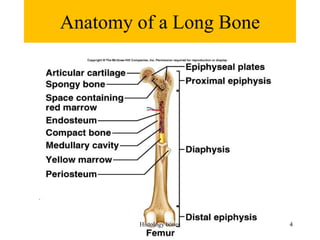
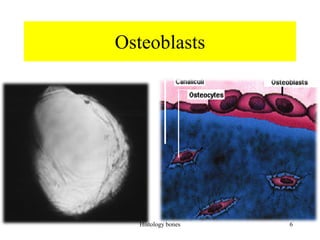
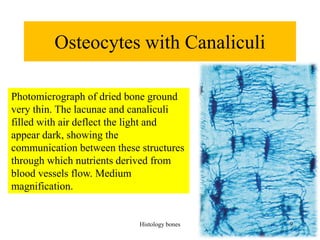
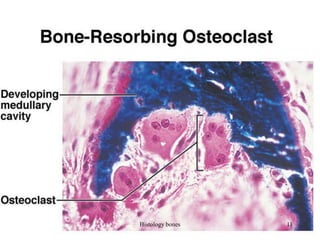
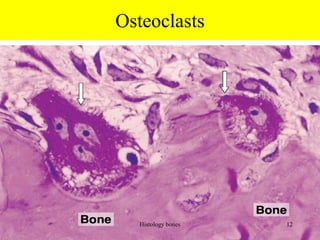
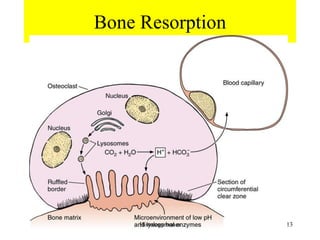
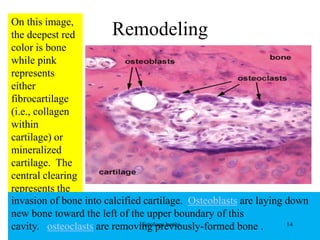
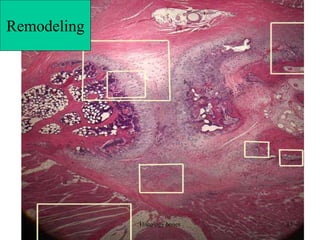
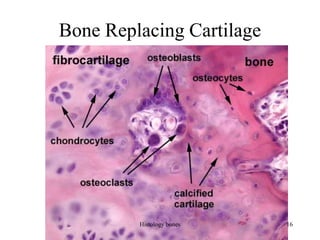
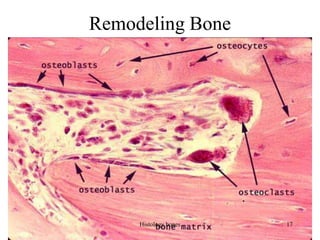
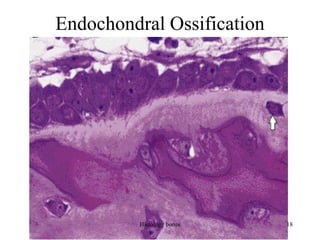
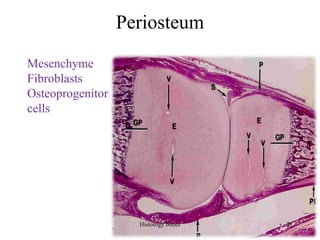
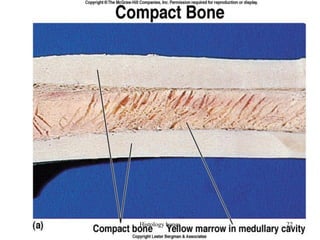
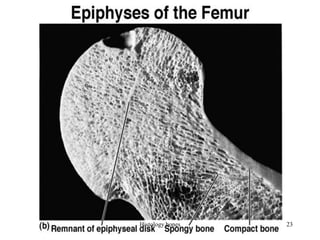
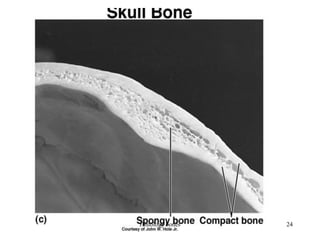
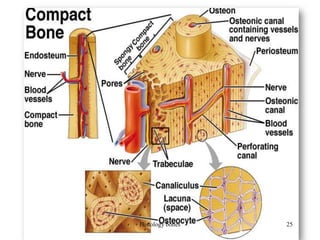
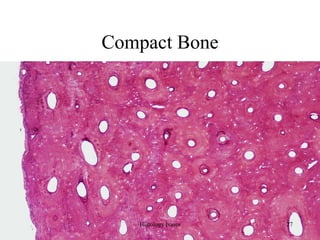
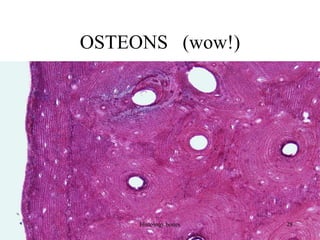
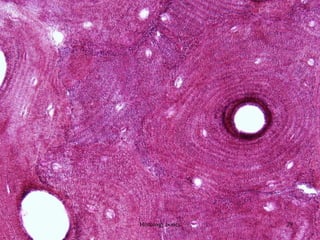
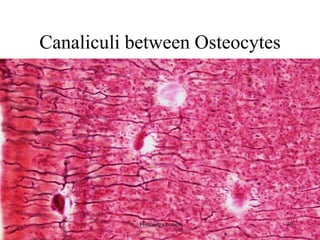
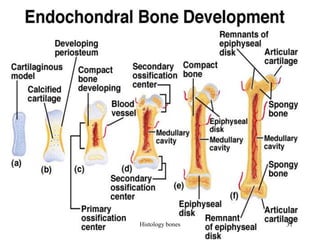
This document discusses the histology of bone. It covers the functions of bone including support, protection, containing bone marrow, and allowing movement. It describes the specialized cells and tissues of bone, including osteoblasts that form bone, osteocytes within the bone matrix, and osteoclasts that resorb bone. The document discusses bone anatomy, the remodeling process, endochondral ossification, and features of compact bone such as osteons and canaliculi connecting osteocytes.