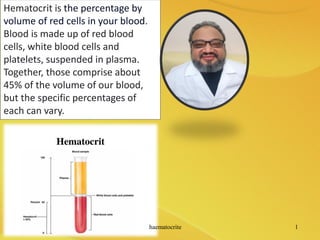
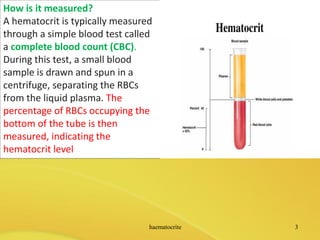
Hematocrit is a measurement of the percentage of red blood cells in the total blood volume. It is an indicator of the blood's oxygen carrying capacity. A hematocrit level is obtained through a complete blood count test, where a blood sample is spun in a centrifuge to separate red blood cells from plasma for measurement. Normal hematocrit ranges vary by sex and age, and deviations can signal health issues like anemia or polycythemia that should be evaluated by a doctor.