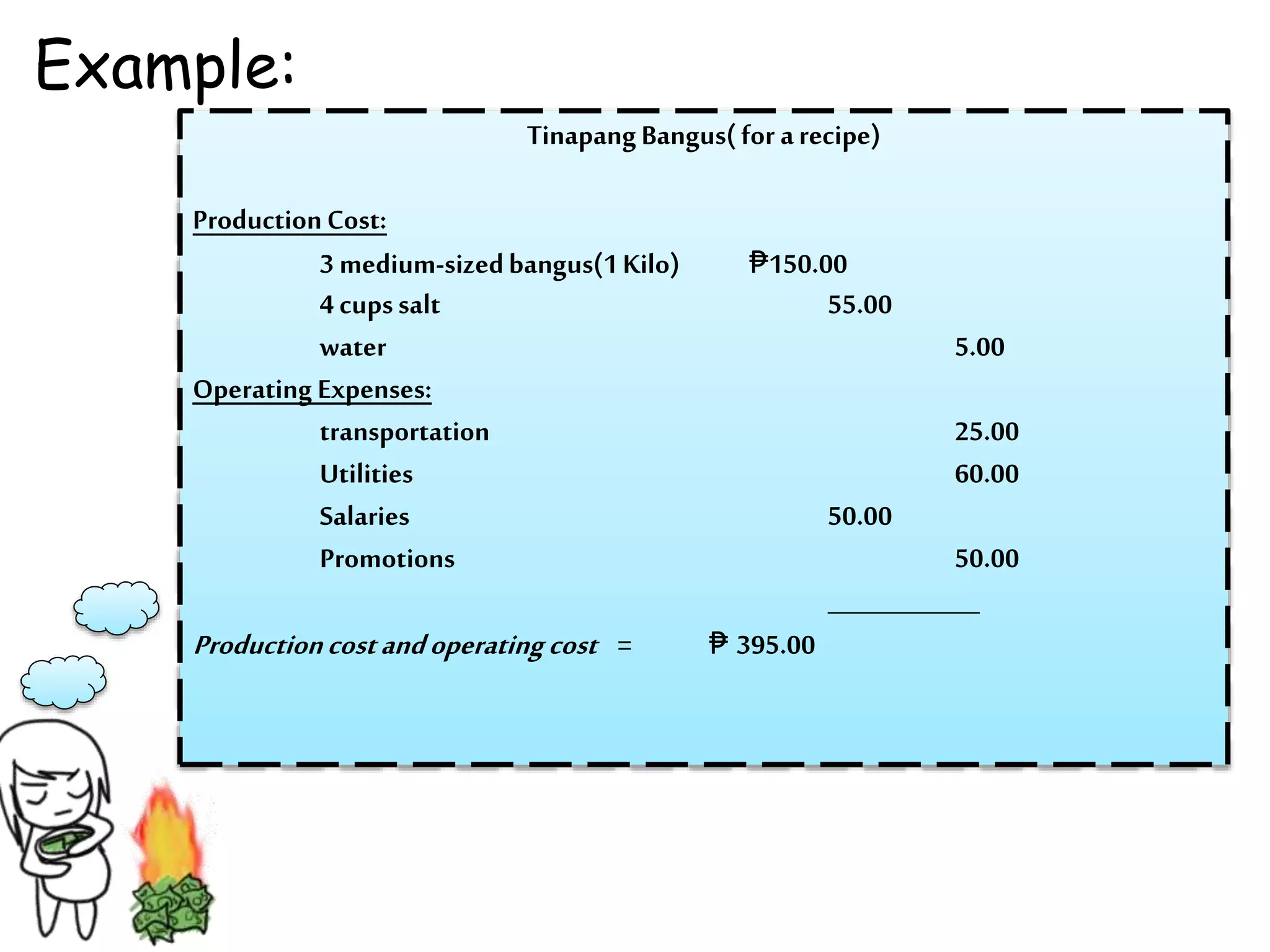
Fish and shellfish play an important role in livelihoods and economies. There are several methods for processing fish and shellfish to preserve them, including freezing, smoking, drying, curing, and canning. Each method has advantages and effects on the flavor, quality, and shelf life of the processed fish or shellfish. Proper processing, packaging, pricing, and marketing of fish and shellfish products are necessary to maintain or improve quality and earn a profit.