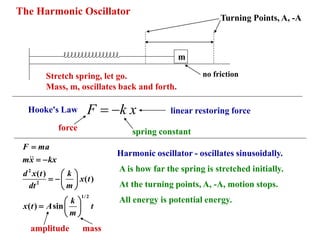
1) The harmonic oscillator model describes an object oscillating back and forth around an equilibrium position due to a restoring force proportional to its displacement.
2) In quantum mechanics, the harmonic oscillator leads to discrete, quantized energy levels equally spaced by an amount of energy hν, where ν is the oscillator frequency. The lowest energy level is not zero due to the uncertainty principle.
3) The wavefunctions and energies of the quantum harmonic oscillator are obtained by solving the Schrödinger equation, which yields the Hermite differential equation. The solutions are Hermite polynomials multiplied by a Gaussian function.