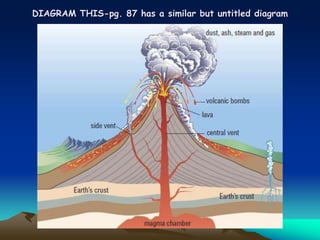
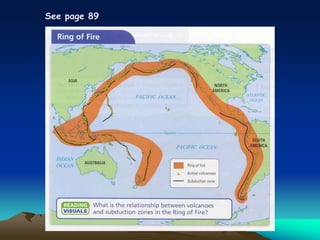
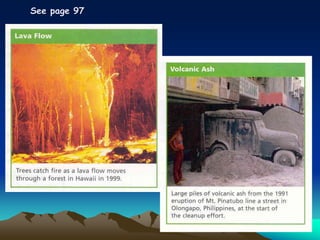
Volcanoes form at plate boundaries and hot spots where magma rises from below the Earth's crust. There are three main types of volcanoes - shield volcanoes which are wide and gently sloping due to low viscosity basaltic lava flows, cinder cone volcanoes which are steep-sided due to explosive eruptions of thicker granitic lava, and composite volcanoes which have characteristics of both types. Factors like the amount of trapped gases and magma viscosity determine eruption styles from quiet effusions to violent explosions. Major volcanic hazards include lava flows, ash falls, pyroclastic flows, landslides, and tsunamis. Scientists monitor volcanoes for warning signs of impending eruptions.