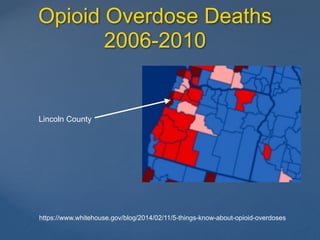
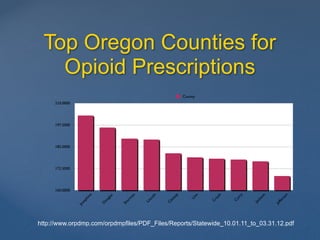
This document discusses harm reduction strategies for patients at high risk of opioid overdose during the current opioid epidemic. It identifies populations at risk, such as those prescribed methadone, at doses over 120mg of morphine equivalents daily, or those prescribed benzodiazepines or sedatives along with opioids. It recommends prescribing nasal naloxone to these at-risk patients and tapering opioid doses to safer levels. For patients requiring long-term opioid treatment, it suggests switching to buprenorphine which has a ceiling effect reducing risk of overdose. The goal is to reduce harm for the "Lost Generation" of patients dependent on opioids.