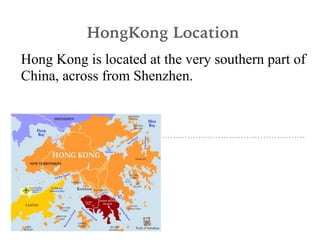
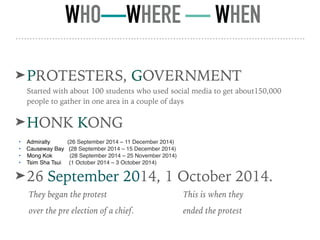
The Hong Kong protests in 2014 were sparked by Chinese interference in Hong Kong's elections. Over 150,000 protesters gathered in Hong Kong over several months to protest China's involvement and assert Hong Kong's independence. The protests were a response to Beijing's plan to pre-screen candidates for the city's executive elections. While the protests ended without achieving electoral reforms, they highlighted tensions over Chinese encroachment on Hong Kong's autonomy and democratic freedoms.