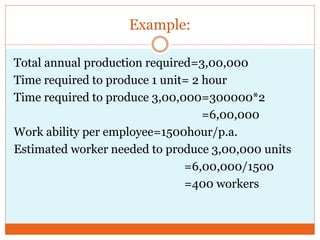
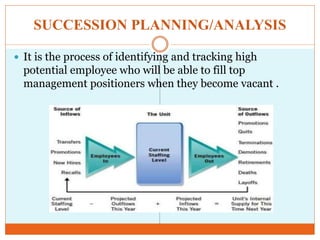
Human resource forecasting is the process of predicting the need for employees and their skills. Techniques for forecasting include managerial judgment (both bottom-up and top-down approaches), brainstorming, the Delphi technique, econometrics models, and work study techniques. Supply forecasting methods include trend analysis, competency models, replacement charts, and succession planning.