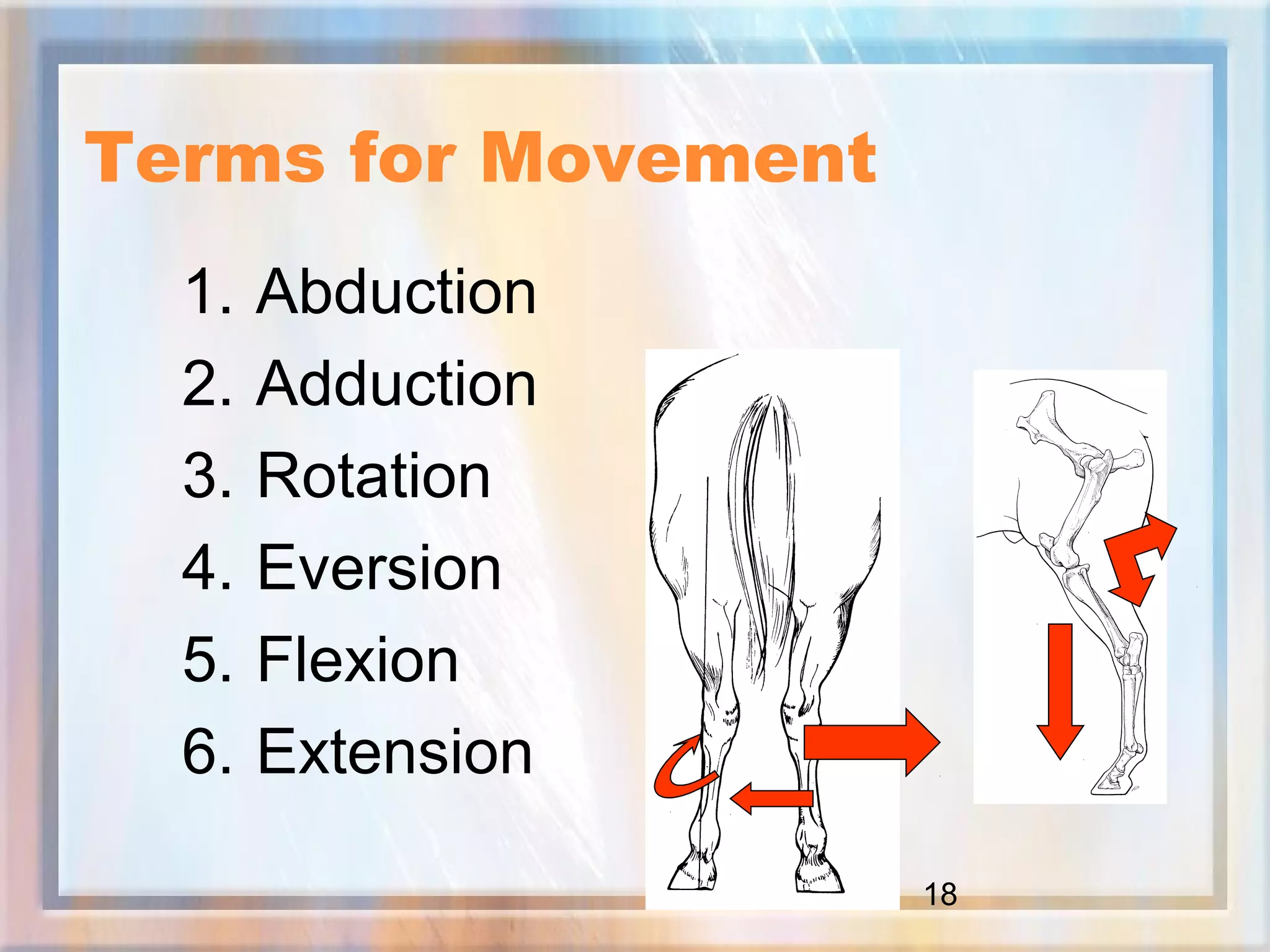
This document provides an overview of medical terminology used in various disciplines. It discusses prefixes, suffixes, and terms used for direction, position, movement, microbiology, pharmacology, and common medical terms. Key areas covered include suffixes for medical disciplines (-ology and -ologist), prefixes indicating direction and position, terms for numeric values, naming conventions for bacteria and viruses, and classifications of drugs. The document aims to familiarize the reader with fundamental terminology across different areas of medicine.