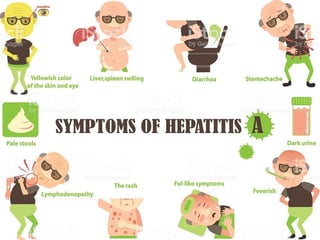
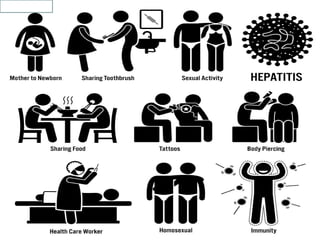
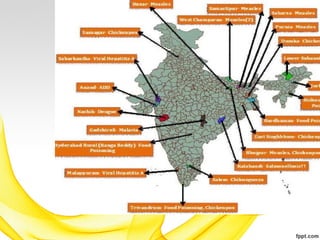
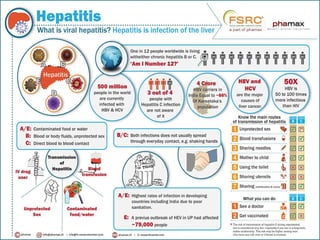
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that can be caused by viruses or toxic substances like alcohol. There are 5 main types of viral hepatitis: A, B, C, D and E. Hepatitis A and E are typically acute diseases spread through contaminated food or water while B, C and D can result in chronic infections spread through blood or bodily fluids. The document outlines the causes, transmission, and prevention of hepatitis A and B. It notes that viral hepatitis poses a serious public health problem in India, where millions are infected with hepatitis B and most are unaware. The Sustainable Development Goals include a target to end viral hepatitis epidemics by 2030 through strategies like increasing treatment rates.