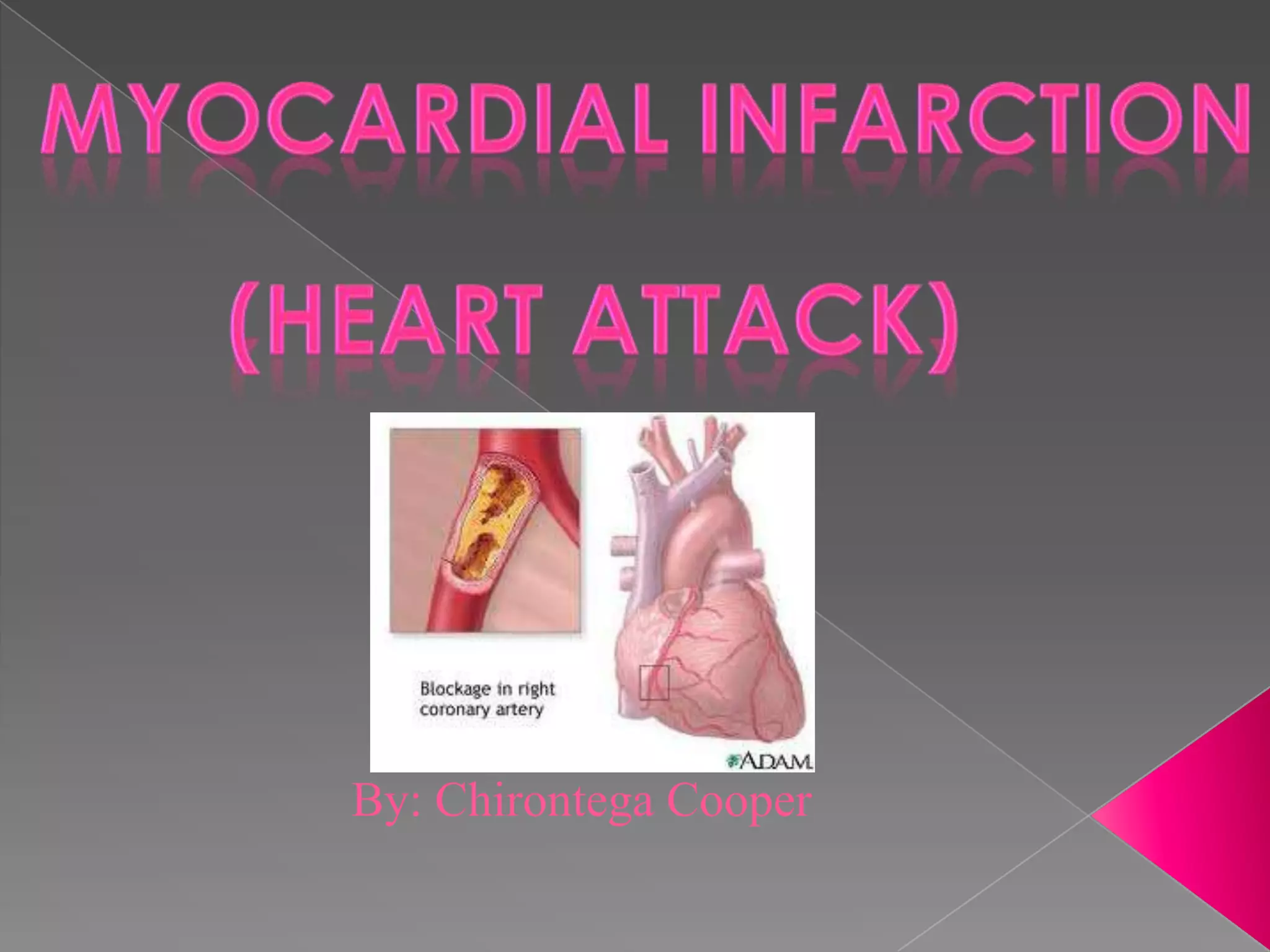
Myocardial infarction, also known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow to the heart is suddenly blocked, reducing oxygen levels and causing the heart to stop working normally. It is the leading cause of death in the United States, with over 1.5 million Americans experiencing heart attacks each year. Common symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, and fainting. Major risk factors include smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity, and heavy alcohol use. Treatment focuses on restoring blood flow and oxygen to the heart through medications and fluids administered intravenously while monitoring the patient in the hospital.