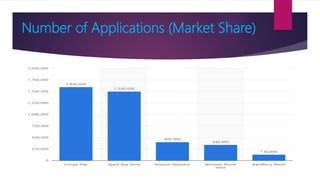
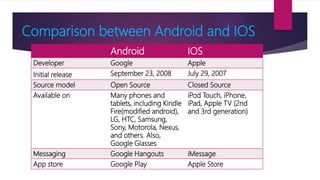
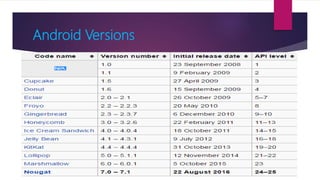
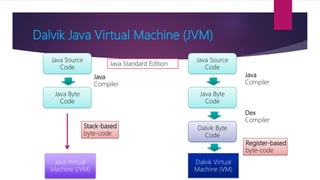
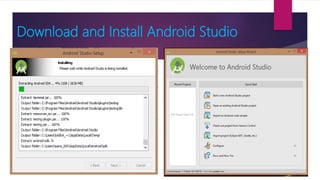
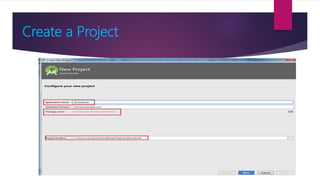
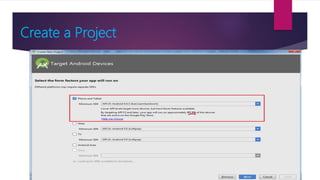
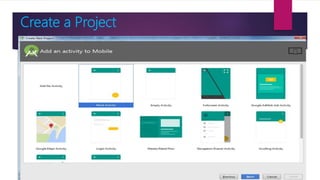
The document provides information on how to become an Android developer. It begins with an introduction by the author and then outlines the agenda which includes understanding the differences between smartphones and feature phones, sample apps and startups, operating systems like Android and iOS, how to earn money from apps, and how to get Android developer jobs. It then dives deeper into topics like what Android is, its architecture, how to learn programming basics in Java, how to connect designs to programming using activities and layouts, and how to connect apps to databases. The document provides resources for people to get started in app development and includes contact information for the author.