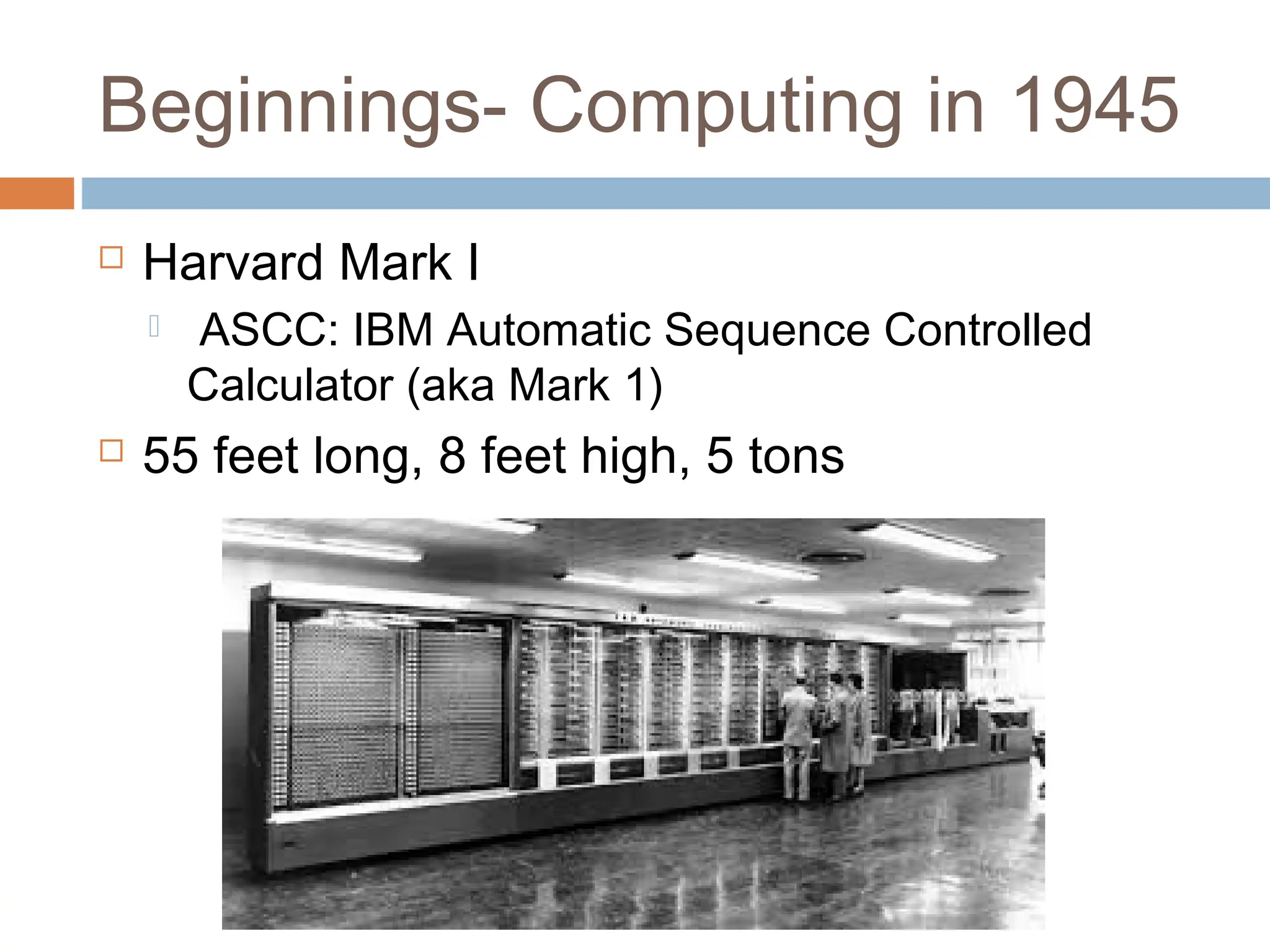
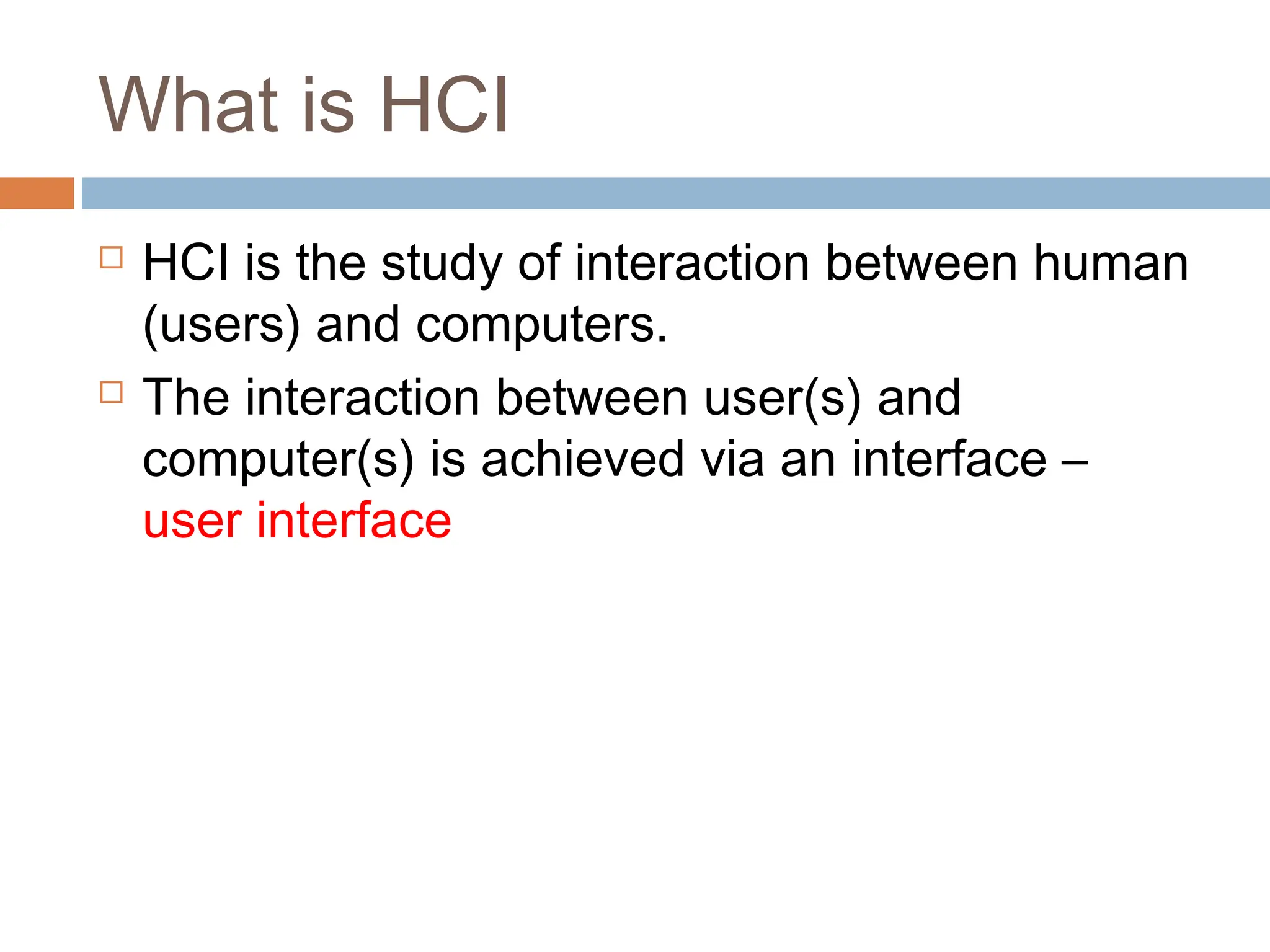
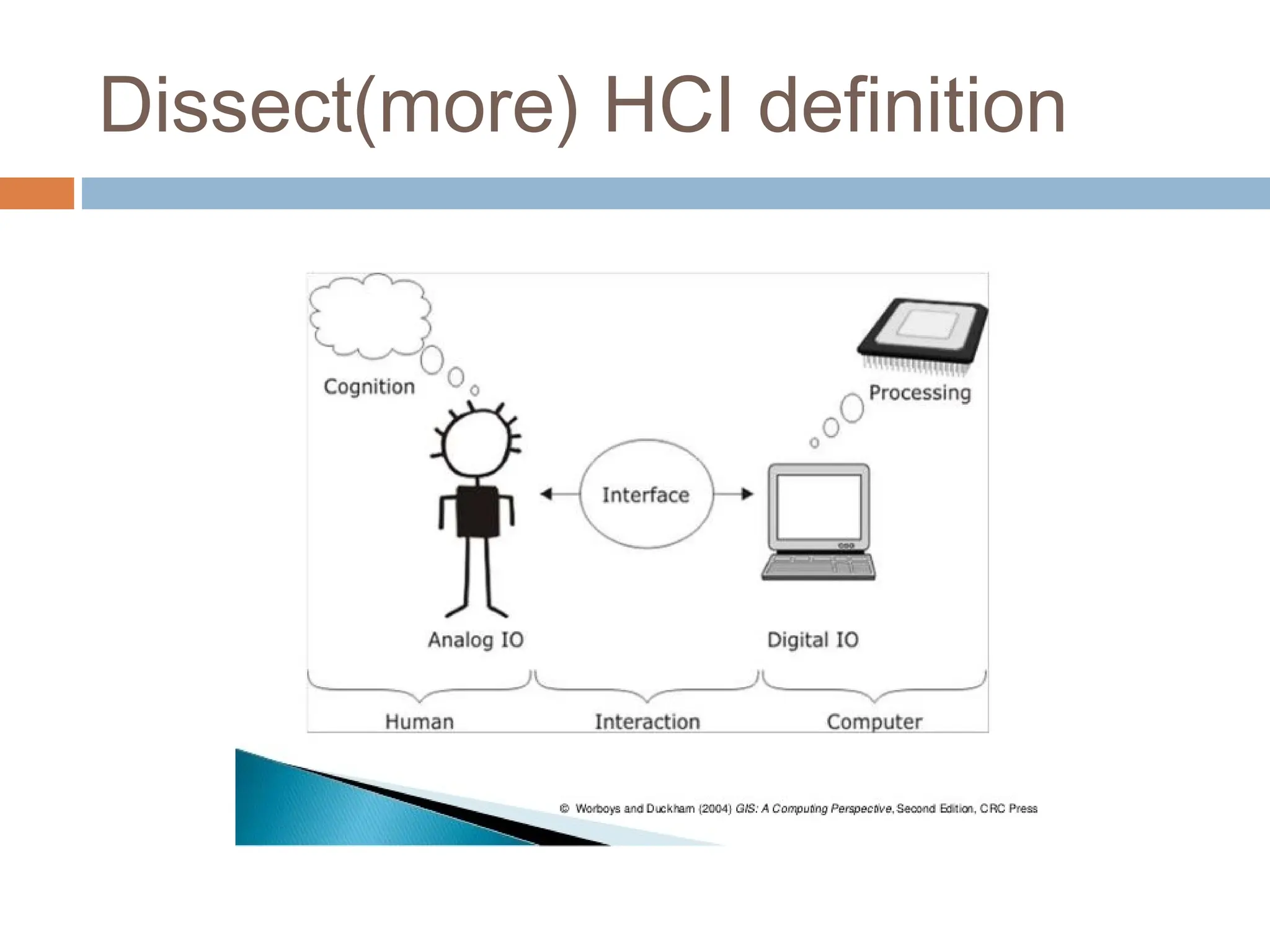
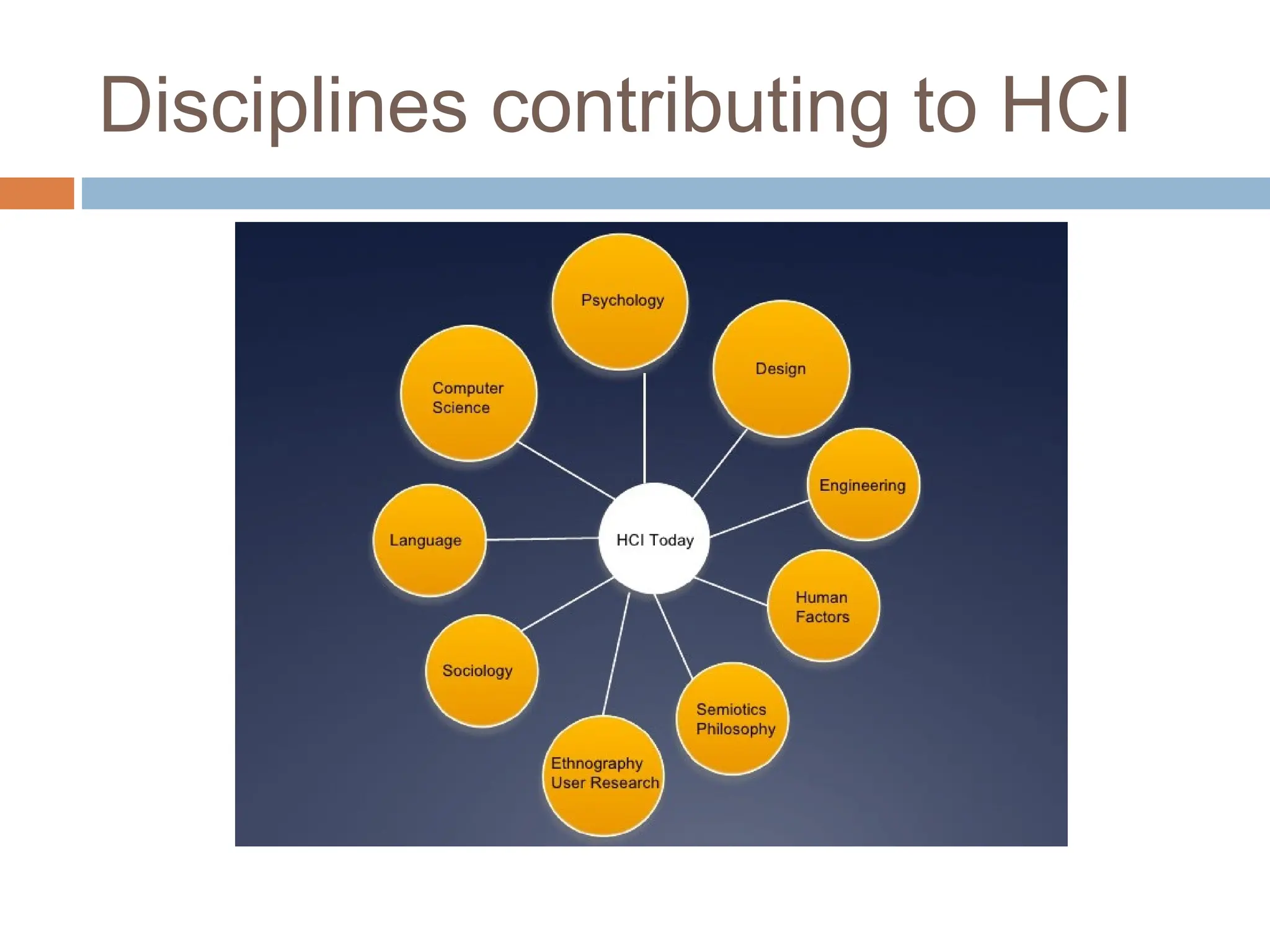
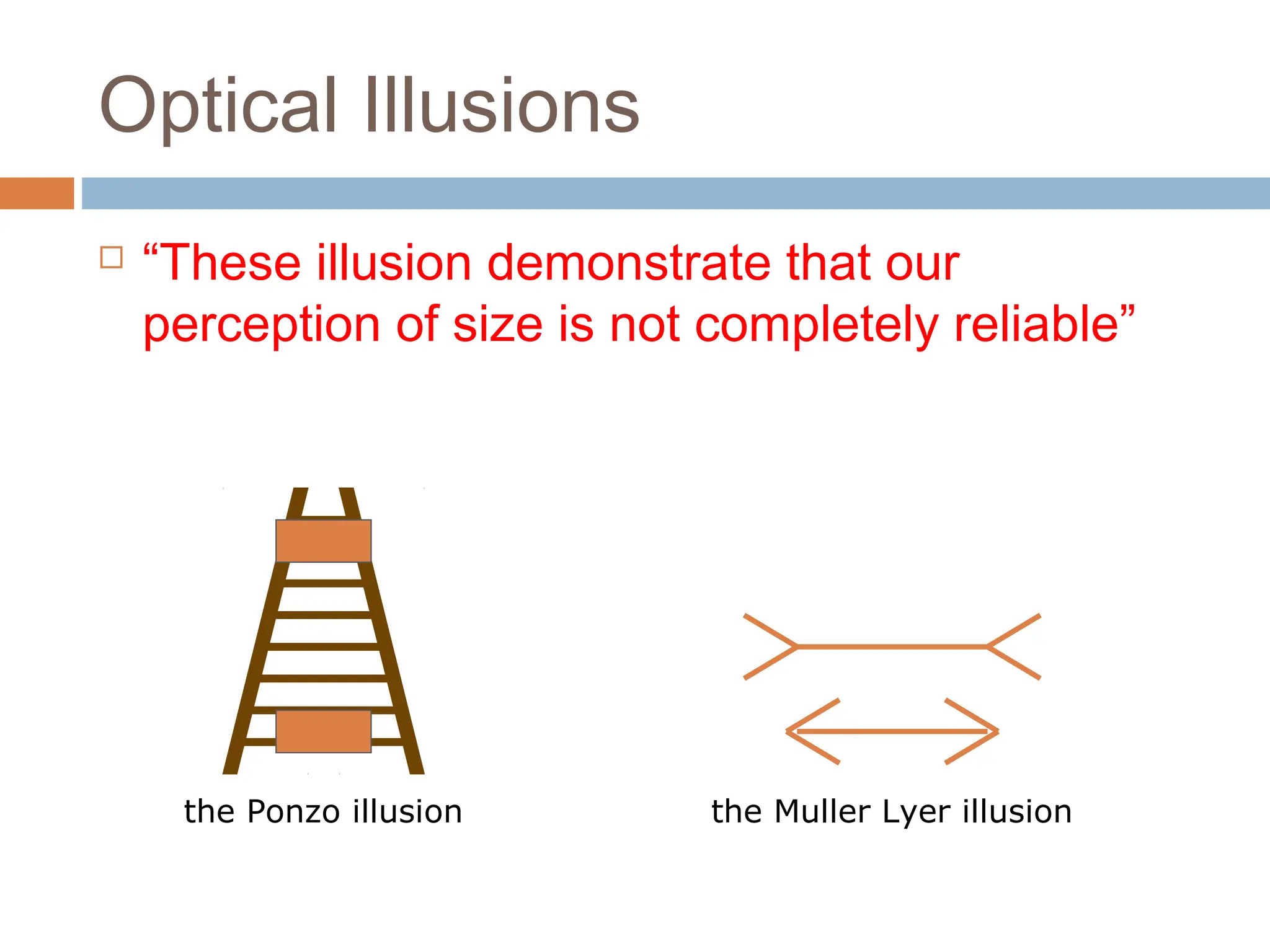
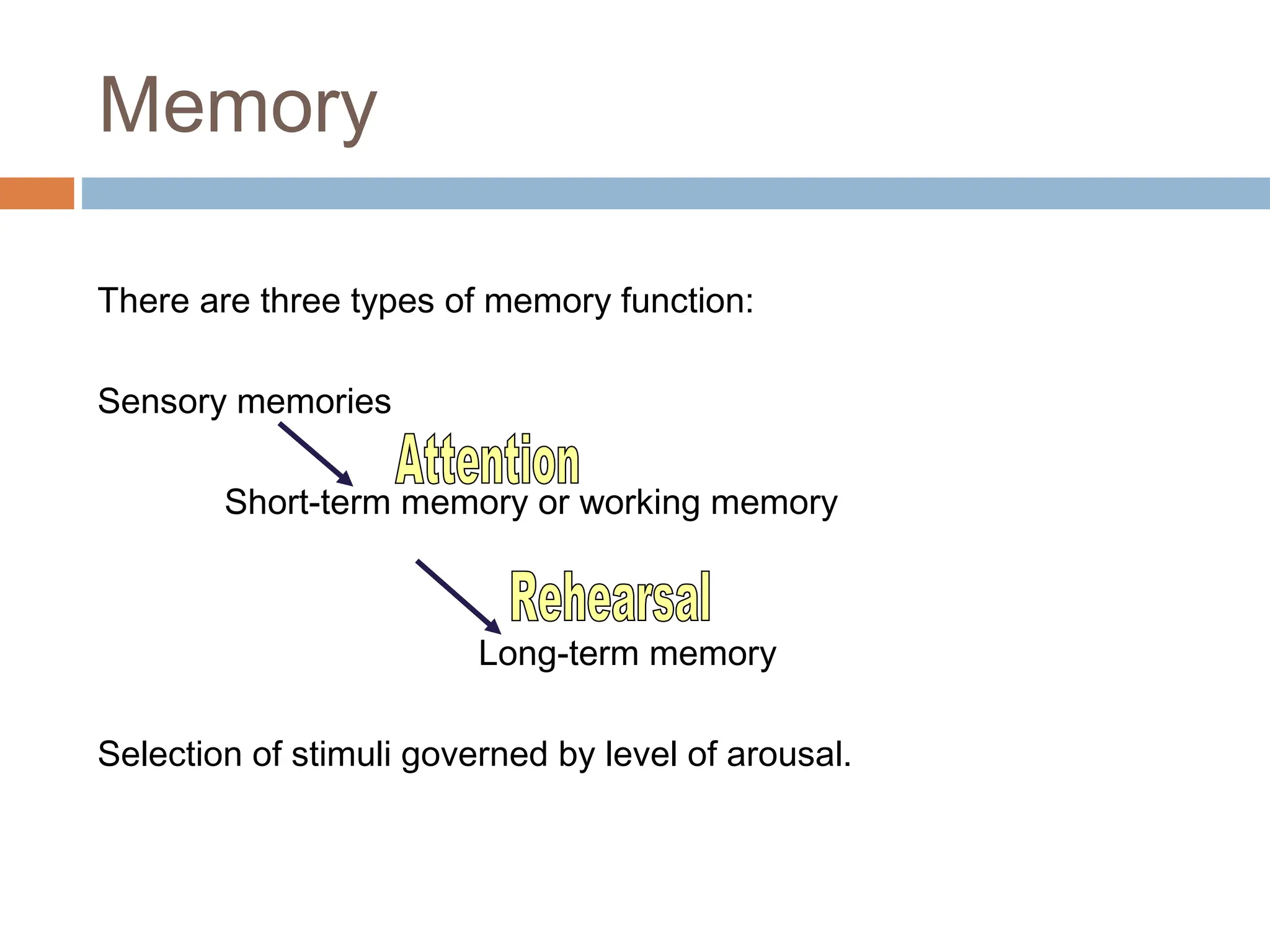
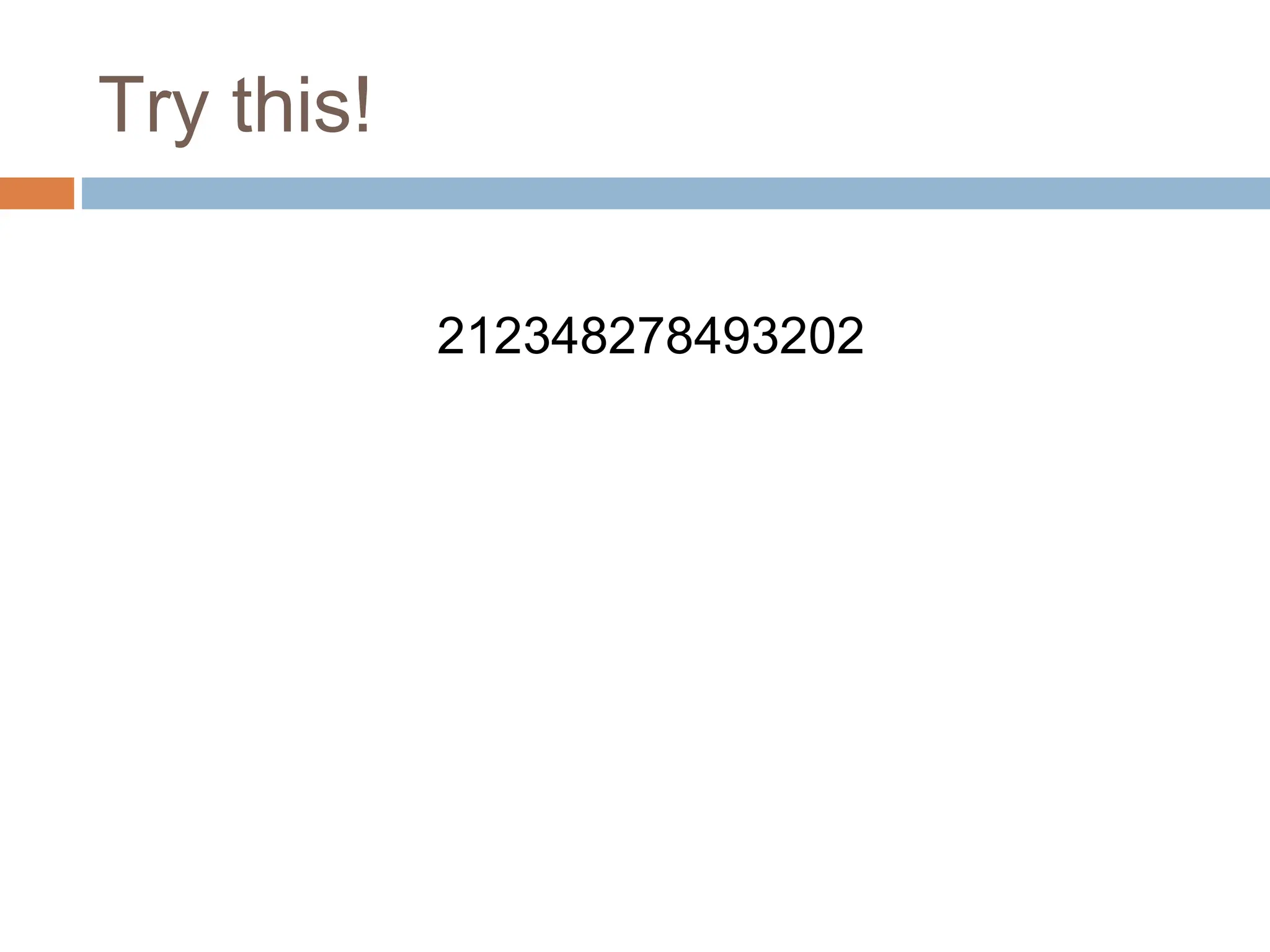
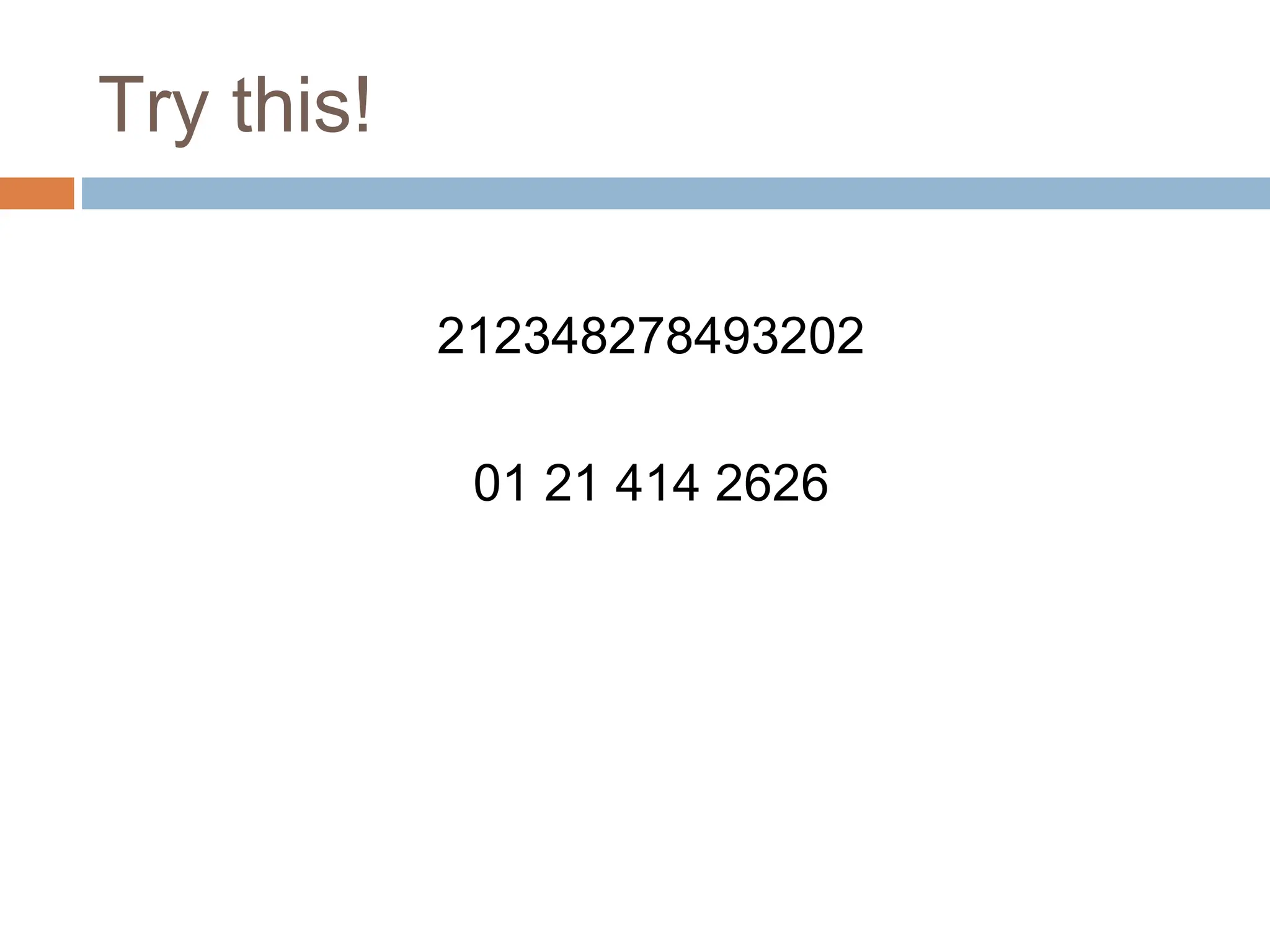
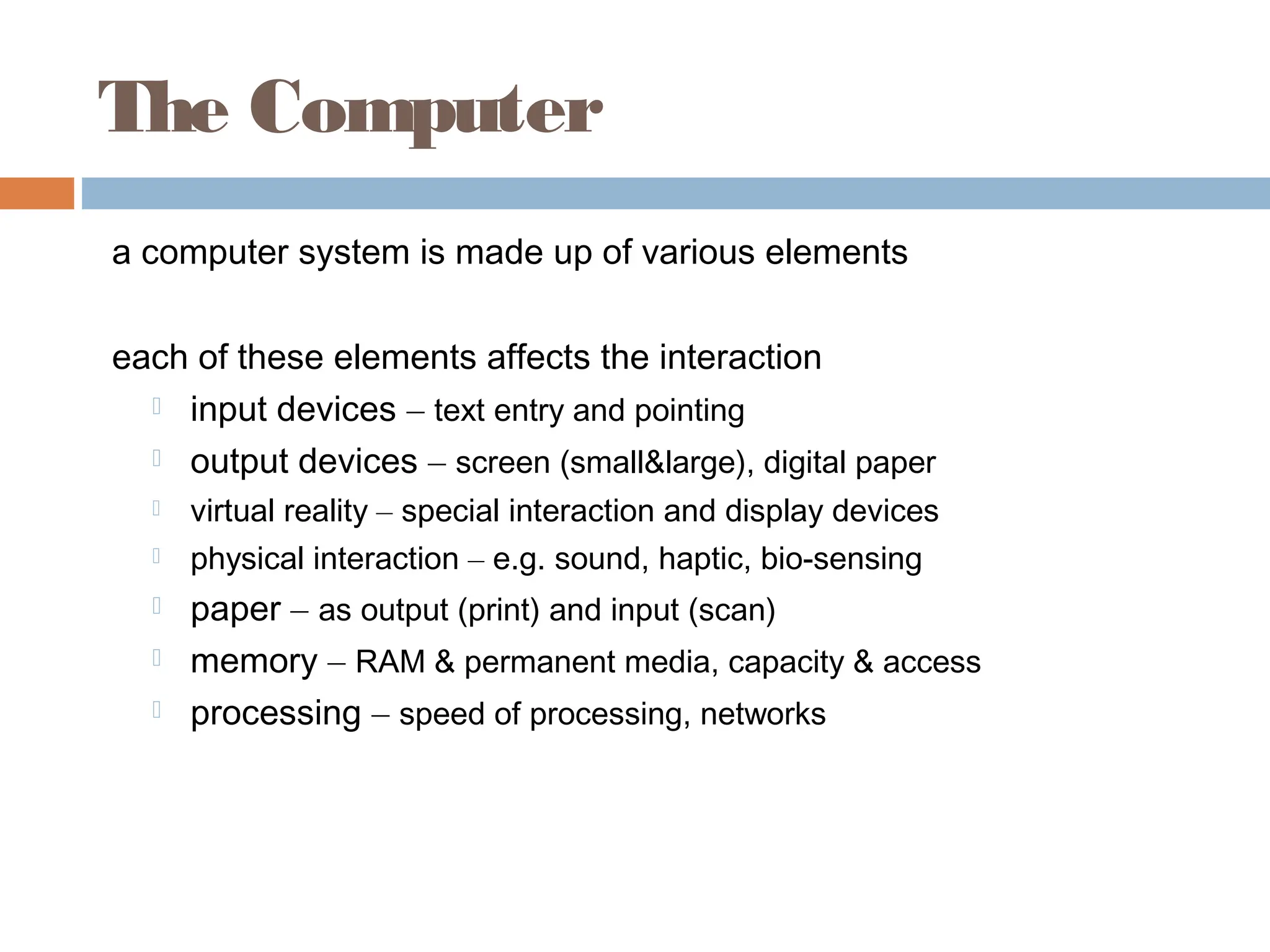
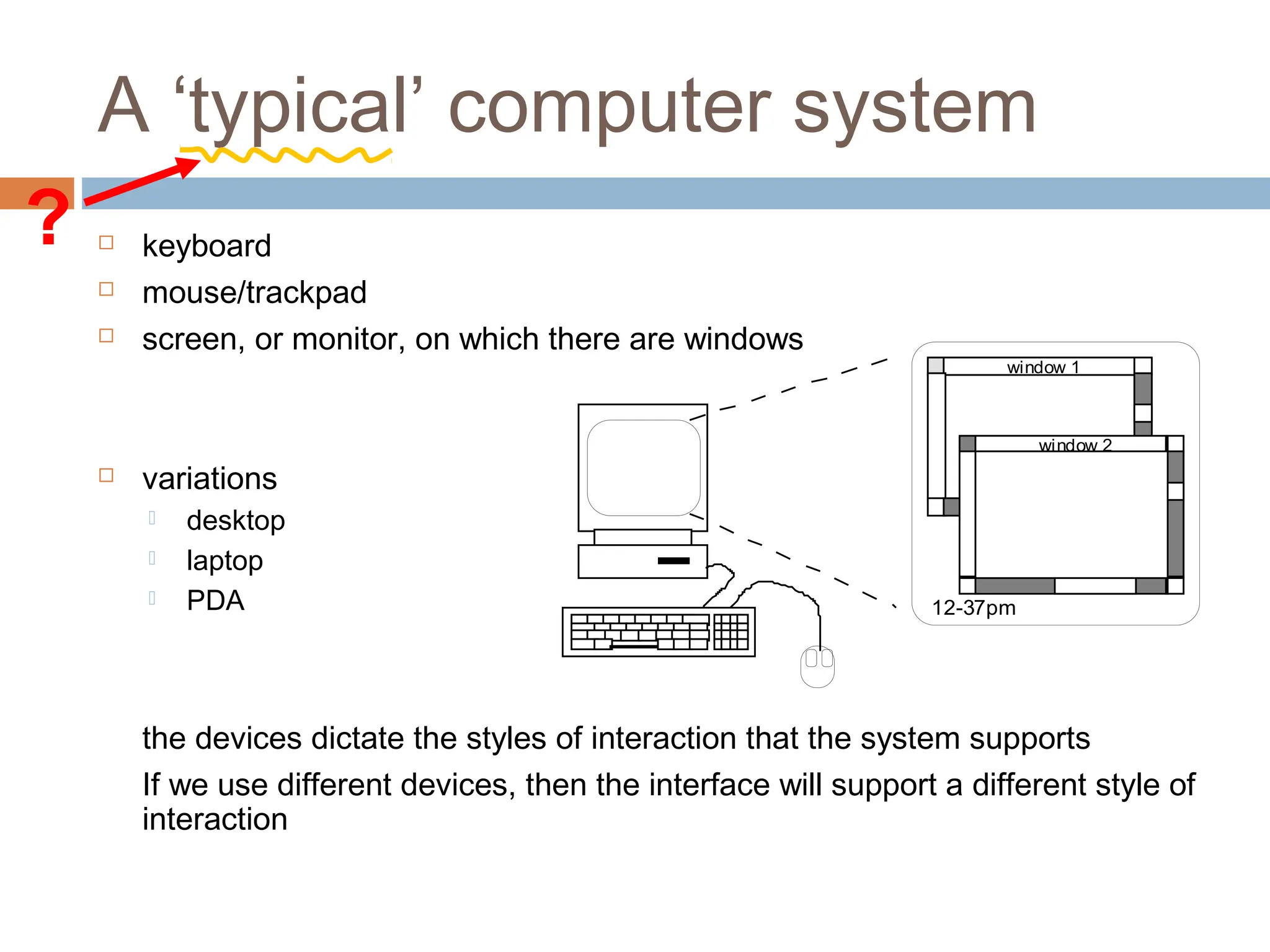
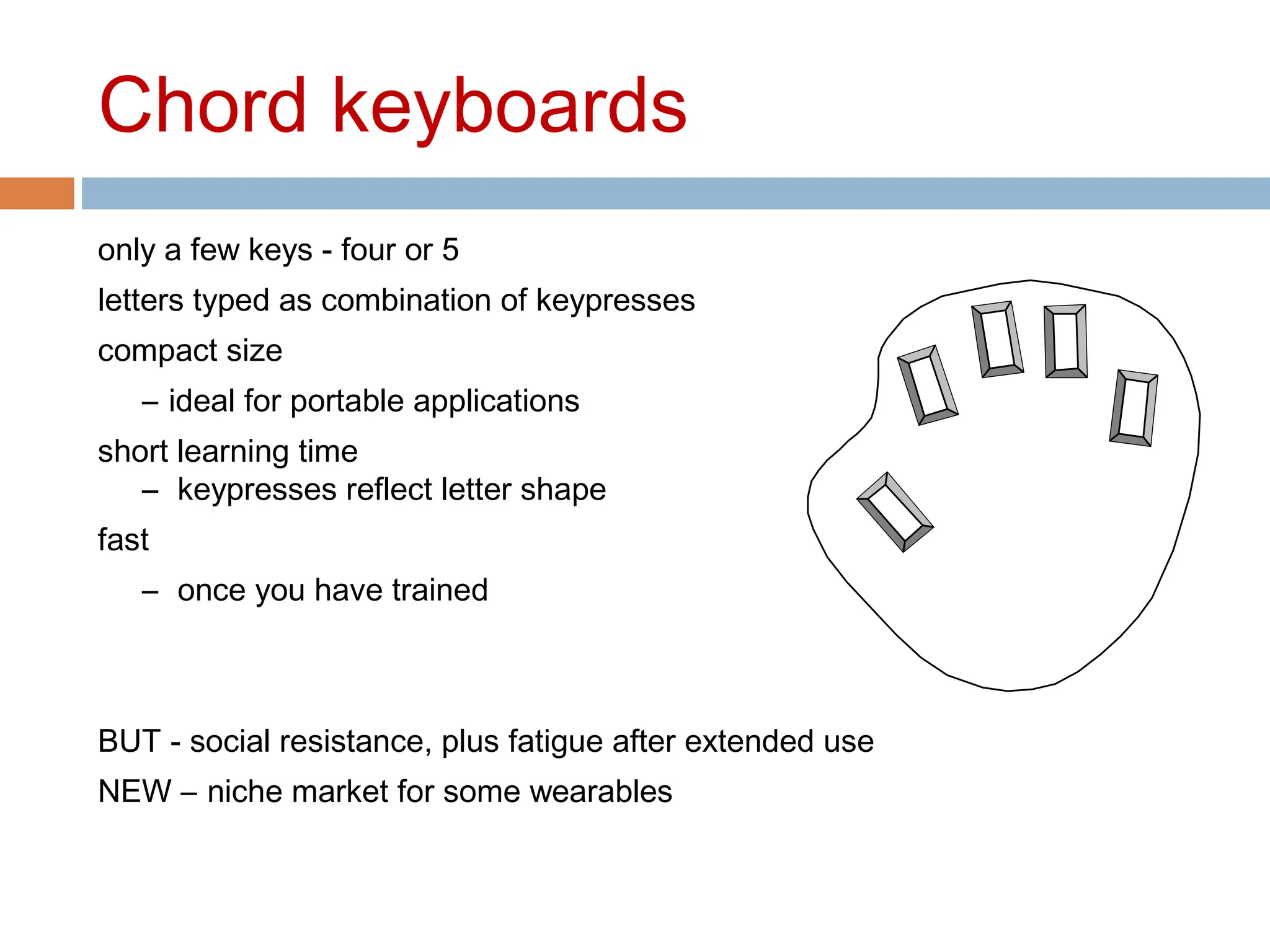
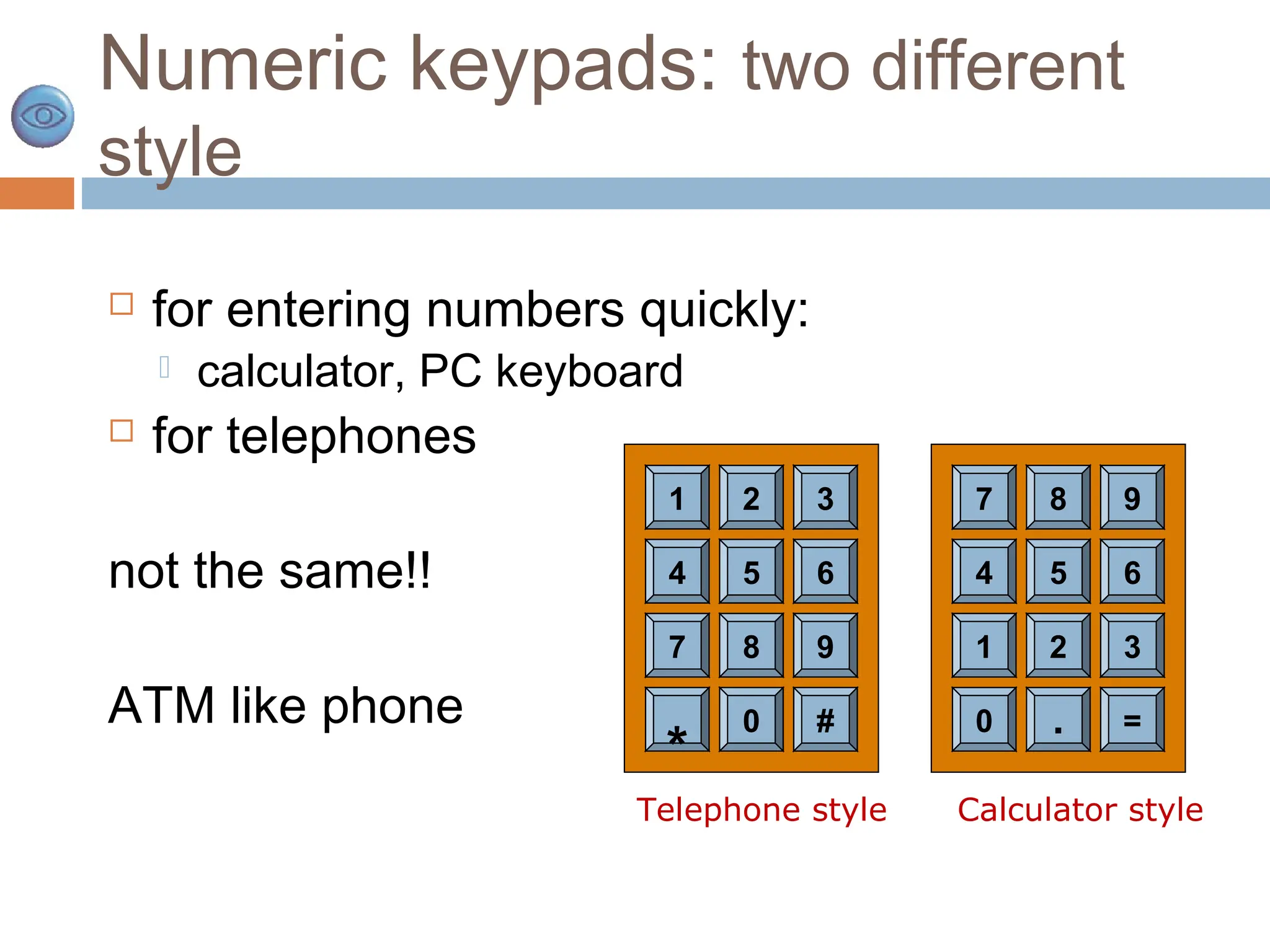
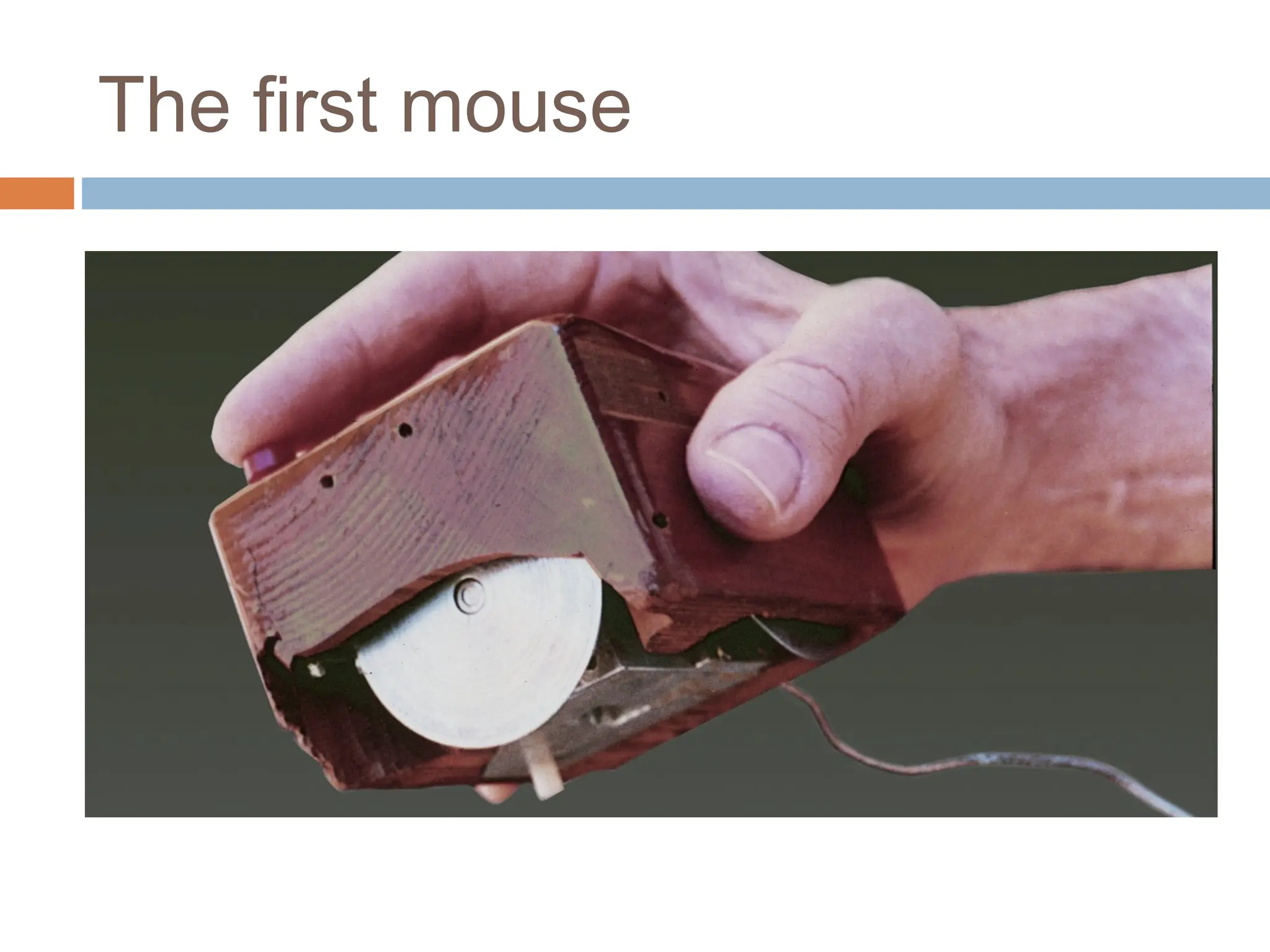
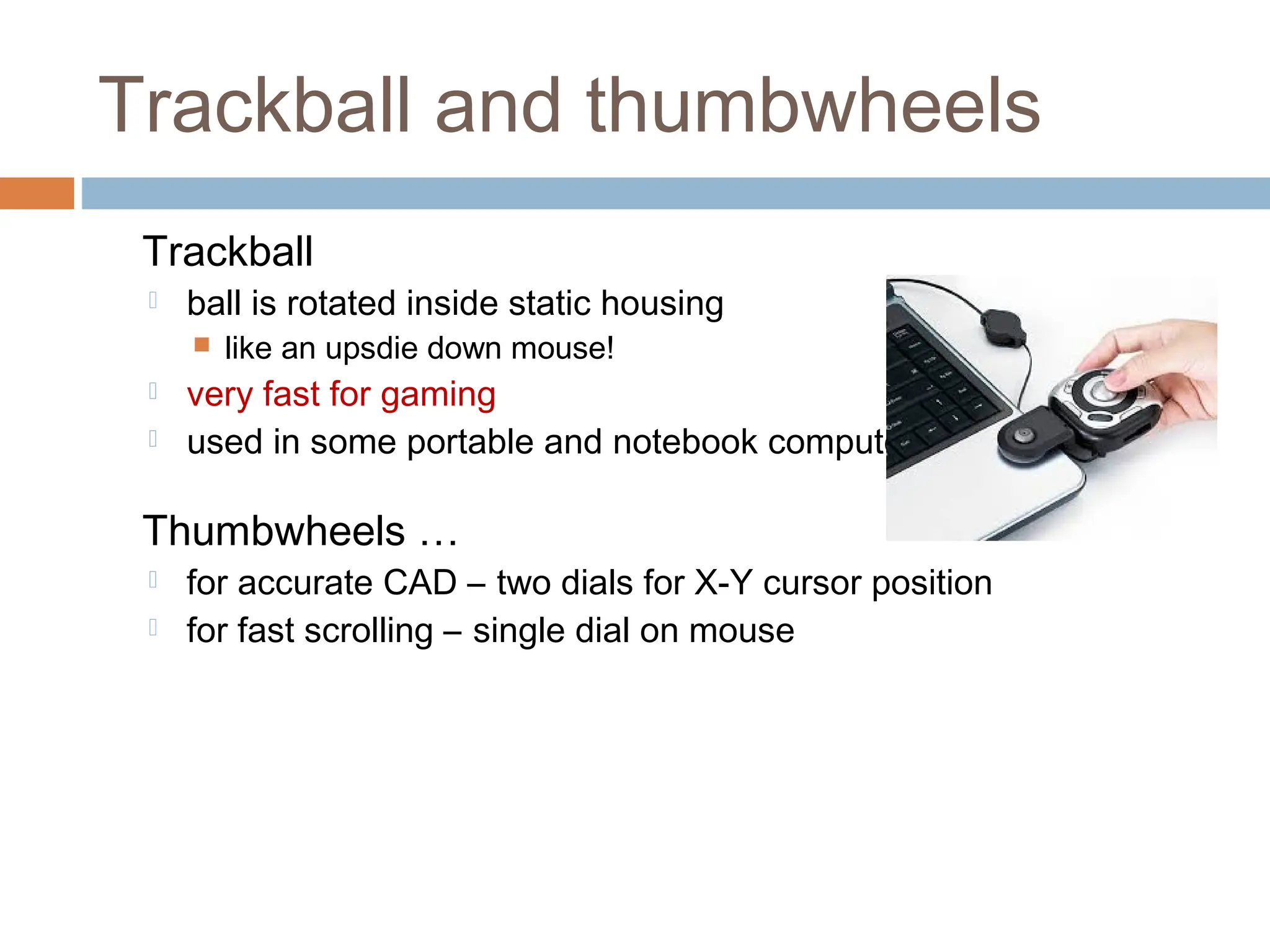
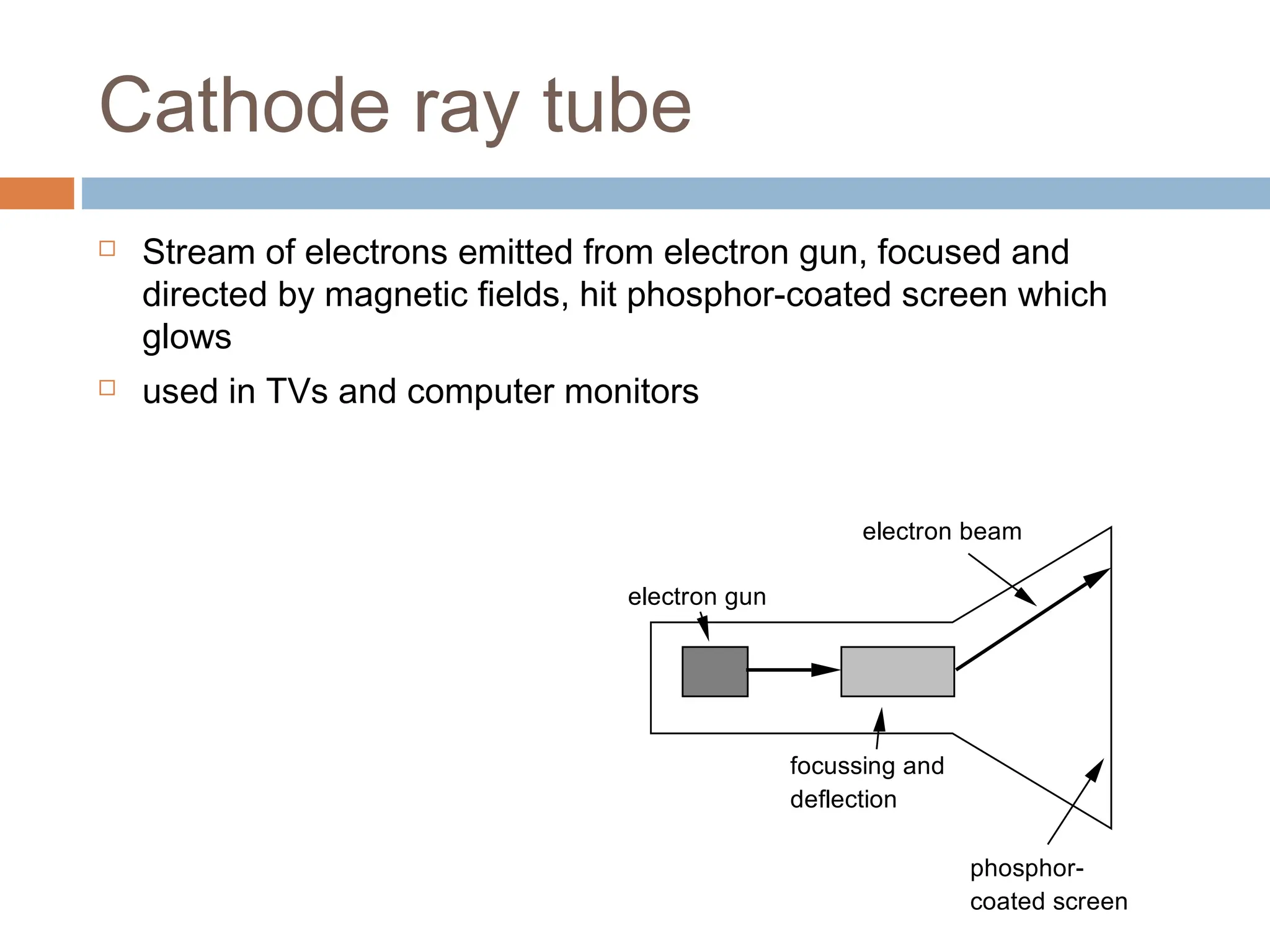
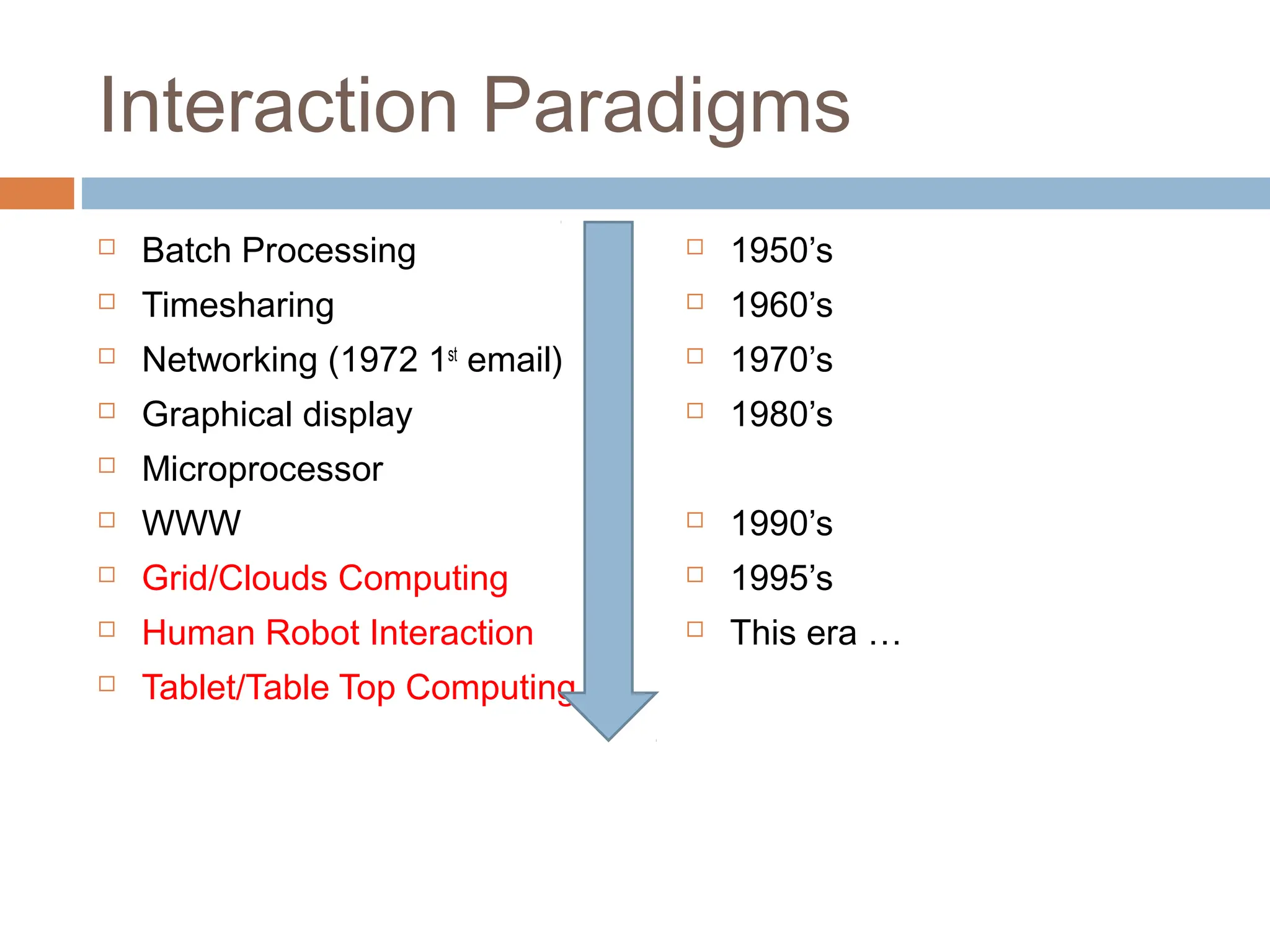
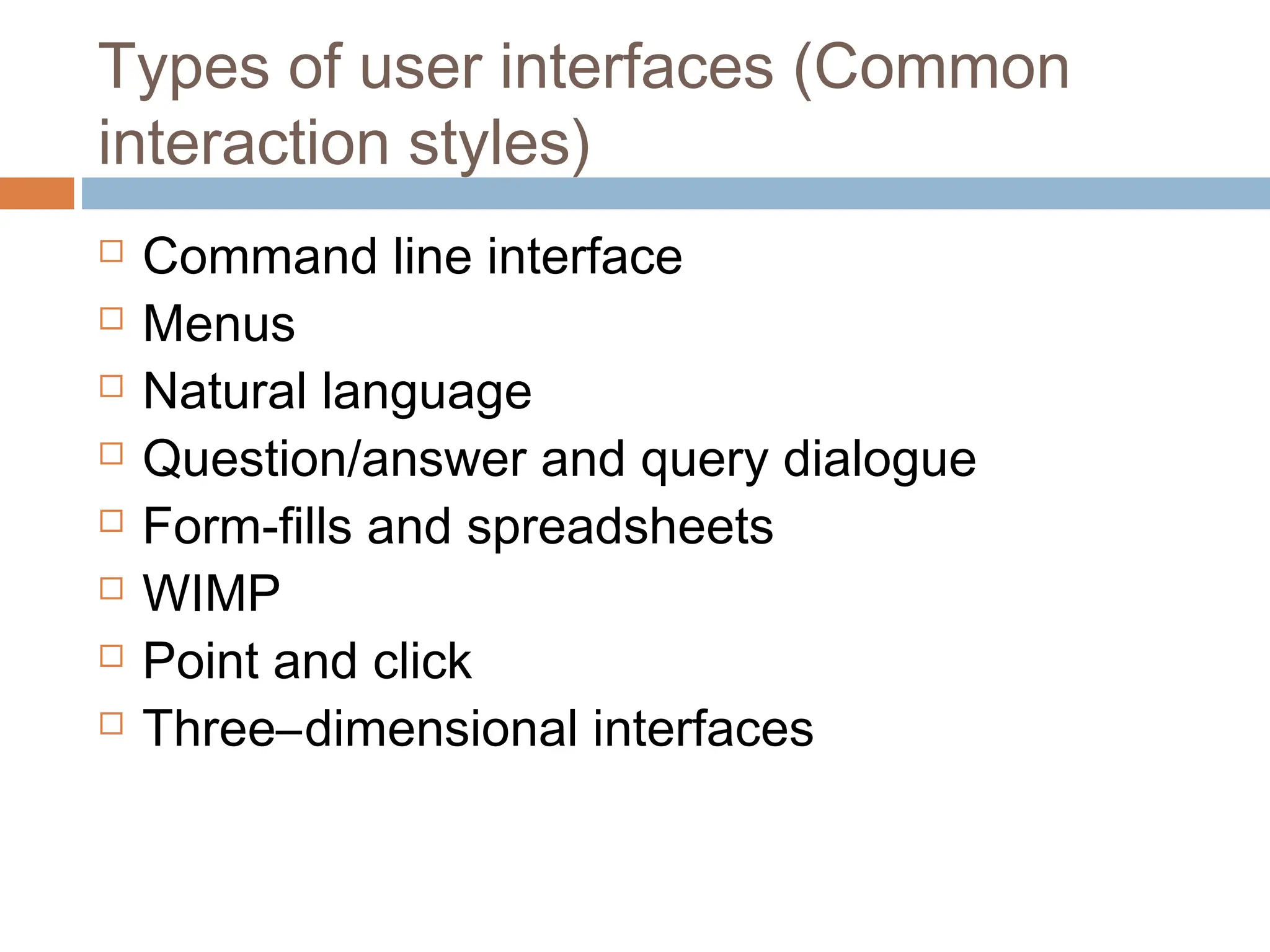
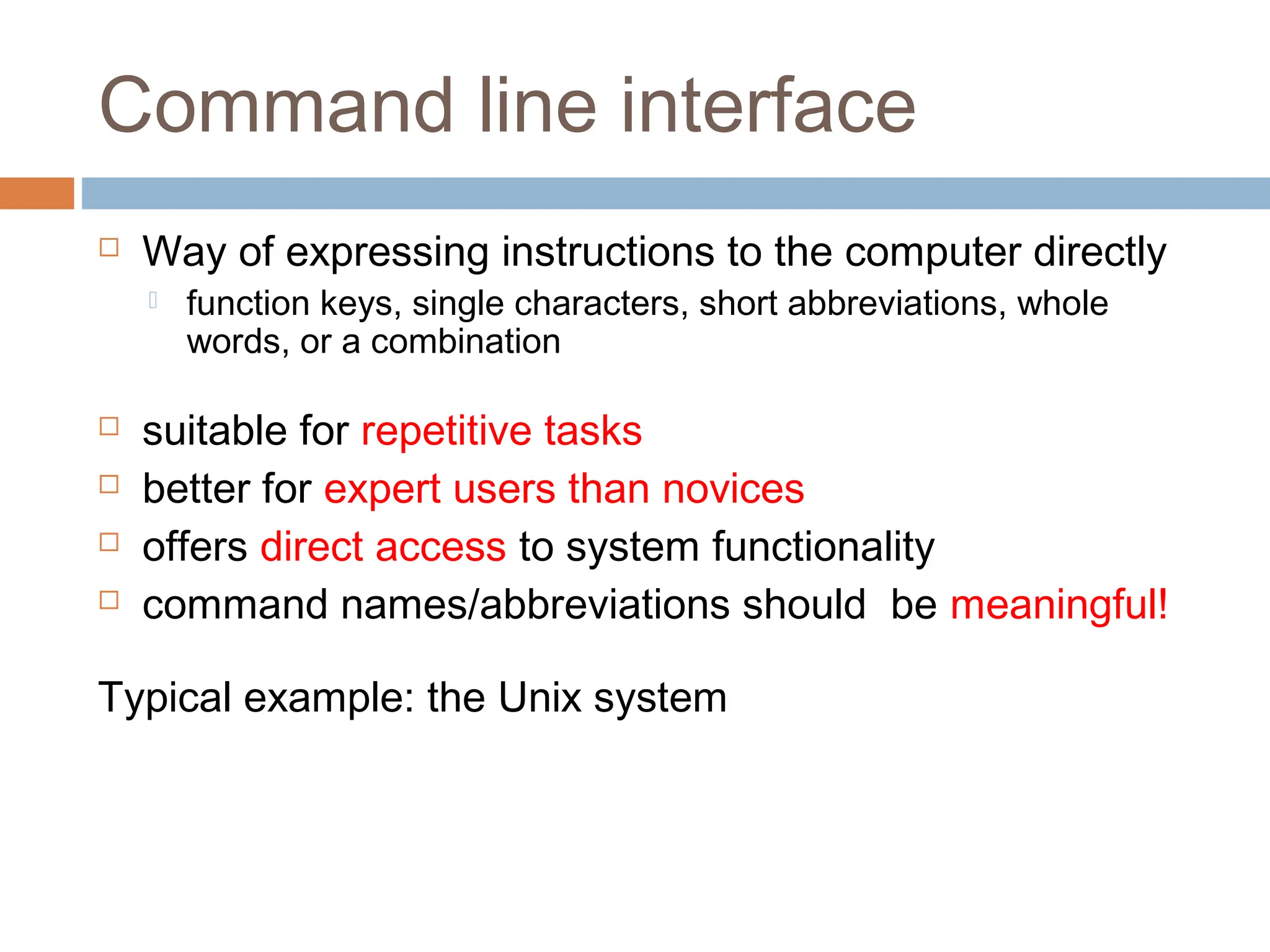
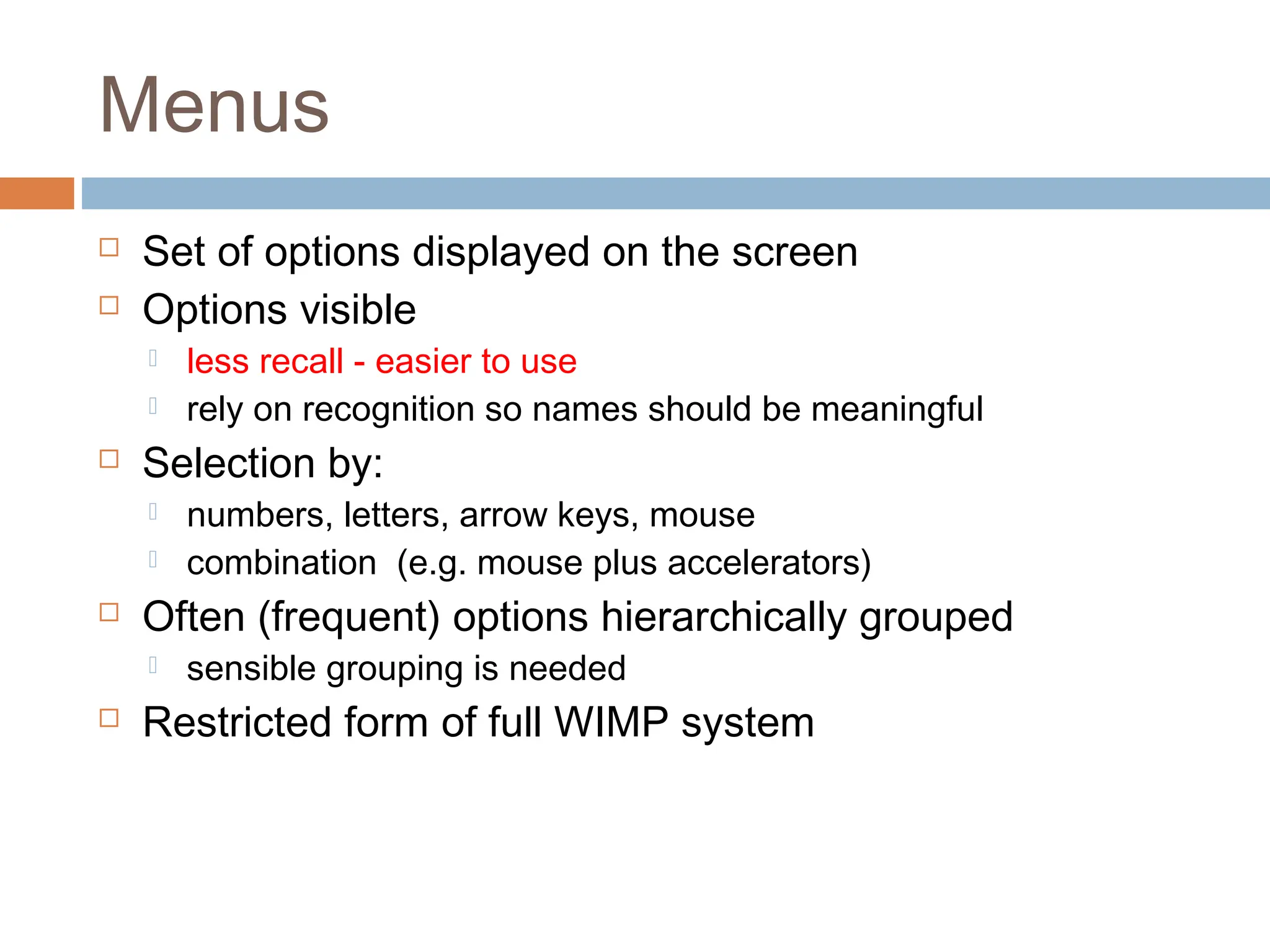
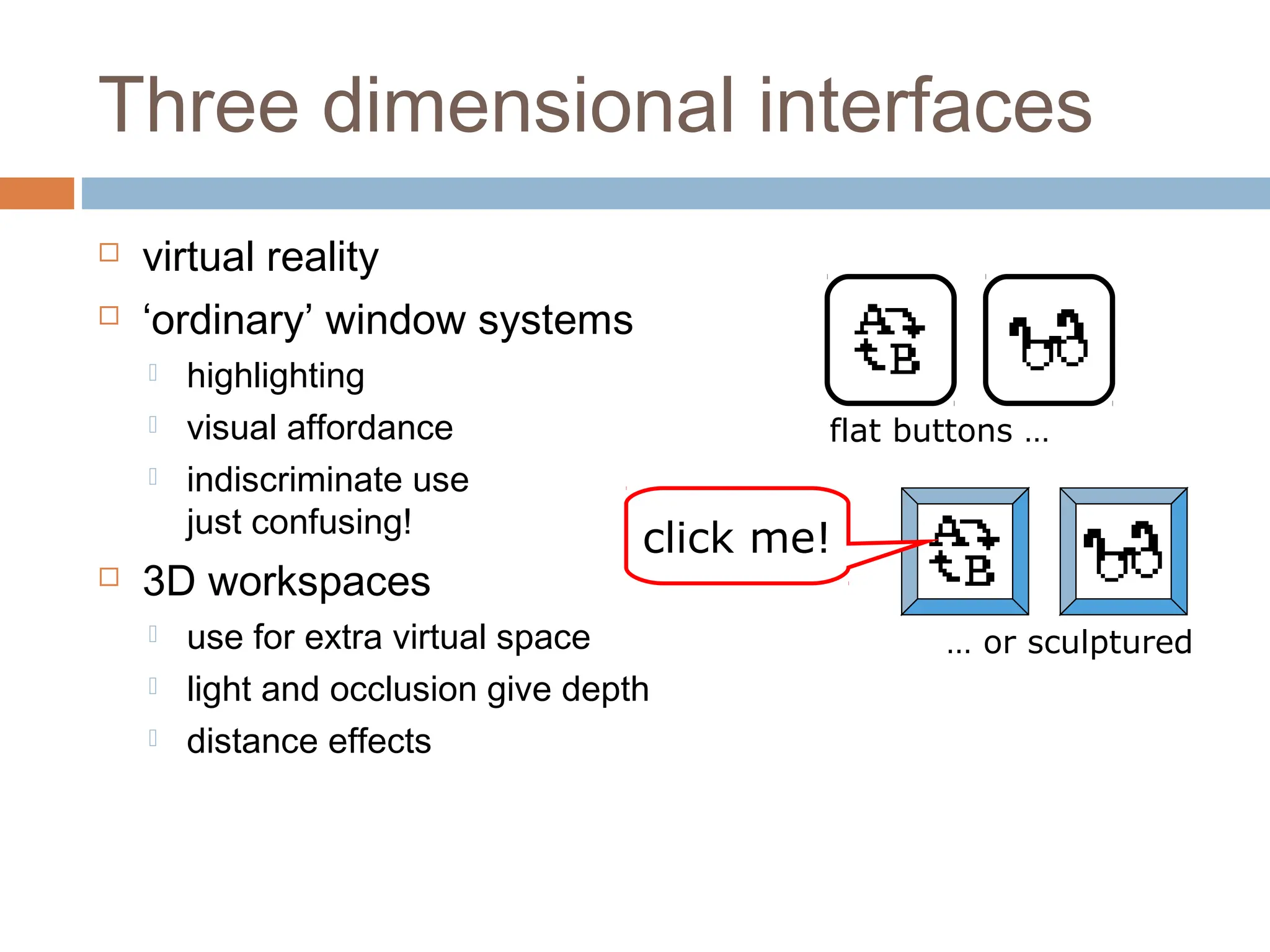
The document discusses the evolution and principles of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), starting from the early complexities of computers in 1945 to modern user interface design. It outlines essential components of HCI, including the importance of understanding human cognition and memory, as well as various interaction paradigms and user interface types. Furthermore, it highlights the significance of usability and design across different computer systems and input devices.