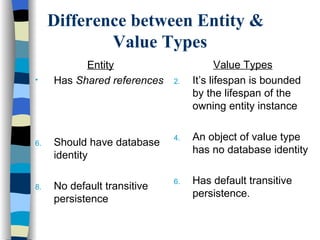
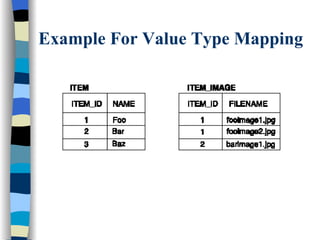
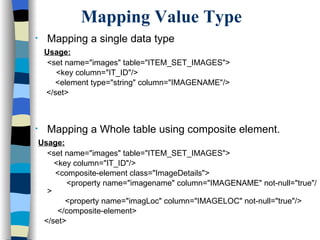
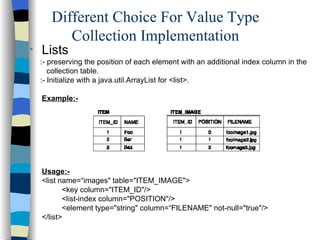
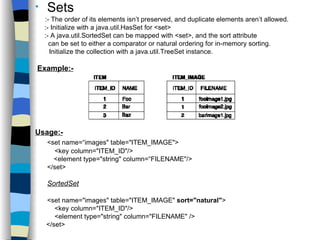
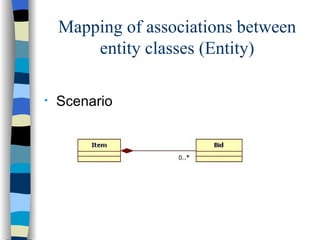
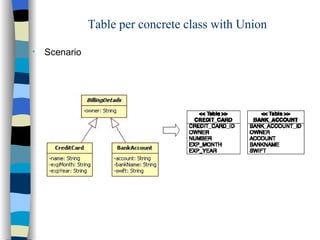
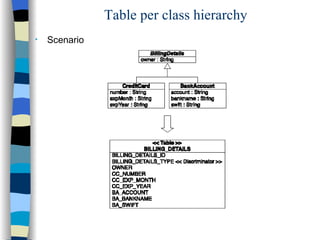
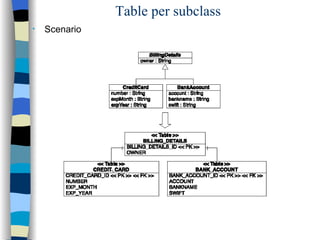
The document discusses different approaches for mapping entity and value types, collections, and associations between entity classes in Hibernate. It provides examples of mapping value type collections as lists, sets, maps, and bags. For entity associations, it demonstrates one-to-many and many-to-one mappings. It also summarizes different inheritance mapping strategies in Hibernate like table per concrete class, table per class hierarchy, and table per subclass.