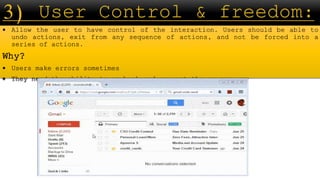
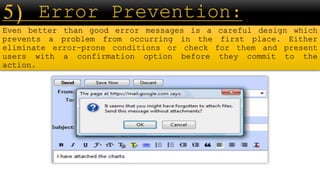
The document outlines evaluation goals and criteria for assessing interactive design, emphasizing expert analysis through cognitive walkthroughs and heuristic evaluations, as well as user participation. It details the importance of continuous evaluation throughout the design lifecycle to enhance usability, functionality, and user experience, while identifying specific usability problems. Additionally, it highlights various evaluation techniques including laboratory studies, field studies, and observational methods to ensure designs meet user needs and expectations.