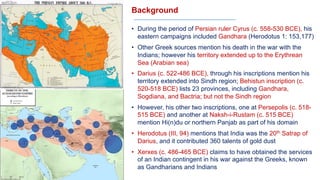
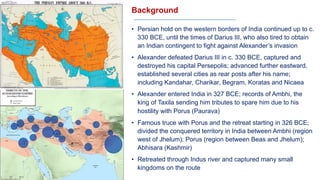
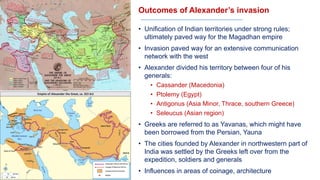
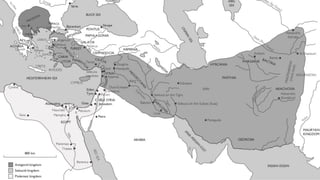
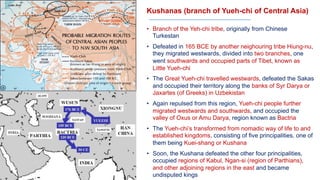
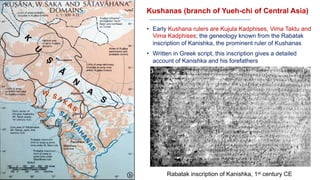
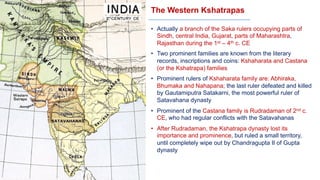
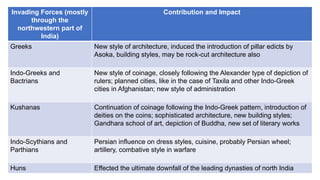
The document discusses various groups that invaded and migrated to India between 500 BCE to 500 CE, including Persians, Greeks, Indo-Greeks, Bactrian Greeks, Sakas, Parthians, Kushanas, Western Kshatrapas, and Huns. It provides background information on their origins and kingdoms, as well as their impacts such as establishing trade routes, advancing new architectural styles, and sometimes weakening existing empires in India. These invasions and migrations made India a melting pot of diverse cultures and religions.