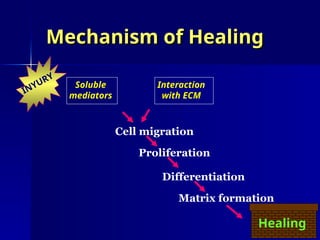
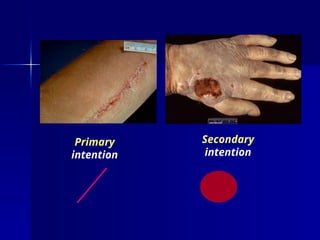
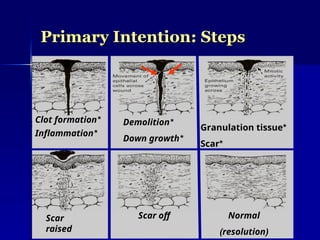
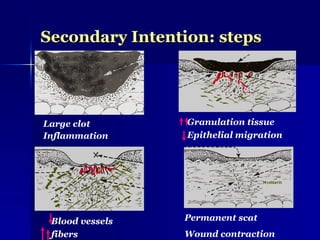
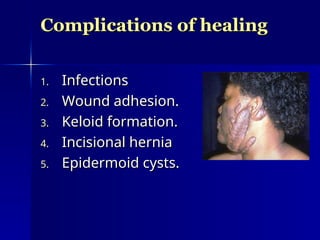
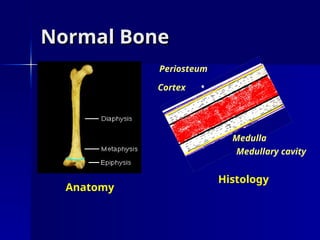
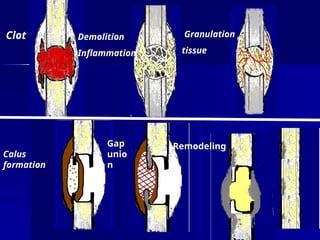
The document discusses the mechanisms of healing and repair in tissues, outlining three processes: healing, repair, and regeneration. It details wound healing types, including primary and secondary intention, and describes the phases involved in each. Additionally, it highlights factors that delay healing and potential complications that may arise during the process.