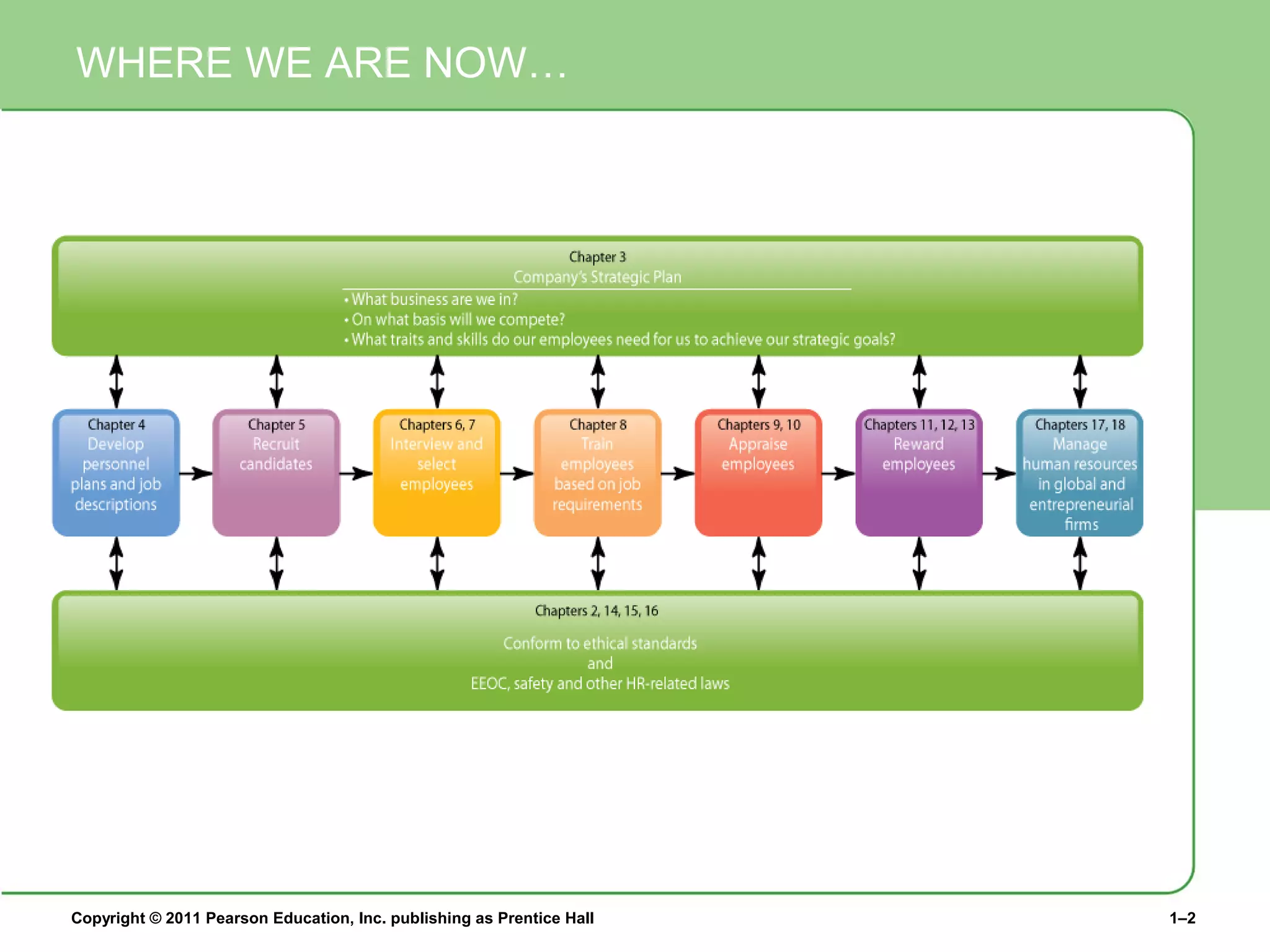
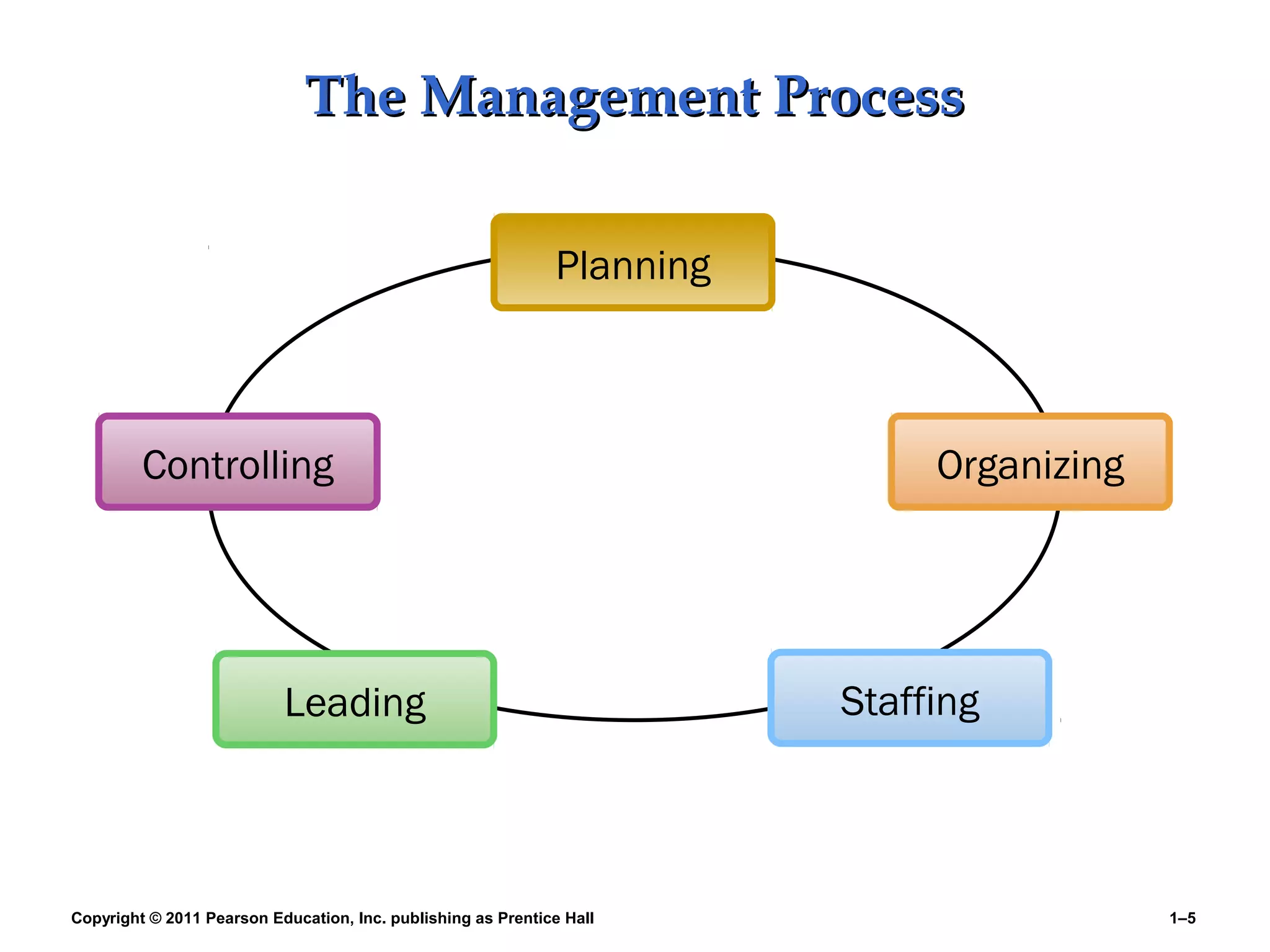
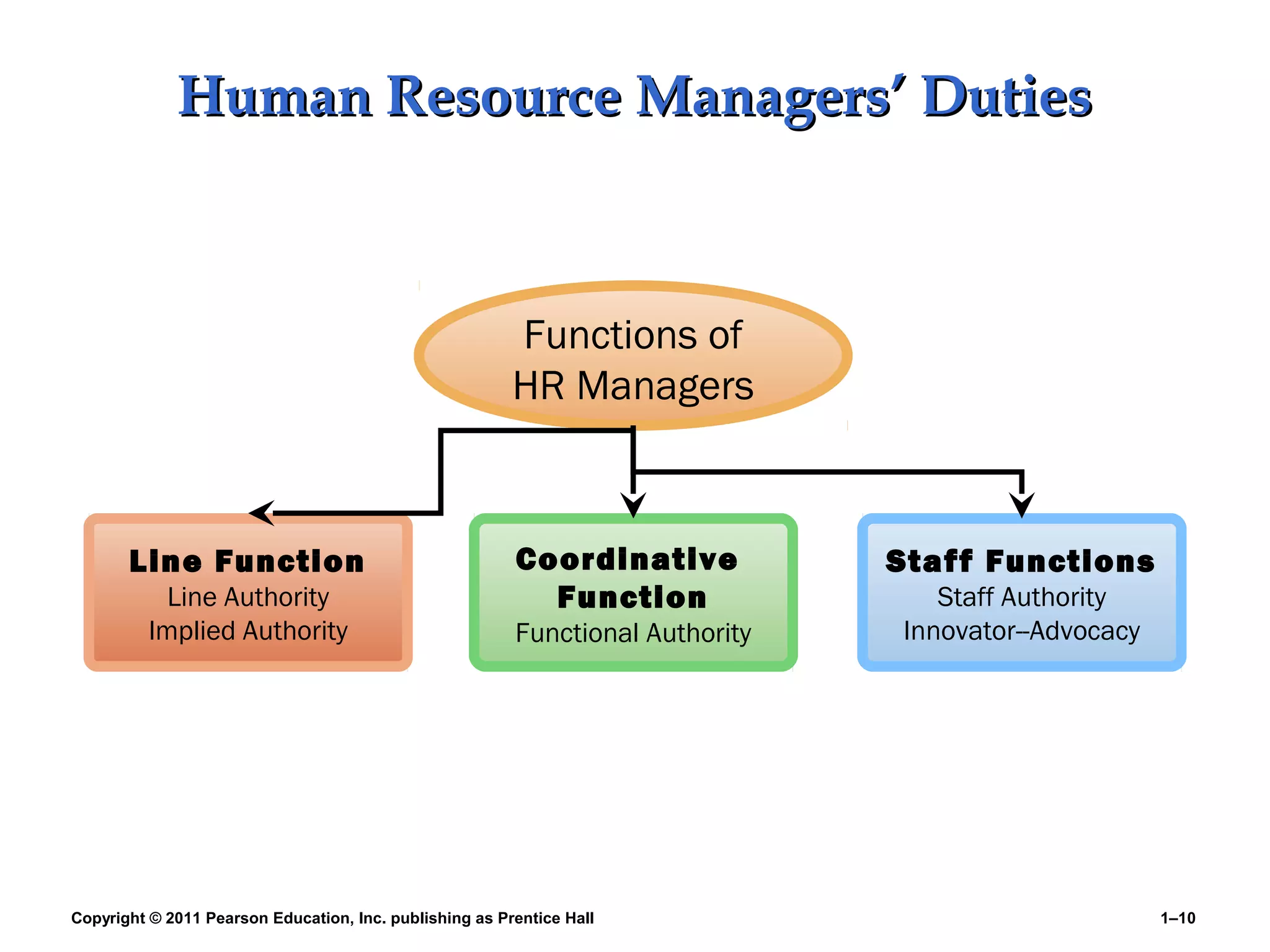
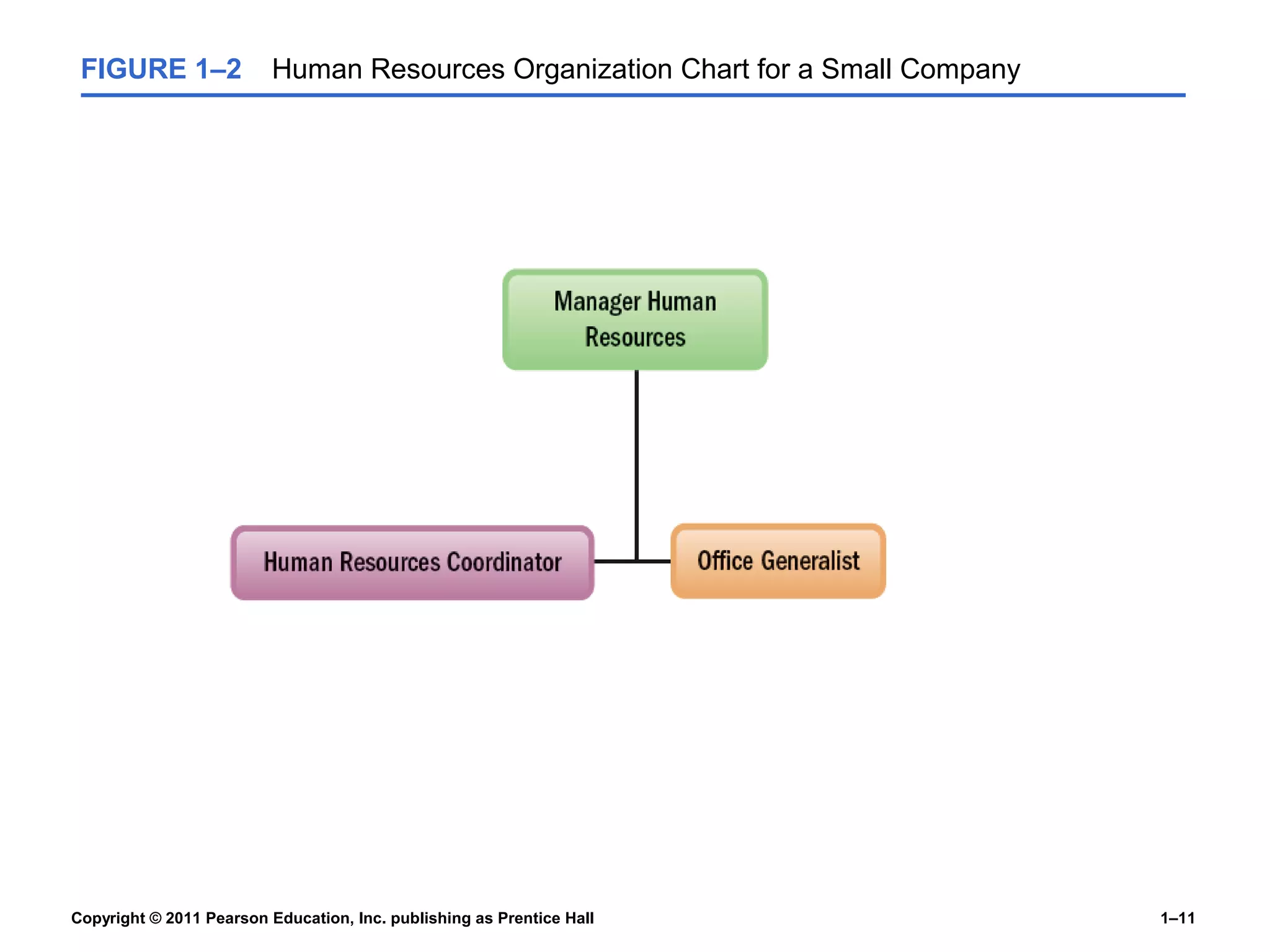
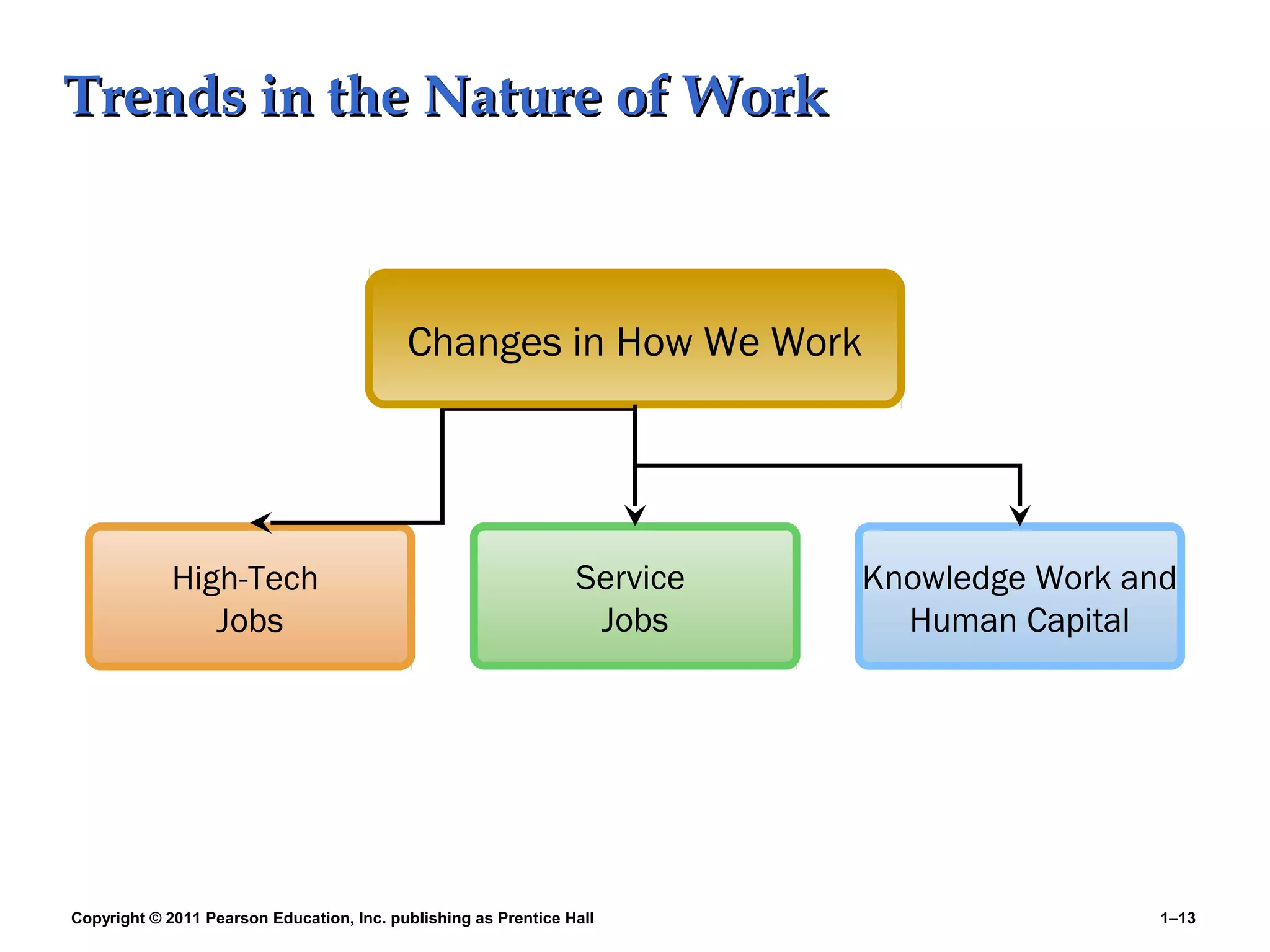
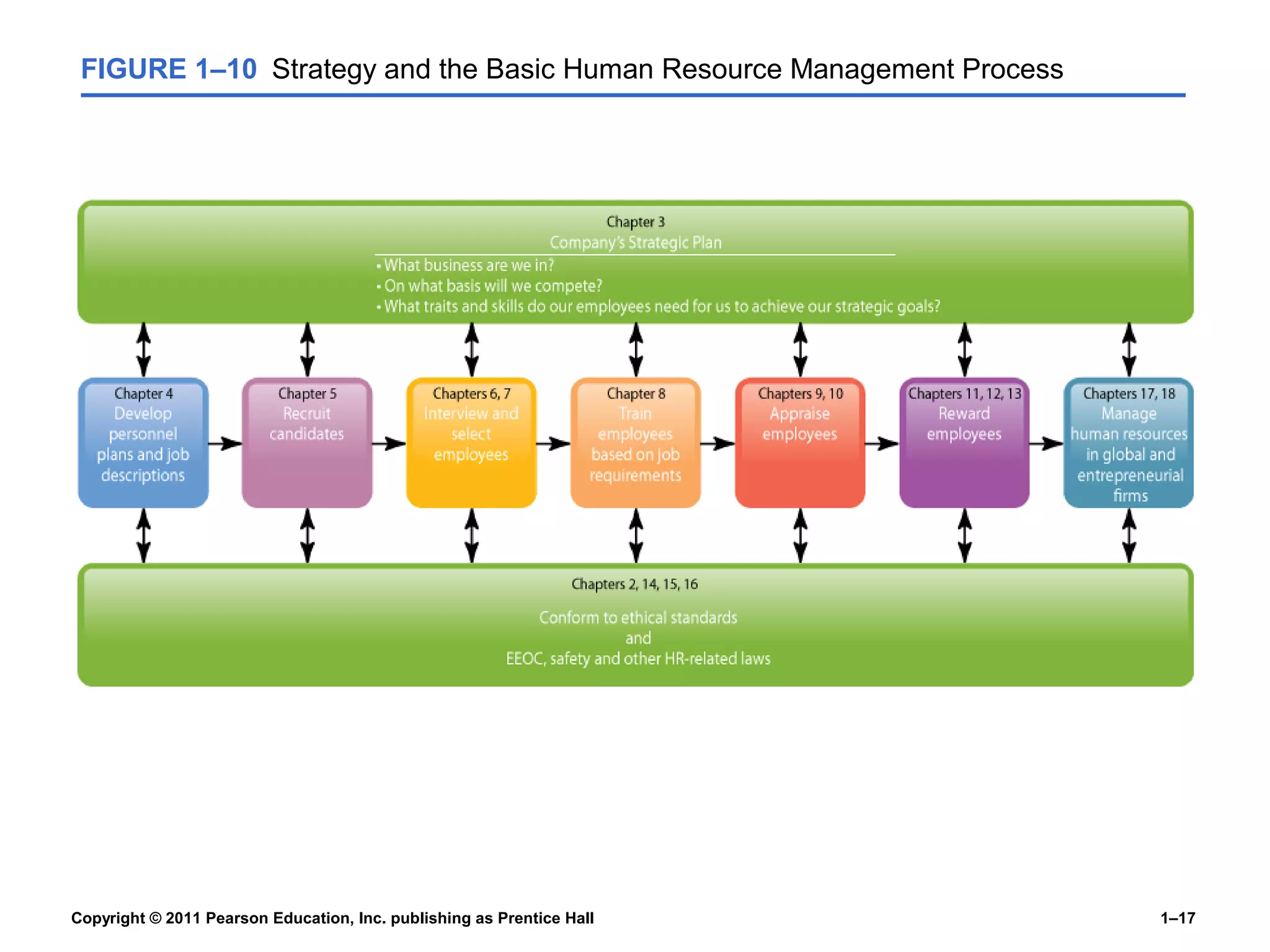
The document summarizes Charlie Cook's PowerPoint presentation on the introduction to human resource management. It defines key terms like HRM, organization, manager, and discusses the responsibilities of line and staff managers. It also outlines trends influencing HRM like globalization, technology, and the changing nature of work. Finally, it provides an overview of the book's basic themes which will examine how HRM is every manager's responsibility and how the workforce is becoming more diverse.