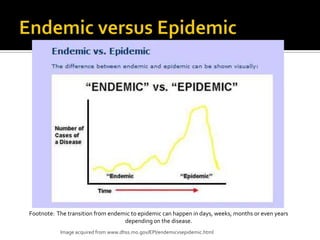
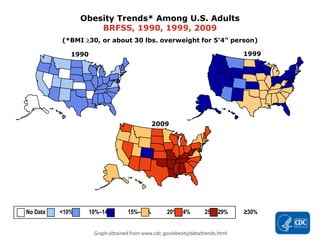
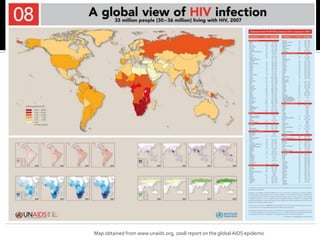
This document defines and distinguishes between endemic, epidemic, and pandemic diseases. Endemic diseases occur at low levels in a population. Epidemics occur in large numbers over a specific area. Pandemics spread over several large areas worldwide, such as the Spanish flu or bubonic plague. The document provides examples of diseases that fall into each category and instructs students to classify infectious disease scenarios.