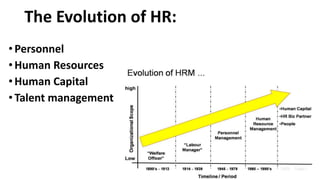
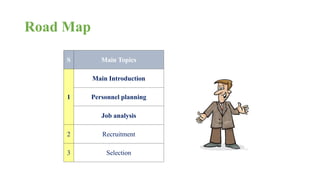
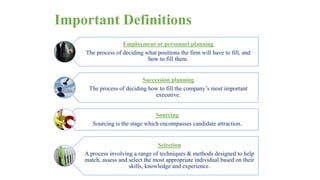
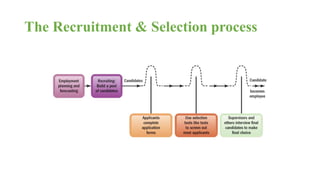
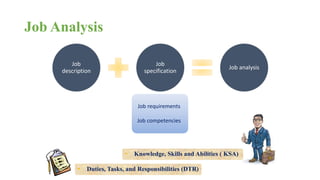
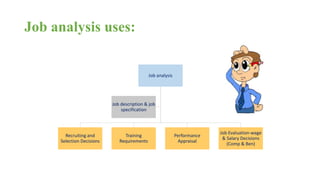
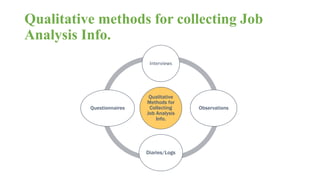
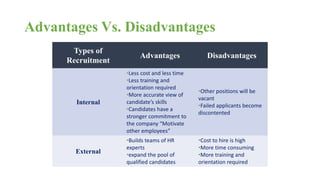
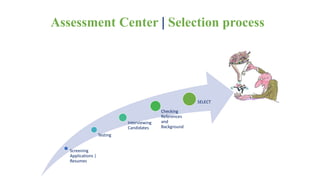
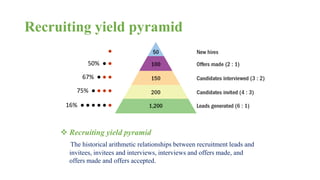
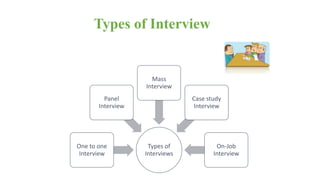
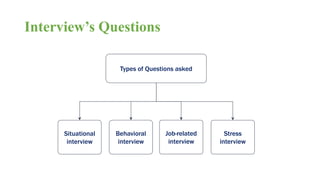
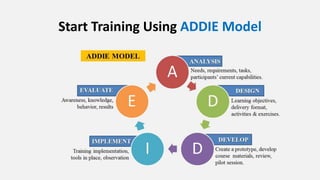
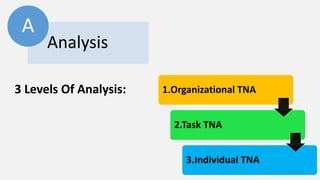
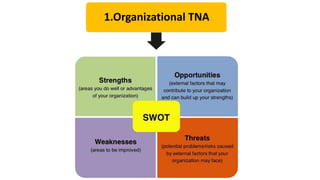
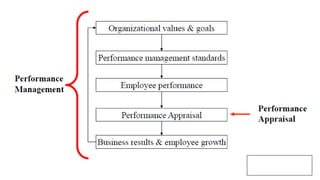
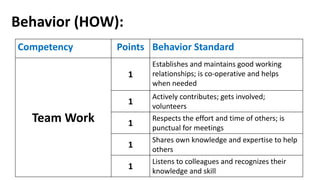
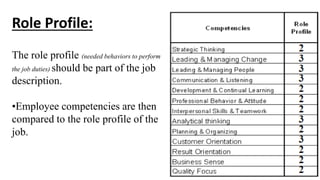
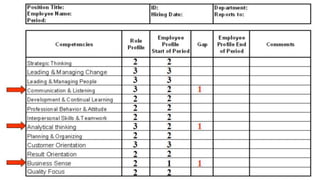
The document discusses HR management practices, including the purpose of HR functions, major HR functions, recruitment and selection processes, training and development, and performance management. Specifically, it covers topics such as job analysis, types of recruitment, interviewing best practices, training needs assessment, and training delivery methods. The overall purpose of HR according to the document is to hire, retain, and develop talents to achieve organizational goals.