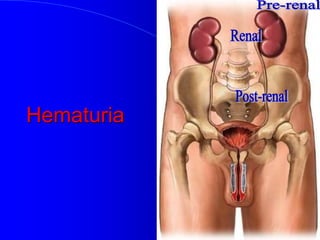
This document discusses the importance of history taking in reaching a diagnosis. It notes that history taking accounts for about 71.7% of making the correct diagnosis. The goals of history taking are listed as building rapport with the patient, formulating a workup plan, reaching a diagnosis, planning management, and creating a medical legal document. Specific tips are provided on how to conduct the history such as introducing yourself, paying full attention to the patient, and allowing family to be present if desired. The classical components of a history are outlined including chief complaint, history of present illness, past medical history, family history, review of systems, social history, drug history and allergies. An example history of hematuria is also provided as