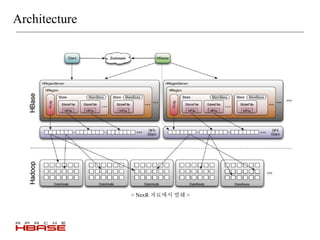
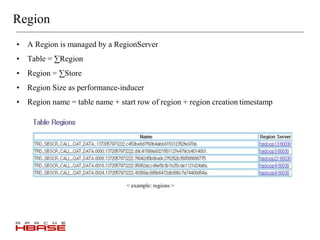
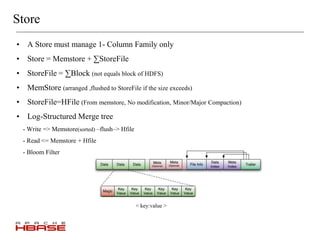
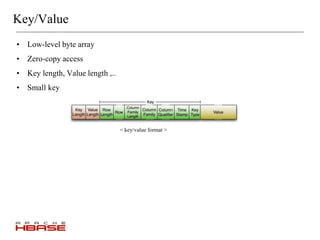
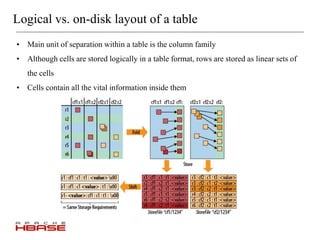
HBase is a distributed, column-oriented database that is modeled after Google's Bigtable. It runs on top of HDFS and provides real-time read/write access to large datasets. HBase tables are split into regions that can be distributed across multiple servers. It uses a log-structured merge tree to store data on disk for efficient read/write operations. HBase is well suited for handling large volumes of randomly accessible data.









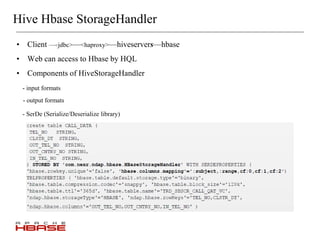
![hbase-site.xml
• hbase.rootdir
- The directory shared by region servers and into which HBase persists. [hdfs://hadoop1:9000/hbase]
• hbase.zookeeper.quorum
- zookeeper servers [ehadoop22,ehadoop23]
• hbase.regionservers.codecs
- Compression codecs [snappy]
• hbsae.hregion.max.filesize
- Maximum HStoreFile size [17179869184]
• hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size
- Memstore will be flushed to disk if size of the memstore exceeds this number of bytes [134217728]
• hbase.hregion.majorcompaction
- The time (in miliseconds) between 'major' compactions of all HStoreFiles in a region [0 -> Disable!!]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hbase-160220235603/85/Hbase-Introduction-22-320.jpg)